|
Masseter
In anatomy, the masseter is one of the muscles of mastication. Found only in mammals, it is particularly powerful in herbivores to facilitate chewing of plant matter. The most obvious muscle of mastication is the masseter muscle, since it is the most superficial and one of the strongest. Structure The masseter is a thick, somewhat quadrilateral muscle, consisting of three heads, superficial, deep and coronoid. The fibers of superficial and deep heads are continuous at their insertion. Superficial head The superficial head, the larger, arises by a thick, tendinous aponeurosis from the zygomatic process of the maxilla, the temporal process of the zygomatic bone and from the anterior two-thirds of the inferior border of the zygomatic arch. Its fibers pass inferior and posterior, to be inserted into the angle of the mandible and inferior half of the lateral surface of the ramus of the mandible. Deep head The deep head is much smaller, and more muscular in texture. It arises from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruxism
Bruxism is excessive teeth grinding or jaw clenching. It is an oral Parafunctional habit, parafunctional activity; i.e., it is unrelated to normal function such as eating or talking. Bruxism is a common behavior; the global prevalence of bruxism (both sleep and awake) is 22.22%. Several symptoms are commonly associated with bruxism, including aching jaw muscles, headaches, hypersensitive teeth, tooth wear, and damage to dental restorations (e.g. crowns and fillings). Symptoms may be minimal, without patient awareness of the condition. If nothing is done, after a while many teeth start wearing down until the whole tooth is gone. There are two main types of bruxism: one occurs during sleep (nocturnal bruxism) and one during wakefulness (awake bruxism). Dental damage may be similar in both types, but the symptoms of sleep bruxism tend to be worse on waking and improve during the course of the day, and the symptoms of awake bruxism may not be present at all on waking, and then wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Mandible
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla). The jawbone is the skull's only movable, posable bone, sharing joints with the cranium's temporal bones. The mandible hosts the lower teeth (their depth delineated by the alveolar process). Many muscles attach to the bone, which also hosts nerves (some connecting to the teeth) and blood vessels. Amongst other functions, the jawbone is essential for chewing food. Owing to the Neolithic advent of agriculture (), human jaws evolved to be smaller. Although it is the strongest bone of the facial skeleton, the mandible tends to deform in old age; it is also subject to fracturing. Surgery allows for the removal of jawbone fragments (or its entirety) as well as regenerative methods. Additionally, the bone is of great forensic significance. Struct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masseteric Artery
The masseteric artery is small and passes laterally through the mandibular notch to the deep surface of the masseter muscle, which it supplies. It anastomoses with the masseteric branches of the external maxillary artery and with the transverse facial artery. See also * Masseteric nerve References Arteries of the head and neck {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygomatic Arch
In anatomy, the zygomatic arch (colloquially known as the cheek bone), is a part of the skull formed by the zygomatic process of temporal bone, zygomatic process of the temporal bone (a bone extending forward from the side of the skull, over the opening of the ear) and the temporal Process (anatomy), process of the zygomatic bone (the side of the cheekbone), the two being united by an oblique Suture (anatomy), suture (the zygomaticotemporal suture); the tendon of the temporal muscle passes medial to (i.e. through the middle of) the arch, to gain insertion into the coronoid process of the mandible (jawbone). The jugal point is the point at the anterior (towards face) end of the upper border of the zygomatic arch where the Masseter muscle, masseteric and Maxilla, maxillary edges meet at an angle, and where it meets the process of the zygomatic bone. The arch is typical of ''Synapsida'' ("fused arch"), a clade of amniotes that includes mammals and their extinct relatives, such as ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporomandibular Joint
In anatomy, the temporomandibular joints (TMJ) are the two joints connecting the jawbone to the skull. It is a bilateral Synovial joint, synovial articulation between the temporal bone of the skull above and the condylar process of mandible below; it is from these bones that its name is derived. The joints are unique in their bilateral function, being connected via the mandible. Structure The main components are the joint capsule, articular disc, mandibular condyles, articular surface of the temporal bone, temporomandibular ligament, stylomandibular ligament, sphenomandibular ligament, and lateral pterygoid muscle. Capsule The articular capsule (capsular ligament) is a thin, loose envelope, attached above to the circumference of the mandibular fossa and the articular tubercle immediately in front; below, to the neck of the condyle of the mandible. Its loose attachment to the neck of the mandible allows for free movement. Articular disc The unique feature of the temporomand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygomatic Process Of The Maxilla
The zygomatic processes (aka. malar) are three processes (protrusions) from other bones of the skull which each articulate with the zygomatic bone. The three processes are: * Zygomatic process of frontal bone from the frontal bone * Zygomatic process of maxilla from the maxilla * Zygomatic process of temporal bone from the temporal bone The term ''zygomatic'' derives . The zygomatic process is occasionally referred to as the zygoma, but this term usually refers to the zygomatic bone or occasionally the zygomatic arch. Zygomatic process of frontal bone The supraorbital margin of the frontal bone ends laterally in its zygomatic process, which is strong and prominent, and articulates with the zygomatic bone. The zygomatic process of the frontal bone extends from the frontal bone laterally and inferiorly. Zygomatic process of maxilla The zygomatic process of the maxilla [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Pterygoid Muscle
The medial pterygoid muscle (or internal pterygoid muscle) is a thick, quadrilateral muscle of the face. It is supplied by the mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve (V). It is important in mastication (chewing). Structure The medial pterygoid muscle consists of two heads. The bulk of the muscle arises as a deep head from just above the medial surface of the lateral pterygoid plate. The smaller, superficial head originates from the maxillary tuberosity and the pyramidal process of the palatine bone. Its fibers pass downward, lateral, and posterior, and are inserted, by a strong tendinous lamina, into the lower and back part of the medial surface of the ramus and angle of the mandible, as high as the mandibular foramen. The insertion joins the masseter muscle to form a common tendinous sling which allows the medial pterygoid and masseter to be powerful elevators of the jaw. Nerve supply The medial pterygoid muscle is supplied by the medial pterygoid nerve, a branc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
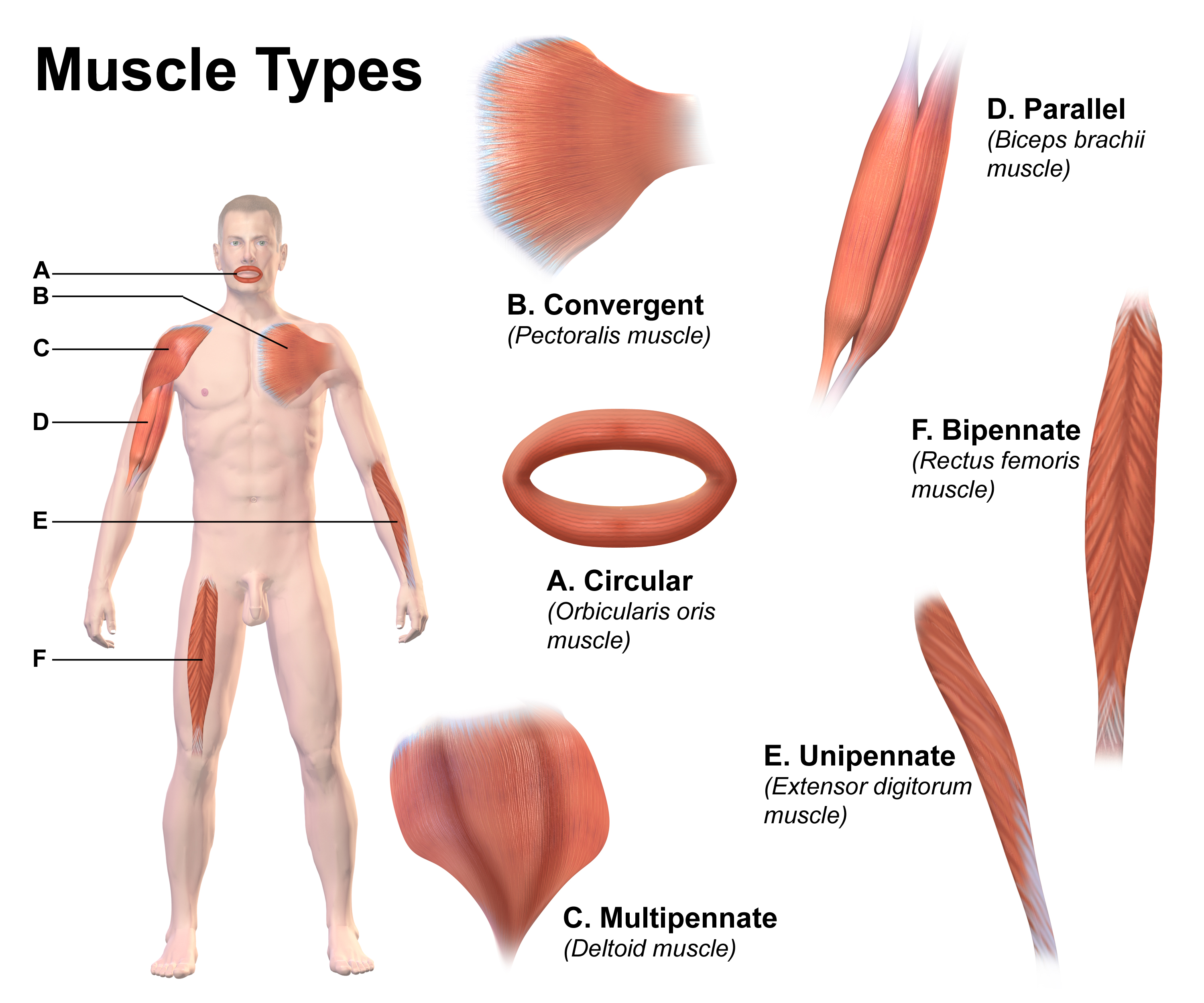
Skeletal Muscles
Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. They are part of the somatic nervous system, voluntary muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The skeletal muscle cells are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are also known as ''muscle fibers''. The tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated muscle tissue, striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. A skeletal muscle contains multiple muscle fascicle, fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the cell fusion, fusion of developmental myoblasts in a process known as myogenesis resulting in long multinucleated cells. In these cells, the cell nucleus, nuclei, termed ''myonuclei'', are located along the inside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronoid Process Of The Mandible
In human anatomy, the mandible's coronoid process () is a thin, triangular eminence, which is flattened from side to side and varies in shape and size. Its anterior border is convex and is continuous below with the anterior border of the ramus. Its ''posterior border'' is concave and forms the anterior boundary of the mandibular notch. The ''lateral surface'' is smooth, and affords insertion to the temporalis and masseter muscles. Its ''medial surface'' gives insertion to the temporalis, and presents a ridge which begins near the apex of the process and runs downward and forward to the inner side of the last molar tooth. Between this ridge and the anterior border is a grooved triangular area, the upper part of which gives attachment to the temporalis, the lower part to some fibers of the buccinator. Clinical significance Fractures of the mandible are common. However, coronoid process fractures are very rare. Isolated fractures of the coronoid process caused by direct trauma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |