|
Membrane Gas Separation
Gas mixtures can be effectively separated by synthetic membranes made from polymers such as polyamide or cellulose acetate, or from ceramic materials. While polymeric membranes are economical and technologically useful, they are bounded by their performance, known as the Robeson limit (permeability must be sacrificed for selectivity and vice versa). This limit affects polymeric membrane use for CO2 separation from flue gas streams, since mass transport becomes limiting and CO2 separation becomes very expensive due to low permeabilities. Membrane materials have expanded into the realm of Silicon dioxide, silica, zeolites, metal-organic frameworks, and perovskites due to their strong thermal and chemical resistance as well as high tunability (ability to be modified and functionalized), leading to increased permeability and selectivity. Membranes can be used for separating gas mixtures where they act as a permeable barrier through which different compounds move across at different rat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Membranes
Synthetic may refer to: Science * Synthetic biology * Synthetic chemical or compound, produced by the process of chemical synthesis * Synthetic elements, chemical elements that are not naturally found on Earth and therefore have to be created in experiments * Organic compound#Synthetic compounds, Synthetic organic compounds synthetic chemical compounds based on carbon (organic compounds). * Synthetic peptide * Synthetic population * Synthetic population (biology) Industry * Synthetic fuel * Synthetic oil * Synthetic marijuana * Synthetic diamond * Synthetic fibers, cloth or other material made from other substances than natural (animal, plant) materials Other * Synthetic position, a concept in finance * Synthetic-aperture radar, a type or radar * Analytic–synthetic distinction, in philosophy * Synthetic language in linguistics, inflected or agglutinative languages * Synthetic intelligence a term emphasizing that true intelligence expressed by computing machines is not an imitat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideal Gas Law
The ideal gas law, also called the general gas equation, is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation of the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first stated by Benoît Paul Émile Clapeyron in 1834 as a combination of the empirical Boyle's law, Charles's law, Avogadro's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. The ideal gas law is often written in an empirical form: pV = nRT where p, V and T are the pressure, volume and Thermodynamic temperature, temperature respectively; n is the amount of substance; and R is the ideal gas constant. It can also be derived from the microscopic kinetic theory of gases, kinetic theory, as was achieved (independently) by August Krönig in 1856 and Rudolf Clausius in 1857. Equation The state function, state of an amount of gas is determined by its pressure, volume, and temperature. The modern form of the equation relates these simply in two main forms. The temperature us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoporous Material
A mesoporous material (or super nanoporous ) is a nanoporous material containing pores with diameters between 2 and 50 nm, according to IUPAC nomenclature. For comparison, IUPAC defines microporous material as a material having pores smaller than 2 nm in diameter and macroporous material as a material having pores larger than 50 nm in diameter. Typical mesoporous materials include some kinds of silica and alumina that have similarly-sized mesopores. Mesoporous oxides of niobium, tantalum, titanium, zirconium, cerium and tin have also been reported. However, the flagship of mesoporous materials is mesoporous carbon, which has direct applications in energy storage devices. Mesoporous carbon has porosity within the mesopore range and this significantly increases the specific surface area. Another very common mesoporous material is activated carbon which is typically composed of a carbon framework with both mesoporosity and microporosity depending on the condit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microscopic Model Of A Nanoporous Membrane
The microscopic scale () is the scale of objects and events smaller than those that can easily be seen by the naked eye, requiring a lens or microscope to see them clearly. In physics, the microscopic scale is sometimes regarded as the scale between the macroscopic scale and the quantum scale. Microscopic units and measurements are used to classify and describe very small objects. One common microscopic length scale unit is the micrometre (also called a ''micron'') (symbol: μm), which is one millionth of a metre. History Whilst compound microscopes were first developed in the 1590s, the significance of the microscopic scale was only truly established in the 1600s when Marcello Malphigi and Antonie van Leeuwenhoek microscopically observed frog lungs and microorganisms. As microbiology was established, the significance of making scientific observations at a microscopic level increased. Published in 1665, Robert Hooke's book Micrographia details his microscopic observations inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
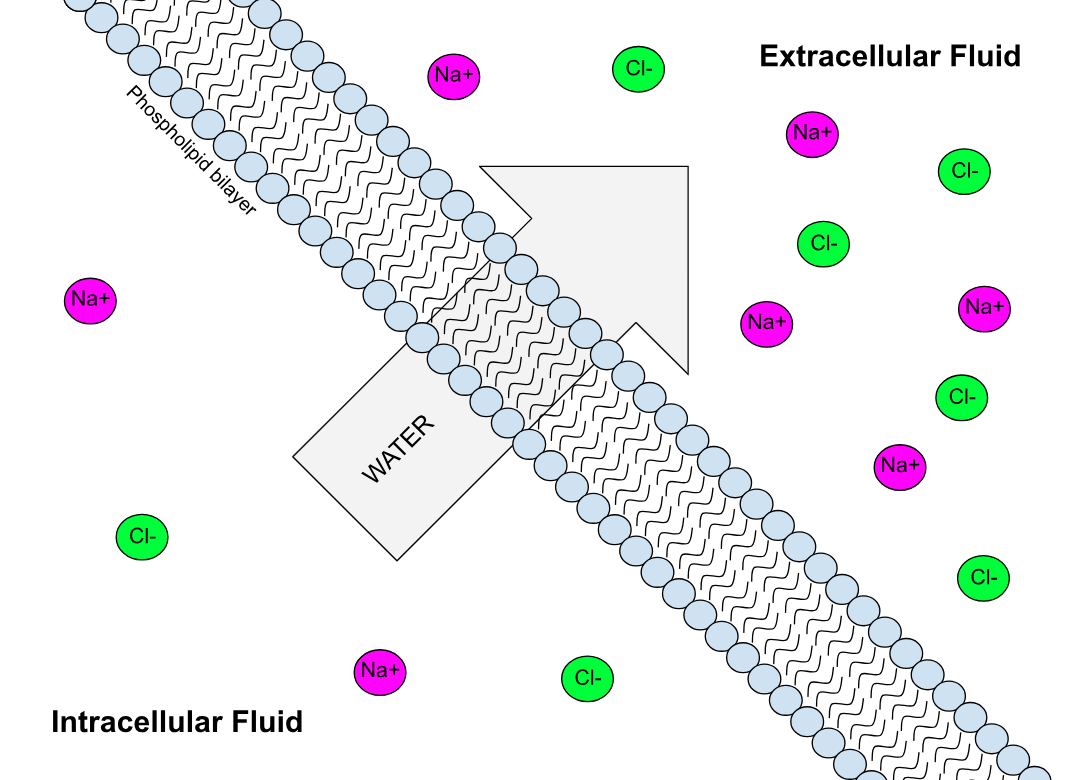
Semipermeable Membrane
Semipermeable membrane is a type of synthetic or biologic, polymeric membrane that allows certain molecules or ions to pass through it by osmosis. The rate of passage depends on the pressure, concentration, and temperature of the molecules or solutes on either side, as well as the permeability of the membrane to each solute. Depending on the membrane and the solute, permeability may depend on solute size, solubility, properties, or chemistry. How the membrane is constructed to be selective in its permeability will determine the rate and the permeability. Many natural and synthetic materials which are rather thick are also semipermeable. One example of this is the thin film on the inside of an egg. Biological membranes are selectively permeable, with the passage of molecules controlled by facilitated diffusion, passive transport or active transport regulated by proteins embedded in the membrane. Biological membranes Phospholipid bilayer A phospholipid bilayer is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reactivity–selectivity Principle
In chemistry the reactivity–selectivity principle or RSP states that a more reactive chemical compound or reactive intermediate is less selective in chemical reactions. In this context selectivity represents the ratio of reaction rates. This principle was generally accepted until the 1970s when too many exceptions started to appear. The principle is now considered obsolete. A classic example of perceived RSP found in older organic chemistry textbooks concerns the free radical halogenation of simple alkanes. Whereas the relatively unreactive bromine reacts with 2-methylbutane predominantly to 2-bromo-2-methylbutane, the reaction with much more reactive chlorine results in a mixture of all four regioisomers. Another example of RSP can be found in the selectivity of the reaction of certain carbocations with azides and water. The very stable triphenylmethyl carbocation derived from solvolysis of the corresponding triphenylmethyl chloride reacts 100 times faster with the azide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymeric Membranes
A polymer () is a substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compounds, produces unique physical properties including toughness, high elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form amorphous and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals. Polymers are studied in the fields of polymer science (which includes polymer chemistry and polymer physics), biophy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polydimethylsiloxane
Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), also known as dimethylpolysiloxane or dimethicone, is a silicone polymer with a wide variety of uses, from cosmetics to industrial lubrication and passive daytime radiative cooling. PDMS is particularly known for its unusual rheological (or flow) properties. It is optically clear and, in general, inert, non-toxic, and non-flammable. It is one of several types of silicone oil (polymerized siloxane). The applications of PDMS range from contact lenses and medical devices to elastomers; it is also present in shampoos (as it makes hair shiny and slippery), food ( antifoaming agent), caulk, lubricants and heat-resistant tiles. Structure The chemical formula of PDMS is , where ''n'' is the number of repeating monomer units. Industrial synthesis can begin from dimethyldichlorosilane and water by the following net reaction: : + (''n''+1) The polymerization reaction evolves hydrochloric acid. For medical and domestic applications, a process wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polysulphone
Polysulfones are a family of high performance thermoplastics. These polymers are known for their toughness and stability at high temperatures. Technically used polysulfones contain an aryl- SO2-aryl subunit. Due to the high cost of raw materials and processing, polysulfones are used in specialty applications and often are a superior replacement for polycarbonates. Three polysulfones are used industrially: polysulfone (PSU), polyethersulfone (PES/PESU) and polyphenylene sulfone (PPSU). They can be used in the temperature range from -100 to +200 °C and are used for electrical equipment, in vehicle construction and medical technology. They are composed of para-linked aromatics, sulfonyl groups and ether groups and partly also alkyl groups. Polysulfones have outstanding resistance to heat and oxidation, hydrolysis resistance to aqueous and alkaline media and good electrical properties. Nomenclature The term "polysulfone" is normally used for polyarylethersulfones (PAES), s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyimide
Polyimide (sometimes abbreviated PI) is a monomer containing imide groups belonging to the class of high-performance plastics. With their high heat-resistance, polyimides enjoy diverse applications in roles demanding rugged organic materials, such as high temperature fuel cells, displays, and various military roles. A classic polyimide is Kapton, which is produced by condensation of pyromellitic dianhydride and 4,4'-oxydianiline.Wright, Walter W. and Hallden-Abberton, Michael (2002) "Polyimides" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. History The first polyimide was discovered in 1908 by Bogart and Renshaw. They found that 4-amino phthalic anhydride does not melt when heated but does release water upon the formation of a high molecular weight polyimide. The first semialiphatic polyimide was prepared by Edward and Robinson by melt fusion of diamines and tetra acids or diamines and diacids/diester. However, the first polyimide of significant co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyethylene
Polyethylene or polythene (abbreviated PE; IUPAC name polyethene or poly(methylene)) is the most commonly produced plastic. It is a polymer, primarily used for packaging (plastic bags, plastic films, geomembranes and containers including bottles, cups, jars, etc.). , over 100 million tonnes of polyethylene resins are being produced annually, accounting for 34% of the total plastics market. Many kinds of polyethylene are known, with most having the chemical formula (C2H4)''n''. PE is usually a mixture of similar polymers of ethylene, with various values of ''n''. It can be ''low-density'' or ''high-density'' and many variations thereof. Its properties can be modified further by crosslinking or copolymerization. All forms are nontoxic as well as chemically resilient, contributing to polyethylene's popularity as a multi-use plastic. However, polyethylene's chemical resilience also makes it a long-lived and decomposition-resistant pollutant when disposed of improperly. Being a h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Membrane Separation Process
A membrane is a selective barrier; it allows some things to pass through but stops others. Such things may be molecules, ions, or other small particles. Membranes can be generally classified into synthetic membranes and biological membranes. Biological membranes include cell membranes (outer coverings of cells or organelles that allow passage of certain constituents); nuclear membranes, which cover a cell nucleus; and tissue membranes, such as mucosae and serosae. Synthetic membranes are made by humans for use in laboratories and industry (such as chemical plants). This concept of a membrane has been known since the eighteenth century but was used little outside of the laboratory until the end of World War II. Drinking water supplies in Europe had been compromised by The War and membrane filters were used to test for water safety. However, due to the lack of reliability, slow operation, reduced selectivity and elevated costs, membranes were not widely exploited. The first use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |