|
Melatonin Receptor 1B
Melatonin receptor 1B, also known as MTNR1B, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MTNR1B'' gene. Function This gene encodes the MT2 protein, one of two high-affinity forms of a receptor for melatonin, the primary hormone secreted by the pineal gland. This gene product is an integral membrane protein that is a G-protein coupled, 7-transmembrane receptor. It is found primarily in the retina and brain; however, this detection requires RT-PCR. It is thought to participate in light-dependent functions in the retina and may be involved in the neurobiological effects of melatonin. Besides the brain and retina this receptor is expressed on the bone forming cells where it regulates their function in depositing bone. Clinical significance Several studies have identified MTNR1B receptor mutations that are associated with increased average blood sugar level and around a 20 percent elevated risk of developing type 2 diabetes.; ; ; ; MTNR1B mRNA is expressed in human islets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Sugar
The blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, blood glucose level, or glycemia is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood. The body tightly regulates blood glucose levels as a part of metabolic homeostasis. For a 70 kg (154 lb) human, approximately four grams of dissolved glucose (also called "blood glucose") is maintained in the blood plasma at all times. Glucose that is not circulating in the blood is stored in skeletal muscle and liver cells in the form of glycogen; in fasting individuals, blood glucose is maintained at a constant level by releasing just enough glucose from these glycogen stores in the liver and skeletal muscle in order to maintain homeostasis. Glucose can be transported from the intestines or liver to other tissues in the body via the bloodstream. Cellular glucose uptake is primarily regulated by insulin, a hormone produced in the pancreas. Once inside the cell, the glucose can now act as an energy source as it undergoes the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current Alzheimer Research
''Current Alzheimer Research'' is a peer-reviewed medical journal covering the neurobiology, genetics, pathogenesis, and treatment strategies of Alzheimer's disease. Abstracting and indexing The journal is indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2019 impact factor of 3.047, ranking it 65th out of 197 journals in the category "Clinical Neurology". (Web of Science The Web of Science (WoS; previously known as Web of Knowledge) is a paid-access platform that provides (typically via the internet) access to multiple databases that provide reference and citation data from academic journals, conference proceedi ...) References External links * {{Official website, https://benthamscience.com/journals/current-alzheimer-research/ Alzheimer's disease journals Neuroscience journals Academic journals established in 2004 Bentham Science Publishers academic journals English-language journals Journals published between 13 and 25 times per yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discovery And Development Of Melatonin Receptor Agonists
Melatonin receptor agonists are analogues of melatonin that bind to and activate the melatonin receptor. Agonists of the melatonin receptor have a number of therapeutic applications including treatment of sleep disorders and depression. The discovery and development of melatonin receptor agonists was motivated by the need for more potent analogues than melatonin, with better pharmacokinetics and longer half-lives. Melatonin receptor agonists were developed with the melatonin structure as a model. The melatonin receptors are G protein-coupled receptors and are expressed in various tissues of the body. There are two subtypes of the receptor in humans, melatonin receptor 1 (MT1) and melatonin receptor 2 (MT2). Melatonin and melatonin receptor agonists, on market or in clinical trials, all bind to and activate both receptor types. The binding of the agonists to the receptors has been investigated since 1986, yet is still not fully understood. When melatonin receptor agonists bind t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melatonin Receptor
Melatonin receptors are G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) which bind melatonin. Three types of melatonin receptors have been cloned. The MT1 (or Mel1A or MTNR1A) and MT2 (or Mel1B or MTNR1B) receptor subtypes are present in humans and other mammals, while an additional melatonin receptor subtype MT3 (or Mel1C or MTNR1C) has been identified in amphibia and birds. The receptors are crucial in the signal cascade of melatonin. In the field of chronobiology, melatonin has been found to be a key player in the synchrony of biological clocks. Melatonin secretion by the pineal gland has circadian rhythmicity regulated by the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) found in the brain. The SCN functions as the timing regulator for melatonin; melatonin then follows a feedback loop to decrease SCN neuronal firing. The receptors MT1 and MT2 control this process. Melatonin receptors are found throughout the body in places such as the brain, the retina of the eye, the cardiovascular system, the liv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a Receptor (biochemistry), receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are Cell (biology), cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an Receptor antagonist, antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist. Etymology The word originates from the Ancient Greek, Greek word (''agōnistēs''), "contestant; champion; rival" < (''agōn''), "contest, combat; exertion, struggle" < (''agō''), "I lead, lead towards, conduct; drive." Types of agonists Receptor (biochemistry), Receptors can be activated by either endogenous agonists (such as hormones and neurotransmitters) or exogenous agonists (such as medication, drugs), resulting in a biological response. A physiological agonism an ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor Antagonist
A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a receptor rather than activating it like an agonist. Antagonist drugs interfere in the natural operation of receptor proteins.Pharmacology Guide: In vitro pharmacology: concentration-response curves ." '' GlaxoWellcome.'' Retrieved on December 6, 2007. They are sometimes called blockers; examples include alpha blockers, beta b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islets Of Langerhans
The pancreatic islets or islets of Langerhans are the regions of the pancreas that contain its endocrine (hormone-producing) cells, discovered in 1869 by German pathological anatomist Paul Langerhans. The pancreatic islets constitute 1–2% of the pancreas volume and receive 10–15% of its blood flow. The pancreatic islets are arranged in density routes throughout the human pancreas, and are important in the metabolism of glucose. Structure There are about 1 million islets distributed throughout the pancreas of a healthy adult human. While islets vary in size, the average diameter is about 0.2 mm.:928 Each islet is separated from the surrounding pancreatic tissue by a thin, fibrous, connective tissue capsule which is continuous with the fibrous connective tissue that is interwoven throughout the rest of the pancreas.:928 Microanatomy Hormones produced in the pancreatic islets are secreted directly into the blood flow by (at least) five types of cells. In rat islets, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
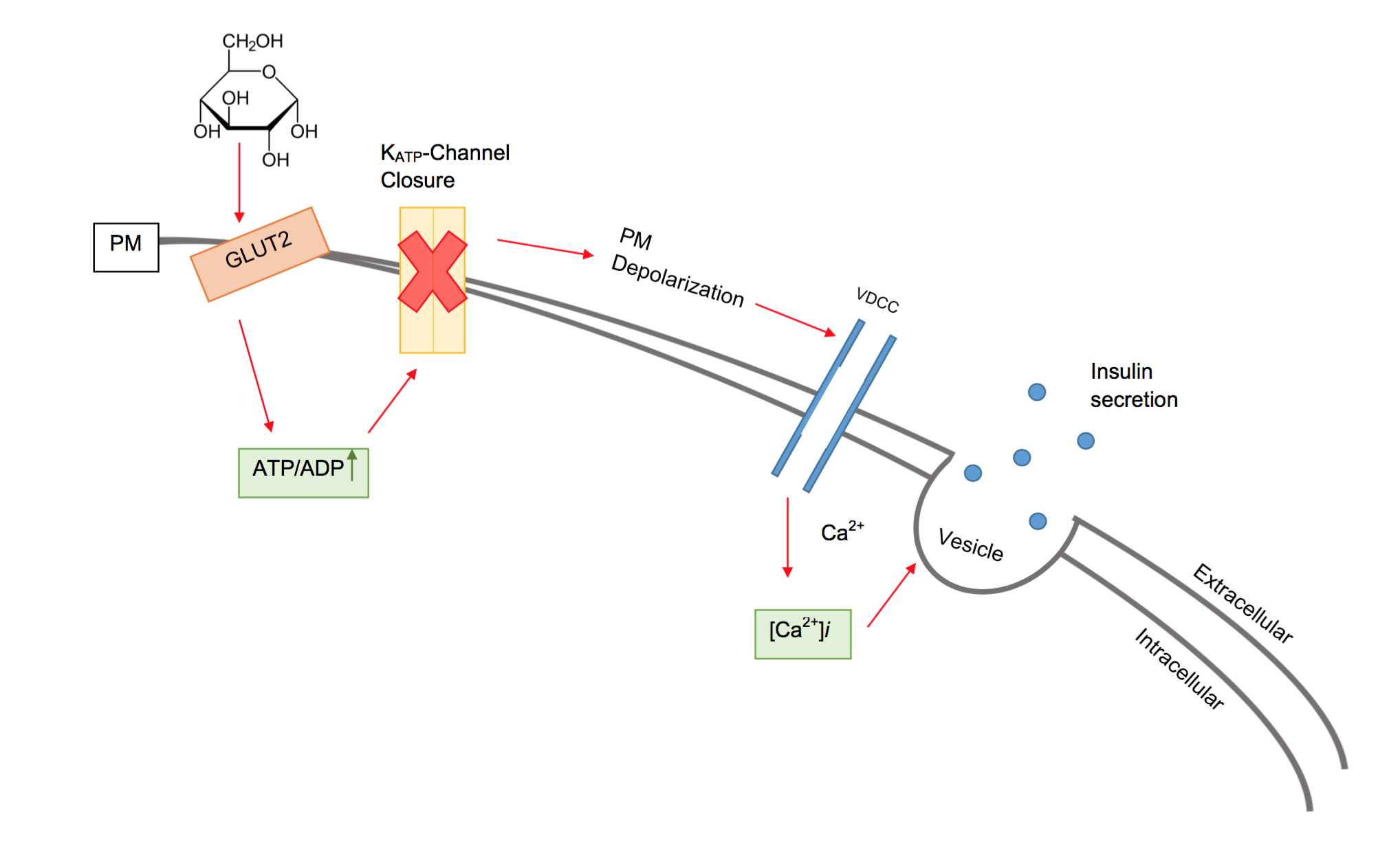
Beta Cell
Beta cells (β-cells) are specialized endocrine cells located within the pancreatic islets of Langerhans responsible for the production and release of insulin and amylin. Constituting ~50–70% of cells in human islets, beta cells play a vital role in maintaining blood glucose levels. Problems with beta cells can lead to disorders such as diabetes. Function The function of beta cells is primarily centered around the synthesis and secretion of hormones, particularly insulin and amylin. Both hormones work to keep blood glucose levels within a narrow, healthy range by different mechanisms. Insulin facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells, allowing them to use it for energy or store it for future use. Amylin helps regulate the rate at which glucose enters the bloodstream after a meal, slowing down the absorption of nutrients by inhibit gastric emptying. Insulin synthesis Beta cells are the only site of insulin synthesis in mammals. As glucose stimulates insulin secretion, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry (ICC) is a common laboratory technique that is used to anatomically visualize the localization of a specific protein or antigen in cells by use of a specific primary antibody that binds to it. The primary antibody allows visualization of the protein under a fluorescence microscope when it is bound by a secondary antibody that has a conjugated fluorophore. ICC allows researchers to evaluate whether or not cells in a particular sample express the antigen in question. In cases where an immunopositive signal is found, ICC also allows researchers to determine which sub-cellular compartments are expressing the antigen. Immuno''cyto''chemistry vs. immuno''histo''chemistry Immunocytochemistry differs from immunohistochemistry in that the former is performed on samples of intact cells that have had most, if not all, of their surrounding extracellular matrix removed. This includes individual cells that have been isolated from a block of solid tissue, cells grown wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue and unexplained weight loss. Other symptoms include increased hunger, having a sensation of pins and needles, and sores (wounds) that heal slowly. Symptoms often develop slowly. Long-term complications from high blood sugar include heart disease, stroke, diabetic retinopathy, which can result in blindness, kidney failure, and poor blood flow in the lower limbs, which may lead to amputations. A sudden onset of hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state may occur; however, ketoacidosis is uncommon. Type 2 diabetes primarily occurs as a result of obesity and lack of exercise. Some people are genetically more at risk than others. Type 2 diabetes makes up about 90% of cases of diabetes, with the other 10% due primar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J Pineal Res (journal)
''Journal of Pineal Research'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research on the pineal gland and its hormonal products, chiefly melatonin, in all vertebrate species. Experimental studies on circadian rhythms and sleep are also published by the journal. It is published by John Wiley & Sons and the editor-in-chief is Gianluca Tosini. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 13.007. References External links * {{Official website, http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/10.1111/(ISSN)1600-079X Endocrinology journals Wiley (publisher) academic journals Academic journals established in 1984 English-language journals Physiology journals Neuroscience journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |