|
Manualism
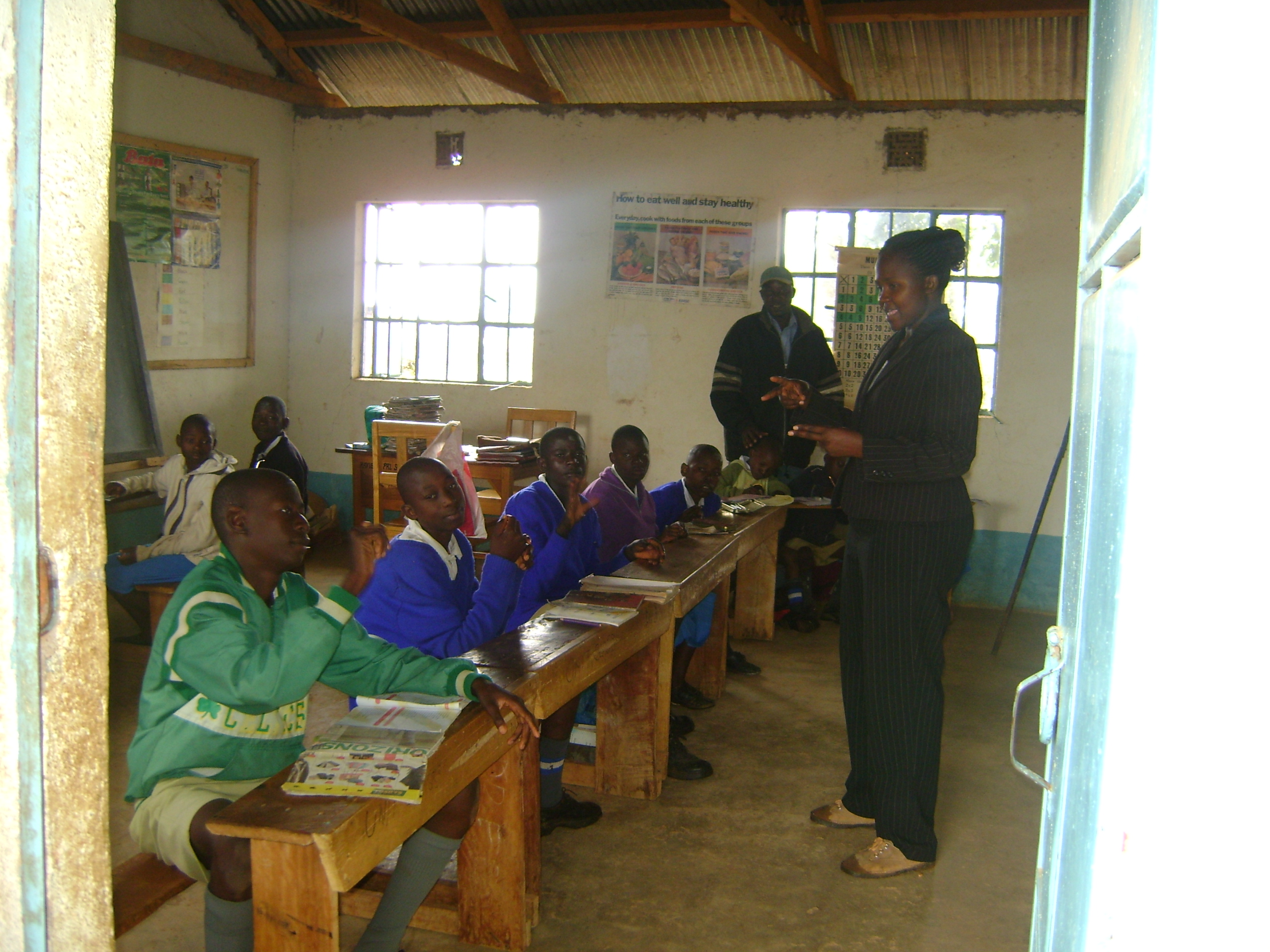
Manualism is a method of Education of the deaf, education of deaf students using sign language within the classroom. Manualism arose in the late 18th century with the advent of free public schools for the deaf in Europe. These teaching methods were brought over to the United States where the American School for the Deaf, first school for the deaf was established in 1817. Today manualism methods are used in conjunction with oralism methods in the majority of American deaf schools. Origins The first manual schools were in Paris, France. Charles-Michel de l'Épée, Abbe de l’Épée, a Catholic priest, encountered two teenage deaf girls while he visited a family in the poor part of the city. He decided to take it upon himself to educate them. He invented a technique called "methodical signing" from the signs the girls already used, with the combination of methods influenced by the writings of Johann Konrad Ammann and Juan Pablo Bonet. He created a one-hand manual alphabet to be ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oralism
Oralism is the education of deaf students through oral language by using lip reading, speech, and mimicking the mouth shapes and breathing patterns of speech.Through Deaf Eyes. Diane Garey, Lawrence R. Hott. DVD, PBS (Direct), 2007. Oralism came into popular use in the United States around the late 1860s. In 1867, the Clarke School for the Deaf in Northampton, Massachusetts, was the first school to start teaching in this manner. Oralism and its contrast, manualism, manifest differently in deaf education and are a source of controversy for involved communities. Listening and Spoken Language, a technique for teaching deaf children that emphasizes the child's perception of auditory signals from hearing aids or cochlear implants, is how oralism continues on in the current day. History 16th and 17th century Fray Pedro Ponce de León (1520–1584) is often credited as the inventor of deaf education. Later, Juan Pablo Bonet (–1633) published ''Reducción de las letras y ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles-Michel De L'Épée
Charles-Michel de l'Épée (; 24 November 1712 – 23 December 1789) was an 18th-century French philanthropic educator who has become known as the "Father of the Deaf". He founded Institut National de Jeunes Sourds de Paris, the first public school for the deaf, in 1760. Overview Charles-Michel de l'Épée was born to a wealthy family in Versailles (city), Versailles, the seat of political power in what was then the most powerful kingdom of Europe. He studied to be a Catholic priest.L'Echo Magazine, le mensuel des sourds No. 794. Octobre 2012, p. 5 L'Épée then turned his attention toward charitable services for the poor, and, on one foray into the slums of Paris, he had a chance encounter with two young deaf sisters who communicated using a sign language.* Massieu, Jean; Laurent Clerc; and Roch Ambroise Cucurron Sicard. 181''Recueil des définitions et réponses les plus remarquables de Massieu et Clerc, sourds-muets, aux diverses questions qui leur ont été faites dans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Education Of The Deaf
Deaf education is the education of students with any degree of hearing loss, hearing loss or deafness. This may involve, but does not always, individually-planned, systematically-monitored teaching methods, adaptive materials, accessible settings, and other interventions designed to help students achieve a higher level of self-sufficiency and success in the school and community than they would achieve with a typical classroom education. There are different language modalities used in educational setting where students get varied communication methods. A number of countries focus on training teachers to teach deaf students with a variety of approaches and have organizations to support and advocate for deaf students. Identifying deaf students Children may be identified as candidates for deaf education from their audiogram or medical history. Hearing loss is generally described as slight, mild, moderate, severe, or profound, depending upon how well a person can hear the intensities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manualism And Oralism
Deaf education is the education of students with any degree of hearing loss or deafness. This may involve, but does not always, individually-planned, systematically-monitored teaching methods, adaptive materials, accessible settings, and other interventions designed to help students achieve a higher level of self-sufficiency and success in the school and community than they would achieve with a typical classroom education. There are different language modalities used in educational setting where students get varied communication methods. A number of countries focus on training teachers to teach deaf students with a variety of approaches and have organizations to support and advocate for deaf students. Identifying deaf students Children may be identified as candidates for deaf education from their audiogram or medical history. Hearing loss is generally described as slight, mild, moderate, severe, or profound, depending upon how well a person can hear the intensities of frequenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Sign Language
American Sign Language (ASL) is a natural language that serves as the predominant sign language of Deaf communities in the United States and most of Anglophone Canadians, Anglophone Canada. ASL is a complete and organized visual language that is expressed by employing both manual and nonmanual features. Besides North America, dialects of ASL and ASL-based creole language, creoles are used in many countries around the world, including much of West Africa and parts of Southeast Asia. ASL is also widely learned as a second language, serving as a lingua franca. ASL is most closely related to French Sign Language (LSF). It has been proposed that ASL is a creole language of LSF, although ASL shows features atypical of creole languages, such as agglutination, agglutinative morphology. ASL originated in the early 19th century in the American School for the Deaf (ASD) in Hartford, Connecticut, from a situation of language contact. Since then, ASL use has been propagated widely by schools ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris, France
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, fourth-most populous city in the European Union and the List of cities proper by population density, 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2022. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, culture, Fashion capital, fashion, and gastronomy. Because of its leading role in the French art, arts and Science and technology in France, sciences and its early adoption of extensive street lighting, Paris became known as the City of Light in the 19th century. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an official estimated population of 12,271,794 inhabitants in January 2023, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martha's Vineyard, Massachusetts
Martha's Vineyard, often simply called the Vineyard, is an island in the U.S. state of Massachusetts, lying just south of Cape Cod. It is known for being a popular, affluent summer colony, and includes the smaller peninsula Chappaquiddick Island. It is the 58th largest island in the U.S., with a land area of about , and the third-largest on the East Coast, after Long Island and Mount Desert Island. Martha's Vineyard constitutes the bulk of Dukes County, Massachusetts, which also includes the Elizabeth Islands and the island of Nomans Land. The island's year-round population has considerably increased since the 1960s. In the 2023 Martha's Vineyard Commission report, the year-round population was 20,530, an increase from 16,460 in 2010. The summer population swells to more than 200,000 people. About 56 percent of the Vineyard's 14,621 homes are seasonally occupied. A study by the Martha's Vineyard Commission in 2006 found that the cost of living on the island is 60 percent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bimodal Bilingualism
Bimodal bilingualism is an individual or community's bilingual competency in at least one oral language and at least one sign language, which utilize two different modalities. An oral language consists of a vocal-aural modality versus a signed language which consists of a visual-spatial modality. A substantial number of bimodal bilinguals are children of deaf adults (CODA) or other hearing people who learn sign language for various reasons. Deaf people as a group have their own sign language(s) and culture that is referred to as Deaf, but invariably live within a larger hearing culture with its own oral language. Thus, "most deaf people are bilingual to some extent in n orallanguage in some form". In discussions of multilingualism in the United States, bimodal bilingualism and bimodal bilinguals have often not been mentioned or even considered. This is in part because American Sign Language, the predominant sign language used in the U.S., only began to be acknowledged as a natural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Stokoe
William Clarence “Bill” Stokoe Jr. ( ; July 21, 1919 – April 4, 2000) was an American linguist and a long-time professor at Gallaudet University. His research on American Sign Language (ASL) revolutionized the understanding of ASL in the United States and sign languages throughout the world. Stokoe's work led to a widespread recognition that sign languages are true languages, exhibiting syntax and morphology, and are not only systems of gesture. Early life and education William C. Stokoe Jr. was born July 21, 1919, in Lancaster, New Hampshire. Stokoe graduated from Cornell University in 1941, from which he earned his Ph.D. in English in 1946, specializing in medieval literature. From there, he became an instructor of English at Wells College. Career From 1955 to 1970, he served as a professor and chairman of the English department at Gallaudet University, after being recruited to the position by his friend and former classmate Dean George Detmold. He published ''Sign La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallaudet University
Gallaudet University ( ) is a private federally chartered university in Washington, D.C., for the education of the deaf and hard of hearing. It was founded in 1864 as a grammar school for both deaf and blind children. It was the first school for the advanced education of the deaf and hard of hearing in the world and remains the only higher education institution in which all programs and services are specifically designed to accommodate deaf and hard of hearing students. Hearing students are admitted to the graduate school and a small number are also admitted as undergraduates each year. The university was named after Thomas Hopkins Gallaudet, a notable figure in the advancement of deaf education. Gallaudet University is officially bilingual, with American Sign Language (ASL) and written English used for instruction and by the college community. Although there are no specific ASL proficiency requirements for undergraduate admission, many graduate programs require varying deg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William C Stokoe Jr
William is a masculine given name of Germanic origin. It became popular in England after the Norman conquest in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will or Wil, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill, Billie, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie). Female forms include Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the German given name ''Wilhelm''. Both ultimately descend from Proto-Germanic ''*Wiljahelmaz'', with a direct cognate also in the Old Norse name ''Vilhjalmr'' and a West Germanic borrowing into Medieval Latin ''Willelmus''. The Proto-Germanic name is a compound of *''wiljô'' "will, wish, desire" and *''helmaz'' "helm, helmet".Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford Univers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |