|
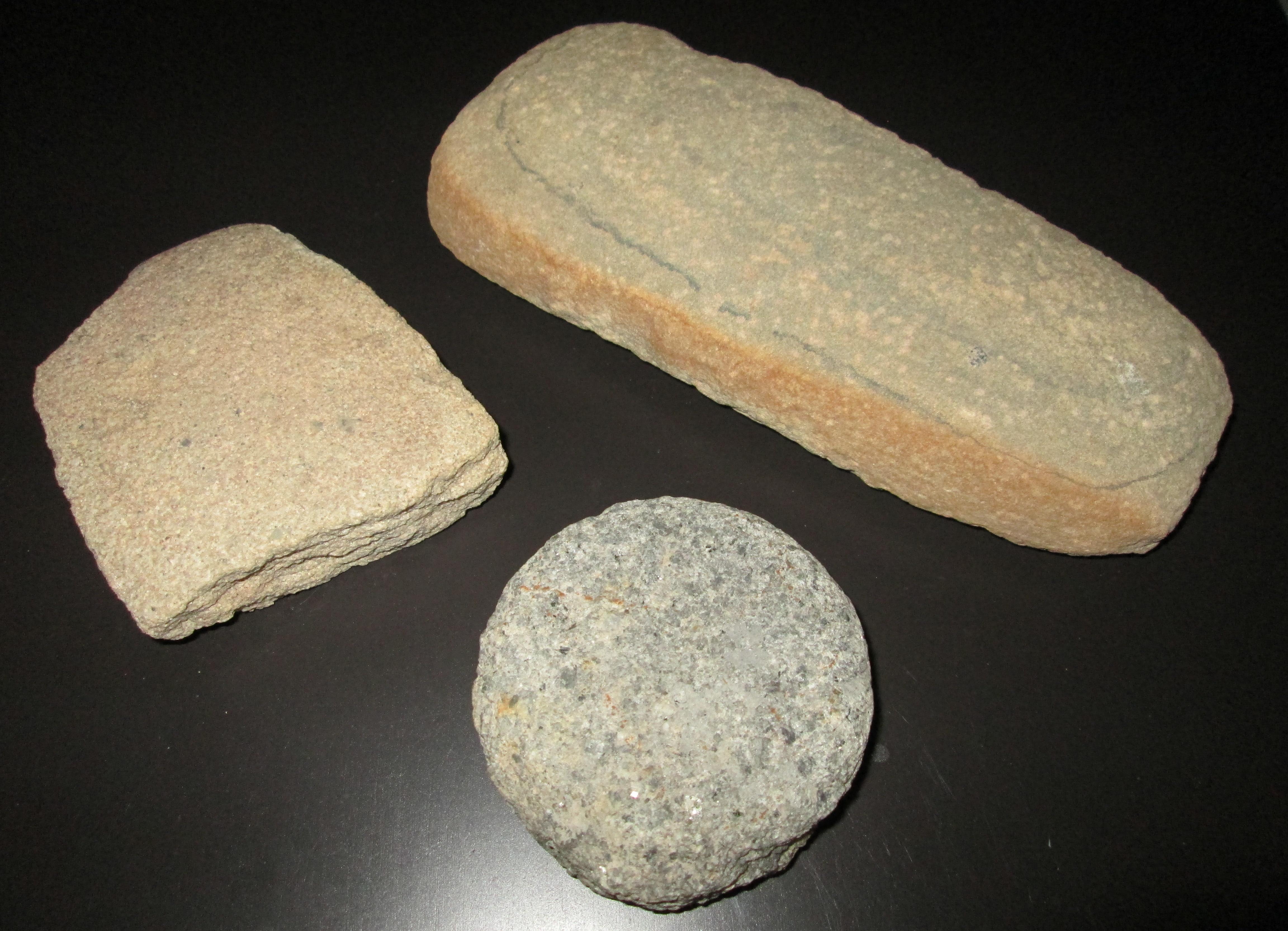
Mano (stone)
A mano ( Spanish for ''hand'') is a ground stone tool used with a metate to process or grind food by hand. It is also known as metlapil, a term derived from Nahuatl. History Manos were used in prehistoric times to process wild seeds, nuts, and other food, generally used with greater frequency in the Archaic period, when people became more reliant upon local wild plant food for their diet. Later, Manos and metates were used to process cultivated maize.Gibbon, Guy E.; Ames, Kenneth M. (1998''Archaeology of Prehistoric Native America: An Encyclopedia''.pp. 107, 166. . In its early use in the American Southwest, the mano and metate were used to grind wild plants. The mano began as a one-handed tool. Once the maize cultivation became more prevalent, the mano became a larger, two-handed tool that more efficiently ground food against an evolved basin or trough metate. Besides food, Manos and metates were used to separate and pulverize clay from earthen debris and stones. The r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native American Manos Arizona 2014
Native may refer to: People * '' Jus sanguinis'', nationality by blood * '' Jus soli'', nationality by location of birth * Indigenous peoples, peoples with a set of specific rights based on their historical ties to a particular territory ** Native Americans (other) In arts and entertainment * Native (band), a French R&B band * Native (comics), a character in the X-Men comics universe * ''Native'' (album), a 2013 album by OneRepublic * ''Native'' (2016 film), a British science fiction film * ''The Native'', a Nigerian music magazine In science * Native (computing), software or data formats supported by a certain system * Native language, the language(s) a person has learned from birth * Native metal, any metal that is found in its metallic form, either pure or as an alloy, in nature * Native species, a species whose presence in a region is the result of only natural processes * List of Australian plants termed "native", whose common name is of the form "native . . . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Pueblo People
The Ancestral Puebloans, also known as Ancestral Pueblo peoples or the Basketmaker-Pueblo culture, were an ancient Native American culture of Pueblo peoples spanning the present-day Four Corners region of the United States, comprising southeastern Utah, northeastern Arizona, northwestern New Mexico, and southwestern Colorado. They are believed to have developed, at least in part, from the Oshara tradition, which developed from the Picosa culture. The Ancestral Puebloans lived in a range of structures that included small family pit houses, larger structures to house clans, grand pueblos, and cliff-sited dwellings for defense. They had a complex network linking hundreds of communities and population centers across the Colorado Plateau. They held a distinct knowledge of celestial sciences that found form in their architecture. The kiva, a congregational space that was used mostly for ceremonies, was an integral part of the community structure. Archaeologists continue to debate w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native American Cuisine
Native Americans (also called American Indians, First Americans, or Indigenous Americans) are the Indigenous peoples of the United States, particularly of the lower 48 states and Alaska. They may also include any Americans whose origins lie in any of the indigenous peoples of North or South America. The United States Census Bureau publishes data about "American Indians and Alaska Natives", whom it defines as anyone "having origins in any of the original peoples of North and South America ... and who maintains tribal affiliation or community attachment". The census does not, however, enumerate "Native Americans" as such, noting that the latter term can encompass a broader set of groups, e.g. Native Hawaiians, which it tabulates separately. The European colonization of the Americas from 1492 resulted in a precipitous decline in the size of the Native American population because of newly introduced diseases, including weaponized diseases and biological warfare by colonizers,C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Tools Of The Americas
Indigenous may refer to: *Indigenous peoples *Indigenous (ecology), presence in a region as the result of only natural processes, with no human intervention *Indigenous (band), an American blues-rock band *Indigenous (horse), a Hong Kong racehorse * ''Indigenous'' (film), Australian, 2016 See also *Indigenous Australians *Indigenous language *Indigenous peoples in Canada *Indigenous religion *Missing and Murdered Indigenous Women Missing and Murdered Indigenous Women are instances of violence against Indigenous women in Canada and the United States, notably those in the First Nations in Canada and Native American communities, but also amongst other Indigenous peoples s ... * Native (other) * * {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexican Food Preparation Utensils
Mexican may refer to: Mexico and its culture *Being related to, from, or connected to the country of Mexico, in North America ** People *** Mexicans, inhabitants of the country Mexico and their descendants *** Mexica, ancient indigenous people of the Valley of Mexico ** Being related to the State of Mexico, one of the 32 federal entities of Mexico ** Culture of Mexico *** Mexican cuisine *** historical synonym of Nahuatl, language of the Nahua people (including the Mexica) Arts and entertainment * "The Mexican" (short story), by Jack London * "The Mexican" (song), by the band Babe Ruth * Regional Mexican, a Latin music radio format Films * ''The Mexican'' (1918 film), a German silent film * ''The Mexican'' (1955 film), a Soviet film by Vladimir Kaplunovsky based on the Jack London story, starring Georgy Vitsin * ''The Mexican'', a 2001 American comedy film directed by Gore Verbinski, starring Brad Pitt and Julia Roberts Other uses * USS ''Mexican'' (ID-1655), United State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoamerican Cuisine
Mesoamerican cuisine – (covering Belize, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, northern Costa Rica and Mexico) has four main staples: maize (many varieties based on what climate it is grown in), beans, squash and chili. Other plant-based foods used include: amaranth, avocado, cassava, cherimoya, chia, chocolate, guava, nanche, pineapple, sapodilla, sweet potatoes, yucca and zapote. Historically, various methods and techniques were employed to store, prepare and preserve the foods, most of which remain in use today. Hernán Cortés introduced rice and wheat to Mesoamerica, prior to which time milpa (known as the cornfield) was one of the main sources of sustenance. Some traditional foods featured in the cuisine include: Atole (a drink made using masa) and Chocolate Atole (with the addition of chocolate) also known as champurrado. Two classic maize dishes are: boiling maize in water and lime, mixing with chili peppers and eating as gruel; dough preparation for flat c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoamerican Artifacts
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area that begins in the southern part of North America and extends to the Pacific coast of Central America, thus comprising the lands of central and southern Mexico, all of Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, and parts of Honduras, Nicaragua and northwestern part of Costa Rica. As a cultural area, Mesoamerica is defined by a mosaic of cultural traits developed and shared by its indigenous cultures. In the pre-Columbian era, many indigenous societies flourished in Mesoamerica for more than 3,000 years before the Spanish colonization of the Americas began on Hispaniola in 1493. In world history, Mesoamerica was the site of two historical transformations: (i) primary urban generation, and (ii) the formation of New World cultures from the mixtures of the indigenous Mesoamerican peoples with the European, African, and Asian peoples who were introduced by the Spanish colonization of the Americas. Mesoamerica is one of the six areas in the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithics
Lithic may refer to: *Relating to stone tools ** Lithic analysis, the analysis of stone tools and other chipped stone artifacts ** Lithic core, the part of a stone which has had flakes removed from it ** Lithic flake, the portion of a rock removed to make a tool ** Lithic reduction, the process of removing flakes from a stone to make a tool **Lithic technology, the array of techniques to produce tools from stone * Lithic fragment (geology), pieces of rock, eroded to sand size, and now sand grains in a sedimentary rock * Lithic sandstone, sandstone with a significant component of (above) lithic fragments * Lithic stage, the North American prehistoric period before 10,000 years ago See also *Stone Age **Paleolithic **Mesolithic **Neolithic The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Grinding Tools
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin and contains essential nutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is ingested by an organism and assimilated by the organism's cells to provide energy, maintain life, or stimulate growth. Different species of animals have different feeding behaviours that satisfy the needs of their metabolisms and have evolved to fill a specific ecological niche within specific geographical contexts. Omnivorous humans are highly adaptable and have adapted to obtaining food in many different ecosystems. Humans generally use cooking to prepare food for consumption. The majority of the food energy required is supplied by the industrial food industry, which produces food through intensive agriculture and distributes it through complex food processing and food distribution systems. This system of conventional agriculture relies he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quern-stone
A quern-stone is a stone tool for hand-grinding a wide variety of materials, especially for various types of grains. They are used in pairs. The lower stationary stone of early examples is called a ''saddle quern'', while the upper mobile stone is called a ''muller'', ''rubber'', or ''handstone''. The upper stone was moved in a back-and-forth motion across the saddle quern. Later querns are known as ''rotary querns''. The central hole of a rotary quern is called the ''eye'', and a dish in the upper surface is known as the ''hopper''. A ''handle slot'' contained a handle which enabled the rotary quern to be rotated. They were first used in the Neolithic era to grind cereals into flour. Design The upper stones were usually concave while the lower ones were convex. Quern-stones are frequently identifiable by their grooved working surfaces which enabled the movement of flour. Sometimes a millrind was present as a piece of wood (or other material), which allowed the cereal et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grinding Slab
250px, Stone slab in east-central California used to grind acorns In archaeology, a grinding slab is a ground stone artifact generally used to grind plant materials into usable size, though some slabs were used to shape other ground stone artifacts. Some grinding stones are portable; others are not and, in fact, may be part of a stone outcropping. Grinding slabs used for plant processing typically acted as a coarse surface against which plant materials were ground using a portable hand stone, or mano ("hand" in Spanish). Variant grinding slabs are referred to as metates or querns, and have a ground-out bowl. Like all ground stone artifacts, grinding slabs are made of large-grained materials such as granite, basalt, or similar tool stone In archaeology, a tool stone is a type of stone that is used to manufacture stone tools, or tools that use stone as raw material. Generally speaking, tools that require a sharp edge are made using cryptocrystalline materials that frac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bedrock Mortar
A bedrock mortar (BRM) is an anthropogenic circular depression in a rock outcrop or naturally occurring slab, used by people in the past for grinding of grain, acorns or other food products. There are often a cluster of a considerable number of such holes in proximity indicating that people gathered in groups to conduct food grinding in prehistoric cultures. Correspondingly the alternative name gossip stone is sometimes applied, indicating the social context of the food grinding activity. Typical dimensions of the circular indentations are approximately 12 centimeters (4.7 inch) in diameter by 10 centimeters (3.9 inches) deep, although a considerable range of depths of the cavities have been documented . The bedrock mortar has been identified in a number of world regions, but has been particularly intensely documented in the Americas. An alternative term for the bedrock mortar site is bedrock milling station. Bedrock metate A bedrock mortar should not be confused with a bedroc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |