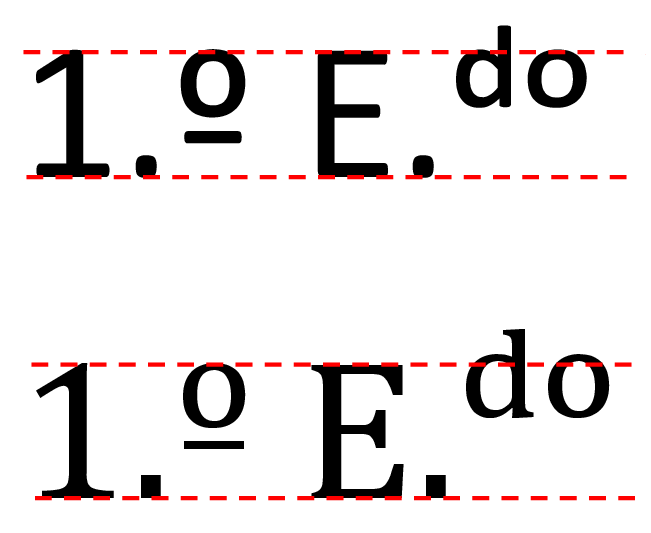|
Masculine Ordinal Indicator
In written languages, an ordinal indicator is a character (typography), character, or group of characters, following a Numerical digit, numeral denoting that it is an Ordinal number (linguistics), ordinal number, rather than a Names of numbers in English#Cardinal numbers, cardinal number. Historically these letters were "elevated terminals", that is to say the last few letters of the full word denoting the ordinal form of the number displayed as a superscript. Probably originating with Latin scribes, the character(s) used vary in different languages. In English ordinal numbers, English orthography, this corresponds to the suffixes ''st'', ''nd'', ''rd'', ''th'' in written ordinals (represented either on the line ''1st'', ''2nd'', ''3rd'', ''4th'' or as subscript and superscript, superscript ). Also commonly encountered in Romance languages are the superscript or Superior letter, superior (and often underlined) masculine ordinal indicator, , and feminine ordinal indicator, . In f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circle Symbol (other)
Circle symbol may refer to: Art and Music *, music symbol denoting a: **diminished triad **diminished seventh chord *, an Ensō, a hand drawn circle in Zen art Language *˚, ring diacritic *º, masculine ordinal indicator *o, a common superior letter *Upper and lowercase vowel letters in the: **O or o, Latin alphabet **Ο or omicron, ο, Greek alphabet **О or о, Cyrillic alphabet *𐤏, Semitic/Phoenician letter Ayin, the ancestor of the Greek, Latin, Cyrillic etc. letters Mathematics *, the ring operator denoting function composition *0, the number zero Other *◦, typographical bullet symbol introducing items in a list *°, degree symbol *, gender symbol used to identify female, asexual or non-binary people *◌, dotted circle *◯, the O mark Unicode Unicode provides various circle symbols: See also *Circle (other) * *List of circle topics *O (other) *Ø (other) * *Miscellaneous Mathematical Symbols-B (Unicode block) *Geometric Sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underline
An underscore or underline is a line drawn under a segment of text. In proofreading, underscoring is a convention that says "set this text in italic type", traditionally used on manuscript or typescript as an instruction to the printer. Its use to add emphasis in modern finished documents is generally avoided. The (freestanding) underscore character, , also called a low line, or low dash, originally appeared on the typewriter so that underscores could be typed. To produce an underscored word, the word was typed, the typewriter carriage was moved back to the beginning of the word, and the word was overtyped with the underscore character. In modern usage, underscoring is achieved with a markup language, with the Unicode combining low line or as a standard facility of word processing software. The free-standing underscore character is used to indicate word boundaries in situations where spaces are not allowed, such as in computer filenames, email addresses, and in Internet U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degree Sign
The degree symbol or degree sign, , is a glyph or symbol that is used, among other things, to represent degrees of arc (e.g. in geographic coordinate systems), hours (in the medical field), degrees of temperature or alcohol proof. The symbol consists of a small superscript circle. History The word degree is equivalent to Latin gradus which, since the medieval period, could refer to any stage in a graded system of ranks or steps. The number of the rank in question was indicated by ordinal numbers, in abbreviation with the ordinal indicator (a superscript letter ). Use of "degree" specifically for the degrees of arc, used in conjunction with Arabic numerals, became common in the 16th century, but this was initially without the use of an ordinal marker or degree symbol: instead, various abbreviation of ''gradus'' (e.g., Gra., Gr., gr., G.). The modern notation appears in print in the 1570s, with a borderline example by Jacques Pelletier du Mans in 1569, and was popularized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordinal & Degree
Ordinal may refer to: * Ordinal data, a statistical data type consisting of numerical scores that exist on an arbitrary numerical scale * Ordinal date, a simple form of expressing a date using only the year and the day number within that year * Ordinal Priority Approach, a multiple-criteria decision analysis method that aids in solving the group decision-making problems * Ordinal indicator, the sign adjacent to a numeral denoting that it is an ordinal number * Ordinal number in set theory, a number type with order structures * Ordinal number (linguistics), a word representing the rank of a number * Ordinal scale, ranking things that are not necessarily numbers * Ordinal utility (economics): a utility function which is used only to describe the preference ordering between different outcomes. Government * Regnal ordinal, used to distinguish monarchs and popes with the same regnal name Religion * Ordinal (liturgy), particularly in Anglicanism, Lutheranism and Catholicism, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chancery (medieval Office)
A chancery or chancellery () is a medieval writing office, responsible for the production of official documents.Coredon ''Dictionary of Medieval Terms and Phrases'' p. 66 The title of chancellor, for the head of the office, came to be held by important ministers in a number of states, and remains the title of the heads of government in modern Germany and Austria. Chancery hand is a term for various types of handwriting associated with chanceries. Etymology The word ''chancery'' is from French, from Latin, and ultimately refers to the lattice-work partition that divided a section of a church or court, from which also derives chancel, cancel "cross out with lines", and, more distantly, incarcerate "put behind bars" – see '' chancery'' for details. In England In England's medieval government, this office was one of the two main administrative offices, along with the Exchequer. It began as part of the royal household, but by the 13th-century was separate from the househo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vernacular
Vernacular is the ordinary, informal, spoken language, spoken form of language, particularly when perceptual dialectology, perceived as having lower social status or less Prestige (sociolinguistics), prestige than standard language, which is more codification (linguistics), codified, institutionally promoted, literary language, literary, or formal. More narrowly, a particular language variety that does not hold a widespread high-status perception, and sometimes even carries social stigma, is also called a vernacular, vernacular dialect, nonstandard dialect, etc. and is typically its speakers' native language, native variety. Regardless of any such stigma, all nonstandard dialects are full-fledged varieties of language with their own consistent grammatical structure, phonology, sound system, body of vocabulary, etc. Overview Like any native language variety, a vernacular has an internally coherent system of grammar. It may be associated with a particular set of vocabulary, and sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anno Domini
The terms (AD) and before Christ (BC) are used when designating years in the Gregorian calendar, Gregorian and Julian calendar, Julian calendars. The term is Medieval Latin and means "in the year of the Lord" but is often presented using "our Lord" instead of "the Lord", taken from the full original phrase "", which translates to "in the year of our Lord Jesus Christ". The form "BC" is specific to English language, English, and equivalent abbreviations are used in other languages: the Latin (language), Latin form, rarely used in English, is (ACN) or (AC). This calendar era takes as its epoch (date reference), epoch the traditionally reckoned year of the annunciation, conception or Nativity of Jesus, birth of Jesus. Years ''AD'' are counted forward since that epoch and years ''BC'' are counted backward from the epoch. There is no year zero in this scheme; thus the year AD 1 immediately follows the year 1 BC. This dating system was devised in 525 by Dionysius Exiguus but was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desinence
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns and adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs. Suffixes can carry grammatical information (inflectional endings) or lexical information ( derivational/lexical suffixes)''.'' Inflection changes the grammatical properties of a word within its syntactic category. Derivational suffixes fall into two categories: class-changing derivation and class-maintaining derivation. Particularly in the study of Semitic languages, suffixes are called affirmatives, as they can alter the form of the words. In Indo-European studies, a distinction is made between suffixes and endings (see Proto-Indo-European root). A word-final segment that is somewhere between a free morpheme and a bound morpheme is known as a suffixoidKremer, Marion. 1997. ''Person reference and gender in translation: a contrastive investigation of En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scribal Abbreviation
Scribal abbreviations, or sigla (grammatical number, singular: siglum), are abbreviations used by ancient and medieval scribes writing in various languages, including Latin, Greek language, Greek, Old English and Old Norse. In modern Textual criticism, manuscript editing (substantive and mechanical) sigla are the symbols used to indicate the source manuscript (e.g. variations in text between different such manuscripts). History Abbreviated writing, using sigla, arose partly from the limitations of the workable nature of the materials (rock (geology), stone, metal, parchment, etc.) employed in record-making and partly from their availability. Thus, lapidary, lapidaries, engravers, and copyists made the most of the available writing space. Scribal abbreviations were infrequent when writing materials were plentiful, but by the 3rd and 4th centuries AD, writing materials were scarce and costly. During the Roman Republic, several abbreviations, known as sigla (plural of ''siglum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ablative (Latin)
In Latin grammar, the ablative case () is one of the six noun cases. Traditionally, it is the sixth case (). It has forms and functions derived from the Proto-Indo-European ablative, instrumental, and locative. It expresses concepts similar to those of the English prepositions ''from''; ''with'', ''by''; and ''in'', ''at''. It is sometimes called the adverbial case, since phrases in the ablative can be translated as adverbs: , 'with incredible speed', or 'very quickly'. Uses Ablative proper Some uses of the ablative descend from the Proto-Indo-European ablative case. * Ablative of separation implies that some person or thing is separated from another. No active movement from one location to the next occurs; furthermore, ablatives of separation sometimes lack a preposition, particularly with certain verbs like or . For example, , "Cicero kept the enemy away from the city"; , "he freed them from fear". * Ablative of place from which describes active motion away from a place. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apocope
In phonology, apocope () is the omission (elision) or loss of a sound or sounds at the end of a word. While it most commonly refers to the loss of a final vowel, it can also describe the deletion of final consonants or even entire syllables. For instance, in many dialects the 't' in words like 'hot' remains unpronounced in contexts like 'hot potato'. Even longer words, such as 'Worcestershire', can undergo apocope, resulting in 'Worcester'. The resulting word form after apocope has occurred is called an . Etymology ''Apocope'' comes from the Greek () from () "cutting off", from () "away from" and () "to cut". Historical sound change In historical linguistics, ''apocope'' is often the loss of an unstressed vowel. Loss of an unstressed vowel or vowel and nasal * Latin → Portuguese (''sea'') * Vulgar Latin → Spanish (''bread'') * Vulgar Latin → French (''wolf'') * Proto-Germanic → Old, Middle, and Modern English ''land'' * Old English → Modern English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asturian Language
Asturian (; )Art. 1 de lLey 1/1998, de 23 de marzo, de uso y promoción del bable/asturiano [Law 1/93, of March 23, on the Use and Promotion of the Asturian Language/nowiki>] is a West Iberian languages, West Iberian Romance languages, Romance language spoken in the Principality of Asturias, Spain. Asturian is part of a wider linguistic group, the Asturleonese languages. The number of speakers is estimated at 100,000 (native) and 450,000 (second language). The dialects of the Astur-Leonese language family are traditionally classified in three groups: Western, Central, and Eastern. For historical and demographic reasons, the Standard language, standard is based on #Dialects, Central Asturian. Asturian has a distinct grammar, dictionary, and orthography. It is regulated by the Academy of the Asturian Language. Although it is not an official language of Spain, it is protected under the Statute of Autonomy of Asturias and is an elective language in schools. For much of its history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |