|
Megabats
Megabats constitute the family Pteropodidae of the order Chiroptera. They are also called fruit bats, Old World fruit bats, or—especially the genera '' Acerodon'' and ''Pteropus''— flying foxes. They are the only member of the superfamily Pteropodoidea, which is one of two superfamilies in the suborder Yinpterochiroptera. Internal divisions of Pteropodidae have varied since subfamilies were first proposed in 1917. From three subfamilies in the 1917 classification, six are now recognized, along with various tribes. As of 2018, 197 species of megabat had been described. The leading theory of the evolution of megabats has been determined primarily by genetic data, as the fossil record for this family is the most fragmented of all bats. They likely evolved in Australasia, with the common ancestor of all living pteropodids existing approximately 31 million years ago. Many of their lineages probably originated in Melanesia, then dispersed over time to mainland Asia, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nyctimeninae
Megabats constitute the Family (biology), family Pteropodidae of the Order (biology), order Chiroptera. They are also called fruit bats, Old World fruit bats, or—especially the genus, genera ''Acerodon'' and ''Pteropus''—Pteropus, flying foxes. They are the only member of the Superfamily (taxonomy), superfamily Pteropodoidea, which is one of two superfamilies in the suborder Yinpterochiroptera. Internal divisions of Pteropodidae have varied since Subfamily, subfamilies were first proposed in 1917. From three subfamilies in the 1917 classification, six are now recognized, along with various Tribe (biology), tribes. As of 2018, 197 species of megabat had been described. The leading theory of the evolution of megabats has been determined primarily by genetic data, as the fossil record for this family is the most fragmented of all bats. They likely evolved in Australasia, with the common ancestor of all living pteropodids existing approximately 31 million years ago. Man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harpyionycterinae
Megabats constitute the family Pteropodidae of the order Chiroptera. They are also called fruit bats, Old World fruit bats, or—especially the genera '' Acerodon'' and ''Pteropus''— flying foxes. They are the only member of the superfamily Pteropodoidea, which is one of two superfamilies in the suborder Yinpterochiroptera. Internal divisions of Pteropodidae have varied since subfamilies were first proposed in 1917. From three subfamilies in the 1917 classification, six are now recognized, along with various tribes. As of 2018, 197 species of megabat had been described. The leading theory of the evolution of megabats has been determined primarily by genetic data, as the fossil record for this family is the most fragmented of all bats. They likely evolved in Australasia, with the common ancestor of all living pteropodids existing approximately 31 million years ago. Many of their lineages probably originated in Melanesia, then dispersed over time to mainland Asia, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiroptera
Bats are flying mammals of the order Chiroptera (). With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most birds, flying with their very long spread-out digits covered with a thin membrane or patagium. The smallest bat, and arguably the smallest extant mammal, is Kitti's hog-nosed bat, which is in length, across the wings and in mass. The largest bats are the flying foxes, with the giant golden-crowned flying fox (''Acerodon jubatus'') reaching a weight of and having a wingspan of . The second largest order of mammals after rodents, bats comprise about 20% of all classified mammal species worldwide, with over 1,400 species. These were traditionally divided into two suborders: the largely fruit-eating megabats, and the echolocating microbats. But more recent evidence has supported dividing the order into Yinpterochiroptera and Yangochiroptera, with megabats as members of the for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rousettinae
The Rousettinae are a subfamily of megabats. Taxa within this subfamily include: * Tribe Eonycterini **Genus '' Eonycteris'' *** Greater nectar bat, ''E. major'' *** Cave nectar bat, ''E. spelaea'' *** Philippine dawn bat, ''E. robusta'' *tribe Epomophorini **Genus '' Epomophorus'' *** Angolan epauletted fruit bat, ''E. angolensis'' *** Ansell's epauletted fruit bat, ''E. anselli'' *** Peters's epauletted fruit bat, ''E. crypturus'' *** Dobson's epauletted fruit bat, ''E. dobsonii'' *** Gambian epauletted fruit bat, ''E. gambianus'' *** Lesser Angolan epauletted fruit bat, ''E. grandis'' *** Ethiopian epauletted fruit bat, ''E. labiatus'' *** East African epauletted fruit bat, ''E. minimus'' *** Minor epauletted fruit bat, ''E. minor'' *** Wahlberg's epauletted fruit bat, ''E. wahlbergi'' **Genus '' Epomops'' *** Buettikofer's epauletted fruit bat, ''E. buettikoferi'' *** Franquet's epauletted fruit bat, ''E. franqueti'' ** Genus '' Hypsignathus'' *** Hammer-headed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteropodinae
The Pteropodinae are a subfamily of megabats. Taxa within this subfamily are: * Genus '' Acerodon'' ** Sulawesi flying fox, ''A. celebensis'' ** Talaud flying fox, ''A. humilis'' ** Giant golden-crowned flying fox, ''A. jubatus'' ** Palawan fruit bat, ''A. leucotis'' ** Sunda flying fox, ''A. mackloti'' * Genus '' Desmalopex'' ** White-winged flying fox, ''D. leucopterus'' ** Small white-winged flying fox, ''D. microleucopterus'' * Genus '' Eidolon'' — straw-coloured fruit bats ** Madagascan fruit bat, ''E. dupreanum'' **Straw-coloured fruit bat, ''E. helvum'' * Genus '' Mirimiri'' ** Fijian monkey-faced bat, ''M. acrodonta'' * Genus '' Neopteryx'' ** Small-toothed fruit bat, ''N. frosti'' * Genus '' Pteralopex'' - flying monkeys ** Bougainville monkey-faced bat, ''P. anceps'' ** Guadalcanal monkey-faced bat, ''P. atrata'' ** Greater monkey-faced bat, ''P. flanneryi'' ** Montane monkey-faced bat, ''P. pulchra'' ** New Georgian monkey-faced bat, ''P. taki'' *Genus ''Pteropus'' � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cynopterinae
The subfamily Cynopterinae ("flying dogs") comprises 24 species of pteropodid bats distributed exclusively in South and Southeast Asia. The subfamily contains the following genera: * '' Aethalops'' – pygmy fruit bats * '' Alionycteris'' * '' Balionycteris'' * '' Chironax'' * '' Cynopterus'' – dog-faced fruit bats, flying dogs or short-nosed fruit bats * ''Dyacopterus ''Dyacopterus'' is a genus of megabats from south-east Asia. It contains three species, namely: *Brooks's dyak fruit bat, ''Dyacopterus brooksi'' *Dayak fruit bat The dayak fruit bat or dyak fruit bat (''Dyacopterus spadiceus'') is a relativ ...'' – Dayak fruit bats * '' Haplonycteris'' * '' Latidens'' * '' Megaerops'' * '' Otopteropus'' * '' Penthetor'' * '' Ptenochirus'' – musky fruit bats * '' Sphaerias'' * '' Thoopterus'' References Bats Megabats Mammal subfamilies {{bat-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Though the fossil record is incomplete, numerous studies have demonstrated that there is enough information available to give a good understanding of the pattern of diversification of life on Earth. In addition, the record can predict and fill gaps such as the discovery of '' Tiktaalik'' in the arctic of Canada. Paleontology includes the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are sometimes considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before prin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour, or ecological niche. In addition, palaeontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. About 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomen". The first part of a binomen is the name of a genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name (zoology), specific name or the specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australasia
Australasia is a subregion of Oceania, comprising Australia, New Zealand (overlapping with Polynesia), and sometimes including New Guinea and surrounding islands (overlapping with Melanesia). The term is used in a number of different contexts, including geopolitically, physiogeographically, philologically, and ecologically, where the term covers several slightly different but related regions. Derivation and definitions Charles de Brosses coined the term (as French ''Australasie'') in ''Histoire des navigations aux terres australes'' (1756). He derived it from the Latin for "south of Asia" and differentiated the area from Polynesia (to the east) and the southeast Pacific ( Magellanica). In the late 19th century, the term Australasia was used in reference to the "Australasian colonies". In this sense it related specifically to the British colonies south of Asia: New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Western Australia, Victoria (i.e., the Australian colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superfamily (taxonomy)
In biology, taxonomic rank (which some authors prefer to call nomenclatural rank because ranking is part of nomenclature rather than taxonomy proper, according to some definitions of these terms) is the relative or absolute level of a group of organisms (a ''taxon'') in a hierarchy that reflects evolutionary relationships. Thus, the most inclusive clades (such as Eukarya and Animalia) have the highest ranks, whereas the least inclusive ones (such as ''Homo sapiens'' or ''Bufo bufo'') have the lowest ranks. Ranks can be either relative and be denoted by an indented taxonomy in which the level of indentation reflects the rank, or absolute, in which various terms, such as species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, and domain designate rank. This page emphasizes absolute ranks and the rank-based codes (the Zoological Code, the Botanical Code, the Code for Cultivated Plants, the Prokaryotic Code, and thCode for Viruses require them. However, absolute ranks are not req ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
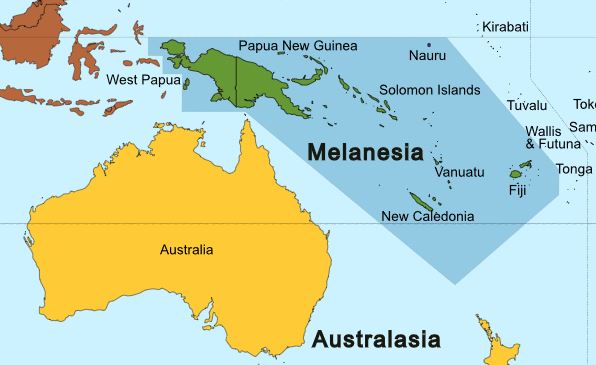
Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from New Guinea in the west to the Fiji Islands in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea. The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Vanuatu, Solomon Islands, and Papua New Guinea. It also includes the West New Guinea, Indonesian part of New Guinea, the French overseas collectivity of New Caledonia, and the Torres Strait Islands. Almost all of the region is in the Southern Hemisphere; only a few small islands that are not politically considered part of Oceania—specifically the northwestern islands of Western New Guinea—lie in the Northern Hemisphere. The name ''Melanesia'' (in French, ''Mélanésie'') was first used in 1832 by French navigator Jules Dumont d'Urville: he coined the terms ''Melanesia'' and ''Micronesia'' to go alongside the pre-existing ''Polynesia'' to designate what he viewed as the three main Ethnicity, ethnic and geographical regions forming the Pacif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the west almost by the Morocco–Spain border. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about , representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltar—the narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa—is only wide. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago. The sea was an important rout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |