|
Matriphagy
Matriphagy is the consumption of the mother by her offspring. The behavior generally takes place within the first few weeks of life and has been documented in some species of insects, nematode worms, pseudoscorpions, and other arachnids as well as in caecilian amphibians. The specifics of how matriphagy occurs varies among different species. However, the process is best-described in the desert spider (''Stegodyphus lineatus''), where the mother harbors nutritional resources for her young through food consumption. The mother can regurgitate small portions of food for her growing offspring, but between 1–2 weeks after hatching, the progeny capitalize on this food source by eating her alive. Typically, offspring only feed on their biological mother as opposed to other females in the population. In other arachnid species, matriphagy occurs after the ingestion of nutritional eggs known as trophic eggs (e.g. Black lace-weaver ''Amaurobius ferox'', crab spider ''Australomisidia ergand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amaurobius Ferox
''Amaurobius ferox'', sometimes known as the black lace-weaver, is a common nocturnal spider belonging to the family Amaurobiidae and genus '' Amaurobius''. Its genus includes three subsocial species, ''A. fenestralis, A. similis'' and ''A. ferox'', all three of which have highly developed subsocial organizations. Description Females of this species range from around 11–16 mm in body length, while males are slightly smaller and more slender, ranging from 8–10 mm. The spider is very dark in color with its primary shades being black, brown, dark red, and tan. The abdomen is rounded and has light yellow pale markings in a unique pattern that is often described as resembling a skull-like mask or delicate skeletal pattern. Habitat and distribution ''Amaurobius ferox'' is usually found near man-made structures. The species prefers dark areas, such as underneath logs or inside cellars, and it often likes to live in moist, shaded crevices including underneath stones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stegodyphus Lineatus
''Stegodyphus lineatus'' (desert spider) is the only European species of the spider genus '' Stegodyphus.'' Male ''S. lineatus'' can grow up to 12 mm long while females can grow up to 15 mm. The colour can range from whitish to almost black. In most individuals the opisthosoma is whitish with two broad black longitudinal stripes. Males and females look similar, but the male is generally richer in contrast and has a bulbous forehead. The species name refers to the black lines on the back of these spiders (not present in all individuals). ''S. lineatus'' is found in the southern Mediterranean region of Europe (south of Barcelona, in Sicily, southern Greece including Crete) and as far east as Tajikistan. Behavior ''Stegodyphus lineatus'' can be found in desert habitats, especially in the Negev desert in Israel and dry Mediterranean climates. These spiders build a web between twigs, mostly residing in low thorny shrubs. They prefer to build their webs in prey conce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannibalism
Cannibalism is the act of consuming another individual of the same species as food. Cannibalism is a common ecological interaction in the animal kingdom and has been recorded in more than 1,500 species. Human cannibalism is also well documented, both in ancient and in recent times. The rate of cannibalism increases in nutritionally poor environments as individuals turn to members of their own species as an additional food source.Elgar, M.A. & Crespi, B.J. (1992) ''Cannibalism: ecology and evolution among diverse taxa'', Oxford University Press, Oxford ngland New York. Cannibalism regulates population numbers, whereby resources such as food, shelter and territory become more readily available with the decrease of potential competition. Although it may benefit the individual, it has been shown that the presence of cannibalism decreases the expected survival rate of the whole population and increases the risk of consuming a relative. Other negative effects may include the increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Offspring
In biology, offspring are the young creation of living organisms, produced either by sexual reproduction, sexual or asexual reproduction. Collective offspring may be known as a brood or progeny. This can refer to a set of simultaneous offspring, such as the chick (young bird), chicks hatched from one clutch (eggs), clutch of eggs, or to all offspring produced over time, as with the brood (honeybee), honeybee. Offspring can occur after mating, artificial insemination, or as a result of cloning. Human offspring (lineal descendant, descendants) are referred to as children; male children are sons and female children are daughters (see Kinship). Overview Offspring contains many parts and properties that are precise and accurate in what they consist of, and what they define. As the offspring of a new species, also known as a child or f1 generation, consist of genes of the father and the mother, which is also known as the parent generation. Each of these offspring contains numerous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nutrition
Nutrition is the biochemistry, biochemical and physiology, physiological process by which an organism uses food and water to support its life. The intake of these substances provides organisms with nutrients (divided into Macronutrient, macro- and Micronutrient, micro-) which can be Metabolism, metabolized to create Food energy, energy and chemical structures; too much or too little of an essential nutrient can cause malnutrition. Nutritional science, the study of nutrition as a hard science, typically emphasizes human nutrition. The type of organism determines what nutrients it needs and how it obtains them. Organisms obtain nutrients by consuming organic matter, consuming inorganic matter, absorbing light, or some combination of these. Some can produce nutrients internally by consuming basic elements, while some must consume other organisms to obtain pre-existing nutrients. All forms of life require carbon, Biological thermodynamics, energy, and water as well as various other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolved
Evolution is the change in the heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, resulting in certain characteristics becoming more or less common within a population over successive generations. The process of evolution has given rise to biodiversity at every level of biological organisation. The scientific theory of evolution by natural selection was conceived independently by two British naturalists, Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace, in the mid-19th century as an explanation for why organisms are adapted to their physical and biological environments. The theory was first set out in detail in Darwin's book ''On the Origin of Species''. Evolution by natural selection is established by observable facts about living organisms: (1) more offspring are often produced than can possibly survive; (2) phenotypic variatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptation
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process of natural selection that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the population during that process. Thirdly, it is a phenotypic trait or adaptive trait, with a functional role in each individual organism, that is maintained and has evolved through natural selection. Historically, adaptation has been described from the time of the ancient Greek philosophers such as Empedocles and Aristotle. In 18th and 19th-century natural theology, adaptation was taken as evidence for the existence of a deity. Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace proposed instead that it was explained by natural selection. Adaptation is related to biological fitness, which governs the rate of evolution as measured by changes in allele frequencies. Often, two or more species co-adapt and co-evolve as they develop adaptations tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paratemnoides Nidificator
''Paratemnoides'' is a genus of pseudoscorpions in the Atemnidae family. It was described in 1991 by Australian arachnologist Arachnology is the scientific study of arachnids, which comprise spiders and related invertebrates such as scorpions, pseudoscorpions, harvestmen, ticks, and mites. Those who study spiders and other arachnids are arachnologists. More narrowly ... Mark Harvey. Species The genus contains the following species: * '' Paratemnoides aequatorialis'' (Beier, 1932) * '' Paratemnoides assimilis'' (Beier, 1932) * '' Paratemnoides borneoensis'' (Beier, 1932) * '' Paratemnoides curtulus'' (Redikorzev, 1938) * '' Paratemnoides ellingseni'' (Beier, 1932) * '' Paratemnoides feai'' (Ellingsen, 1906) * '' Paratemnoides indicus'' (Sivaraman, 1980) * '' Paratemnoides indivisus'' (Tullgren, 1907) * '' Paratemnoides insubidus'' (Tullgren, 1907) * '' Paratemnoides japonicus'' (Morikawa, 1953) * '' Paratemnoides laosanus'' (Beier, 1951) * '' Paratemnoides magnificus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuole
A vacuole () is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in Plant cell, plant and Fungus, fungal Cell (biology), cells and some protist, animal, and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic molecules including enzymes in Solutes, solution, though in certain cases they may contain solids which have been engulfed. Vacuoles are formed by the fusion of multiple membrane Vesicle (biology), vesicles and are effectively just larger forms of these. The organelle has no basic shape or size; its structure varies according to the requirements of the cell. Discovery Antonie van Leeuwenhoek described the plant vacuole in 1676. Contractile vacuoles ("stars") were first observed by Spallanzani (1776) in protozoa, although mistaken for respiratory organs. Félix Dujardin, Dujardin (1841) named these "stars" as ''vacuoles''. In 1842, Matthias Jakob Schleiden, Schleiden applied the term for plant cells, to dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midgut
The midgut is the portion of the human embryo from which almost all of the small intestine and approximately half of the large intestine develop. After it bends around the superior mesenteric artery, it is called the "midgut loop". It comprises the portion of the alimentary canal from the end of the foregut at the opening of the bile duct to the hindgut, about two-thirds of the way through the transverse colon. In addition to representing an important distinction in embryologic development, the tissues derived from the midgut additionally have distinct vascular supply and innervation patterns in the adult gastrointestinal system. In the embryo During standard human embryonic development, the midgut undergoes a process known as physiological herniation around week 6, when rapid growth forces the midgut to temporarily exit the abdominal cavity and reside in the extra-abdominal umbilical cord. At this stage, the midgut begins its initial counterclockwise rotation around the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
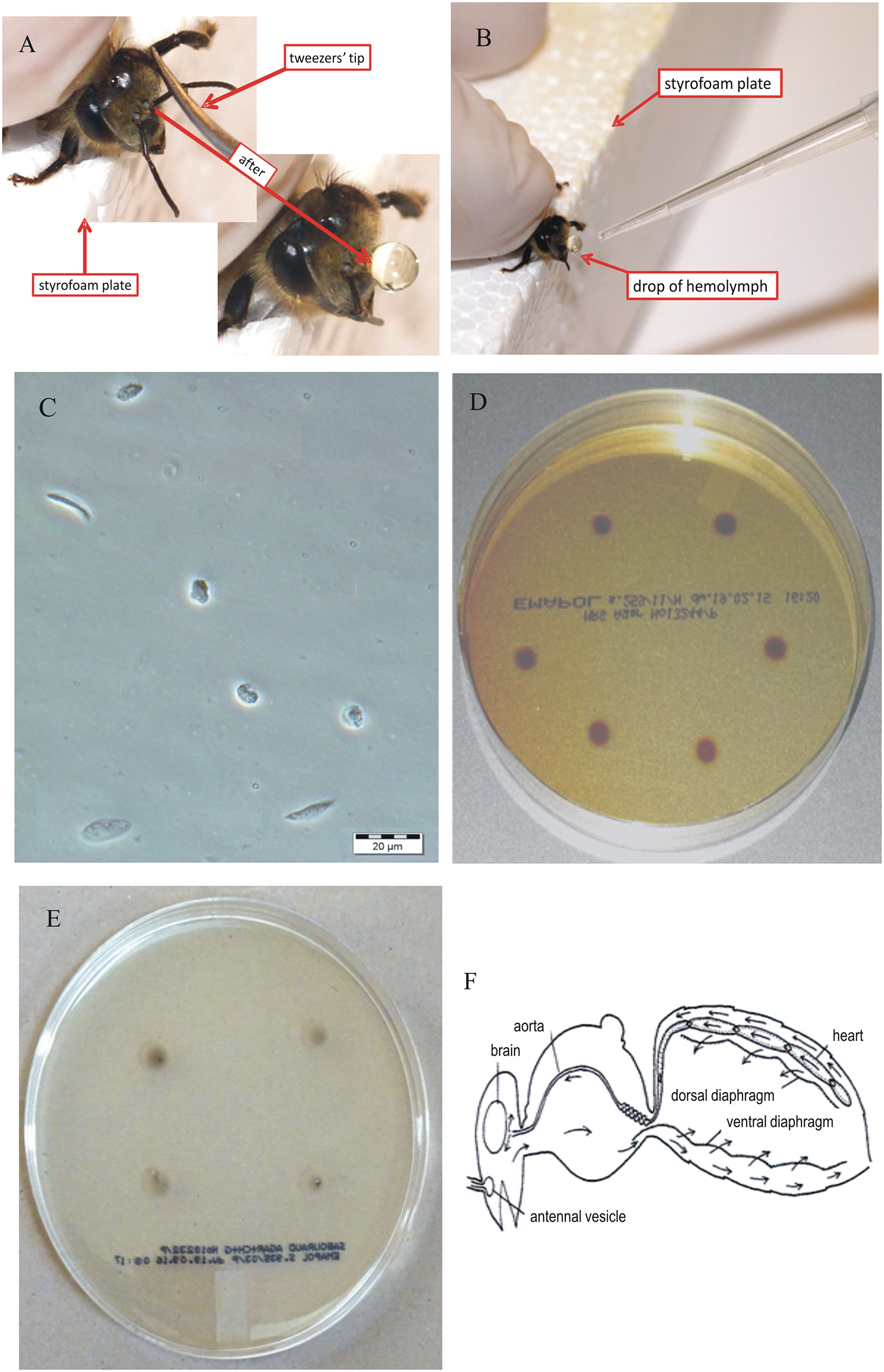
Hemolymph
Hemolymph, or haemolymph, is a fluid, similar to the blood in invertebrates, that circulates in the inside of the arthropod's body, remaining in direct contact with the animal's tissues. It is composed of a fluid plasma in which hemolymph cells called hemocytes are dispersed. In addition to hemocytes, the plasma also contains many chemicals. It is the major tissue type of the open circulatory system characteristic of arthropods (for example, arachnids, crustaceans and insects). In addition, some non-arthropods such as mollusks possess a hemolymphatic circulatory system. Oxygen-transport systems were long thought unnecessary in insects, but ancestral and functional hemocyanin has been found in the hemolymph. Insect "blood" generally does not carry hemoglobin, although hemoglobin may be present in the tracheal system instead and play some role in respiration. Method of transport In the grasshopper, the closed portion of the system consists of tubular hearts and an ao ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |