|
Many-minds Interpretation
The many-minds interpretation of quantum mechanics extends the many-worlds interpretation by proposing that the distinction between worlds should be made at the level of the mind of an individual observer. The concept was first introduced in 1970 by H. Dieter Zeh as a variant of the Hugh Everett interpretation in connection with quantum decoherence, and later (in 1981) explicitly called a many or multi-consciousness interpretation. The name ''many-minds interpretation'' was first used by David Albert and Barry Loewer in 1988. History Interpretations of quantum mechanics The various interpretations of quantum mechanics typically involve explaining the mathematical formalism of quantum mechanics, or to create a physical picture of the theory. While the mathematical structure has a strong foundation, there is still much debate about the physical and philosophical interpretation of the theory. These interpretations aim to tackle various concepts such as: # Evolution of the state o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is the foundation of all quantum physics, which includes quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. Quantum mechanics can describe many systems that classical physics cannot. Classical physics can describe many aspects of nature at an ordinary (macroscopic and Microscopic scale, (optical) microscopic) scale, but is not sufficient for describing them at very small submicroscopic (atomic and subatomic) scales. Classical mechanics can be derived from quantum mechanics as an approximation that is valid at ordinary scales. Quantum systems have Bound state, bound states that are Quantization (physics), quantized to Discrete mathematics, discrete values of energy, momentum, angular momentum, and ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Entanglement
Quantum entanglement is the phenomenon where the quantum state of each Subatomic particle, particle in a group cannot be described independently of the state of the others, even when the particles are separated by a large distance. The topic of quantum entanglement is at the heart of the disparity between classical physics and quantum physics: entanglement is a primary feature of quantum mechanics not present in classical mechanics. Measurement#Quantum mechanics, Measurements of physical properties such as position (vector), position, momentum, Spin (physics), spin, and polarization (waves), polarization performed on entangled particles can, in some cases, be found to be perfectly correlated. For example, if a pair of entangled particles is generated such that their total spin is known to be zero, and one particle is found to have clockwise spin on a first axis, then the spin of the other particle, measured on the same axis, is found to be anticlockwise. However, this behavior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Suicide And Immortality
Quantum suicide is a thought experiment in quantum mechanics and the philosophy of physics. Purportedly, it can falsify any interpretation of quantum mechanics other than the Everett many-worlds interpretation by means of a variation of the Schrödinger's cat thought experiment, from the cat's point of view. Quantum immortality refers to the subjective experience of surviving quantum suicide. This concept is sometimes conjectured to be applicable to real-world causes of death as well. As a thought experiment, quantum suicide is an intellectual exercise in which an abstract setup is followed through to its logical consequences merely to prove a theoretical point. Virtually all physicists and philosophers of science who have described it, especially in popularized treatments, underscore that it relies on contrived, idealized circumstances that may be impossible or exceedingly difficult to realize in real life, and that its theoretical premises are controversial even among supporters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
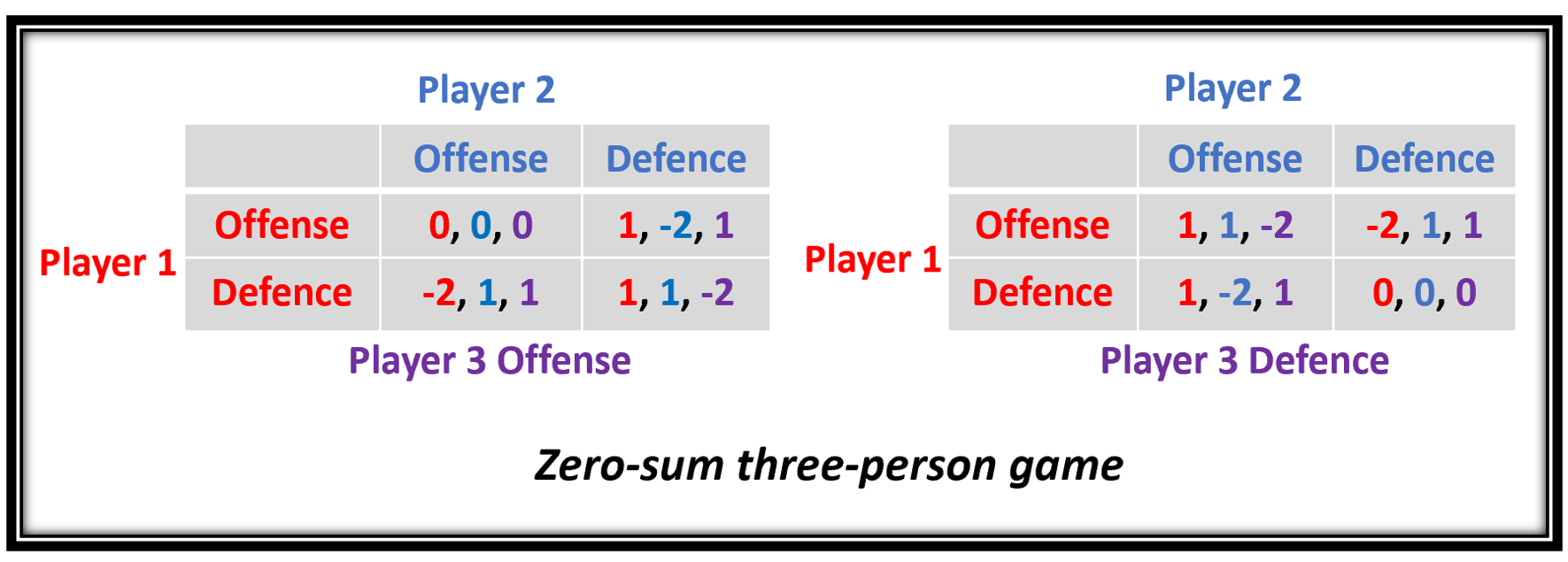
Zero-sum
Zero-sum game is a mathematical representation in game theory and economic theory of a situation that involves two competing entities, where the result is an advantage for one side and an equivalent loss for the other. In other words, player one's gain is equivalent to player two's loss, with the result that the net improvement in benefit of the game is zero. If the total gains of the participants are added up, and the total losses are subtracted, they will sum to zero. Thus, cutting a cake, where taking a more significant piece reduces the amount of cake available for others as much as it increases the amount available for that taker, is a zero-sum game if all participants value each unit of cake equally. Other examples of zero-sum games in daily life include games like poker, chess, sport and bridge where one person gains and another person loses, which results in a zero-net benefit for every player. In the markets and financial instruments, futures contracts and options are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tensor Product
In mathematics, the tensor product V \otimes W of two vector spaces V and W (over the same field) is a vector space to which is associated a bilinear map V\times W \rightarrow V\otimes W that maps a pair (v,w),\ v\in V, w\in W to an element of V \otimes W denoted . An element of the form v \otimes w is called the tensor product of v and w. An element of V \otimes W is a tensor, and the tensor product of two vectors is sometimes called an ''elementary tensor'' or a ''decomposable tensor''. The elementary tensors span V \otimes W in the sense that every element of V \otimes W is a sum of elementary tensors. If bases are given for V and W, a basis of V \otimes W is formed by all tensor products of a basis element of V and a basis element of W. The tensor product of two vector spaces captures the properties of all bilinear maps in the sense that a bilinear map from V\times W into another vector space Z factors uniquely through a linear map V\otimes W\to Z (see the section below ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hilbert Space
In mathematics, a Hilbert space is a real number, real or complex number, complex inner product space that is also a complete metric space with respect to the metric induced by the inner product. It generalizes the notion of Euclidean space. The inner product allows lengths and angles to be defined. Furthermore, Complete metric space, completeness means that there are enough limit (mathematics), limits in the space to allow the techniques of calculus to be used. A Hilbert space is a special case of a Banach space. Hilbert spaces were studied beginning in the first decade of the 20th century by David Hilbert, Erhard Schmidt, and Frigyes Riesz. They are indispensable tools in the theories of partial differential equations, mathematical formulation of quantum mechanics, quantum mechanics, Fourier analysis (which includes applications to signal processing and heat transfer), and ergodic theory (which forms the mathematical underpinning of thermodynamics). John von Neumann coined the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supervenience
In philosophy, supervenience refers to a relation between sets of properties or sets of facts. X is said to ''supervene'' on Y if and only if some difference in Y is necessary for any difference in X to be possible. Examples of supervenience, in which case the truth values of some propositions cannot vary unless the truth values of some other propositions vary, include: * Whether there is a table in the living room supervenes on the positions of molecules in the living room. * The truth value of (A) supervenes on the truth value of its negation, (¬A), and vice versa. Supervenience is of interest to philosophers because it differs from other nearby relations, for example ''entailment''. Some philosophers believe it possible for some A to supervene on some B without being entailed by B. In such cases it may seem puzzling why A should supervene on B and equivalently why changes in A should require changes in B. Two important applications of supervenience involve cases like this. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Many-worlds Interpretation
The many-worlds interpretation (MWI) is an interpretation of quantum mechanics that asserts that the universal wavefunction is Philosophical realism, objectively real, and that there is no wave function collapse. This implies that all Possible world, possible outcomes of quantum measurements are physically realized in different "worlds". The evolution of reality as a whole in MWI is rigidly Determinism, deterministic and principle of locality, local. Many-worlds is also called the relative state formulation or the Everett interpretation, after physicist Hugh Everett III, Hugh Everett, who first proposed it in 1957.Hugh Everett]Theory of the Universal Wavefunction Thesis, Princeton University, (1956, 1973), pp. 1–140. Bryce DeWitt popularized the formulation and named it ''many-worlds'' in the 1970s. See also Cécile DeWitt-Morette, Cecile M. DeWitt, John A. Wheeler (eds,) The Everett–Wheeler Interpretation of Quantum Mechanics, ''Battelle Rencontres: 1967 Lectures in Mathema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consciousness Causes Collapse
The postulate that consciousness causes collapse is an interpretation of quantum mechanics in which consciousness is postulated to be the main mechanism behind the process of measurement in quantum mechanics. It is a historical interpretation of quantum mechanics that is largely discarded by modern physicists. The idea is attributed to Eugene Wigner who wrote about it in the 1960s, but traces of the idea appear as early as the 1930s. Wigner later rejected this interpretation in the 1970s and 1980s. History Earlier work According to Werner Heisenberg recollections in ''Physics and Beyond'', Niels Bohr is said to have rejected the necessity of a conscious observer in quantum mechanics as early as 1927. In his 1932 book '' Mathematical Foundations of Quantum Mechanics'', John von Neumann argued that the mathematics of quantum mechanics allows the collapse of the wave function to be placed at any position in the causal chain from the measurement device to the "subjective perce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics (American Physical Society Journal)
The ''Journal of Applied Physics'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal with a focus on the physics of technology, modern technology. The journal was originally established in 1931 under the name of ''Physics'', and was published by the American Physical Society for its first 7 volumes. In January 1937, ownership was transferred to the American Institute of Physics "in line with the efforts of the American Physical Society to enhance the standing of physics as a profession". The journal's current editor-in-chief is André Anders (Leibniz Institute of Surface Engineering). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor of 2.7. References External links * Physics journals Weekly journals Academic journals established in 1931 English-language journals American Institute of Physics academic journals Hybrid open access journals {{physics-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bell's Inequality
Bell's theorem is a term encompassing a number of closely related results in physics, all of which determine that quantum mechanics is incompatible with local hidden-variable theories, given some basic assumptions about the nature of measurement. The first such result was introduced by John Stewart Bell in 1964, building upon the Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen paradox, which had called attention to the phenomenon of quantum entanglement. In the context of Bell's theorem, "local" refers to the principle of locality, the idea that a particle can only be influenced by its immediate surroundings, and that interactions mediated by physical fields cannot propagate faster than the speed of light. " Hidden variables" are supposed properties of quantum particles that are not included in quantum theory but nevertheless affect the outcome of experiments. In the words of Bell, "If hidden-variable theoryis local it will not agree with quantum mechanics, and if it agrees with quantum mechani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Non-locality
In theoretical physics, quantum nonlocality refers to the phenomenon by which the measurement statistics of a multipartite quantum system do not allow an interpretation with local realism. Quantum nonlocality has been experimentally verified under a variety of physical assumptions. Quantum nonlocality does not allow for faster-than-light communication, and hence is compatible with special relativity and its universal speed limit of objects. Thus, quantum theory is local in the strict sense defined by special relativity and, as such, the term "quantum nonlocality" is sometimes considered a misnomer. Still, it prompts many of the foundational discussions concerning quantum theory. History Einstein, Podolsky and Rosen In the 1935 EPR paper, Albert Einstein, Boris Podolsky and Nathan Rosen described "two spatially separated particles which have both perfectly correlated positions and momenta" as a direct consequence of quantum theory. They intended to use the classical principl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |