|
Managed Decline
Managed decline is a phrase that refers to the management of the decline (or "sunset") phase at the end of a lifecycle, with the goal of minimizing costs or other forms of losses and harm. The concept originated in business where it referred to the management of companies and industries, but has since spread beyond to be used in other contexts. Examples of managed decline include the handling of the textiles, shipbuilding, coal and steel industries in North America and Europe in the 1980s (in 1981, it was proposed for the English city of Liverpool by Chancellor Geoffrey Howe); of the postal delivery services in Europe and the United States in the first decades of the 21st century, of the established churches in western Europe since the 1970s, and that of an individual's quality of life in their final years as they face old age or terminal illness. Decline can be managed through multiple means, including public or industrial policy efforts such as government provision of retraini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrase
In syntax and grammar, a phrase is a group of words or singular word acting as a grammatical unit. For instance, the English expression "the very happy squirrel" is a noun phrase which contains the adjective phrase "very happy". Phrases can consist of a single word or a complete sentence. In theoretical linguistics, phrases are often analyzed as units of syntactic structure such as a constituent. Common and technical use There is a difference between the common use of the term ''phrase'' and its technical use in linguistics. In common usage, a phrase is usually a group of words with some special idiomatic meaning or other significance, such as " all rights reserved", " economical with the truth", " kick the bucket", and the like. It may be a euphemism, a saying or proverb, a fixed expression, a figure of speech, etc.. In linguistics, these are known as phrasemes. In theories of syntax, a phrase is any group of words, or sometimes a single word, which plays a particular r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoffrey Howe
Richard Edward Geoffrey Howe, Baron Howe of Aberavon, (20 December 1926 – 9 October 2015) was a British Conservative politician who served as Deputy Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1989 to 1990. Howe was Margaret Thatcher's longest-serving Cabinet minister, successively holding the posts of Chancellor of the Exchequer, Foreign Secretary, and finally Leader of the House of Commons, deputy prime minister and Lord President of the Council. His resignation on 1 November 1990 is widely considered to have precipitated the leadership challenge that led to Thatcher's resignation three weeks later. Early life Geoffrey Howe was born in 1926 at Port Talbot, Wales, to Benjamin Edward Howe, a solicitor and coroner, and Eliza Florence (née Thomson) Howe. He was to describe himself as a quarter Scottish, a quarter Cornish and half Welsh. He was educated at three independent schools: at Bridgend Preparatory School in Bryntirion, followed by Abberley Hall School ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Collapse
State collapse is the breakdown of government authority in maintaining law and order. It is often used to describe extreme situations in which state institutions are no longer able to function. Rather than a temporary disruption such as a riot or a coup, a collapsed state is the result of a longer-term degenerative process, in which a ruling regime is no longer able to satisfy the demands of societal groups. When a new regime moves in, often led by the military, civil society typically fails to rally around the central government, and societal actors fend for themselves at the local level. Neighboring states interfere politically, sometimes harboring dissidents within their borders, and the informal economy becomes dominant, operating beyond the control of the state and further undermining potential reconstruction. Definitions and examples While the definitions of " failed state" and " fragile state" have been contested for being "too broad and too vague", foreign policy exper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palliative
Palliative care (derived from the Latin root , or 'to cloak') is an interdisciplinary medical caregiving approach aimed at optimizing quality of life and mitigating suffering among people with serious, complex, and often terminal illnesses. Within the published literature, many definitions of palliative care exist. The World Health Organization (WHO) describes palliative care as "an approach that improves the quality of life of patients and their families facing the problems associated with life-threatening illness, through the prevention and relief of suffering by means of early identification and impeccable assessment and treatment of pain and other problems, physical, psychosocial, and spiritual." In the past, palliative care was a disease specific approach, but today the WHO takes a more broad approach, that the principles of palliative care should be applied as early as possible to any chronic and ultimately fatal illness. Palliative care is appropriate for individuals with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Policy
An industrial policy (IP) or industrial strategy of a country is its official strategic effort to encourage the development and growth of all or part of the economy, often focused on all or part of the manufacturing sector. The government takes measures "aimed at improving the competitiveness and capabilities of domestic firms and promoting structural transformation." A country's infrastructure (including transportation, telecommunications and energy industry) is a major enabler of the wider economy and so often has a key role in IP. Industrial policies are interventionist measures typical of mixed economy countries. Many types of industrial policies contain common elements with other types of interventionist practices such as trade policy. Industrial policy is usually seen as separate from broader macroeconomic policies, such as tightening credit and taxing capital gains. Traditional examples of industrial policy include subsidizing export industries and import-substitutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terminal Illness
Terminal illness or end-stage disease is a disease that cannot be cured or adequately treated and is expected to result in the death of the patient. This term is more commonly used for progressive diseases such as cancer, dementia or advanced heart disease than for injury. In popular use, it indicates a disease that will progress until death with near absolute certainty, regardless of treatment. A patient who has such an illness may be referred to as a terminal patient, terminally ill or simply as being terminal. There is no standardized life expectancy for a patient to be considered terminal, although it is generally months or less. Life expectancy for terminal patients is a rough estimate given by the physician based on previous data and does not always reflect true longevity. An illness which is lifelong but not fatal is a chronic condition. Terminal patients have options for disease management after diagnosis. Examples include caregiving, continued treatment, palliative and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Established Church
A state religion (also called religious state or official religion) is a religion or creed officially endorsed by a sovereign state. A state with an official religion (also known as confessional state), while not secular, is not necessarily a theocracy. State religions are official or government-sanctioned establishments of a religion, but the state does not need to be under the control of the religion (as in a theocracy) nor is the state-sanctioned religion necessarily under the control of the state. Official religions have been known throughout human history in almost all types of cultures, reaching into the Ancient Near East and prehistory. The relation of religious cult and the state was discussed by the ancient Latin scholar Marcus Terentius Varro, under the term of '' theologia civilis'' (). The first state-sponsored Christian church was the Armenian Apostolic Church, established in 301 CE. In Christianity, as the term ''church'' is typically applied to a place of wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine United States Minor Outlying Islands, Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in Compact of Free Association, free association with three Oceania, Pacific Island Sovereign state, sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Palau, Republic of Palau. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders Canada–United States border, with Canada to its north and Mexico–United States border, with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chancellor Of The Exchequer
The chancellor of the Exchequer, often abbreviated to chancellor, is a senior minister of the Crown within the Government of the United Kingdom, and head of His Majesty's Treasury. As one of the four Great Offices of State, the Chancellor is a high-ranking member of the British Cabinet. Responsible for all economic and financial matters, the role is equivalent to that of a finance minister in other countries. The chancellor is now always Second Lord of the Treasury as one of at least six lords commissioners of the Treasury, responsible for executing the office of the Treasurer of the Exchequer the others are the prime minister and Commons government whips. In the 18th and early 19th centuries, it was common for the prime minister also to serve as Chancellor of the Exchequer if he sat in the Commons; the last Chancellor who was simultaneously prime minister and Chancellor of the Exchequer was Stanley Baldwin in 1923. Formerly, in cases when the chancellorship was vacant, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
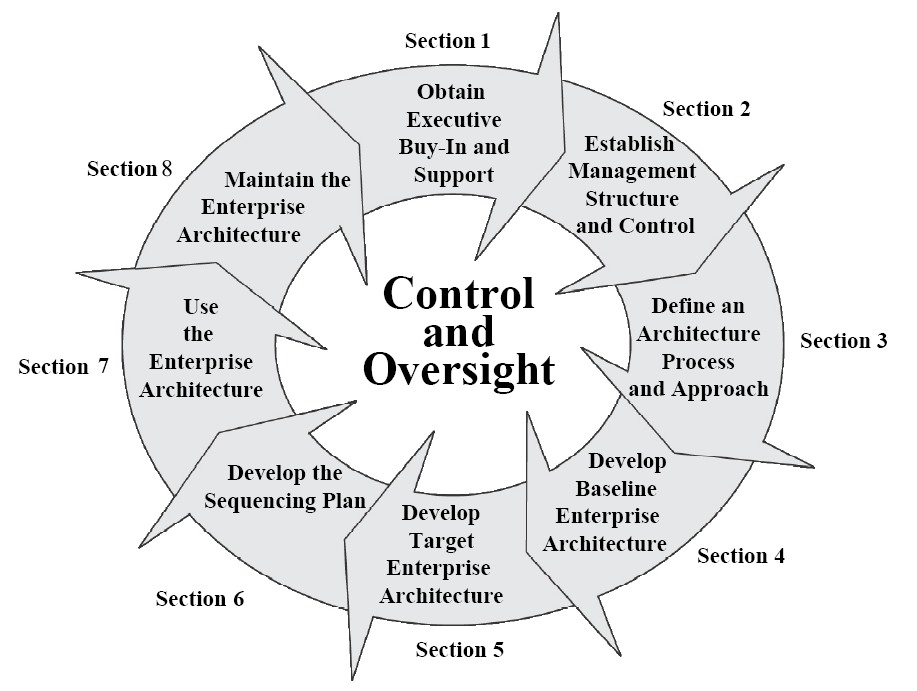
Enterprise Life Cycle
Enterprise life cycle (ELC) in enterprise architecture is the dynamic, iterative process of changing the enterprise over time by incorporating new business processes, new technology, and new capabilities, as well as maintenance, disposition and disposal of existing elements of the enterprise.Chief Information Officer Council (2001)A Practical Guide to Federal Enterprise Architecture/ref> Overview The enterprise life cycle is a key concept in enterprise architecture (EA), enterprise engineering and systems engineering. The Enterprise Architecture process is closely related to similar processes, as program management cycle or systems development life cycle, and has similar properties to those found in the product life cycle.Alain Bernard, Serge Tichkiewitch (2008). ''Methods and Tools for Effective Knowledge Life-Cycle-Management.'' p. 403 The concept of enterprise life cycle aids in the implementation of an enterprise architecture, and the capital planning and investment cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liverpool
Liverpool is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the List of English districts by population, 10th largest English district by population and its ESPON metropolitan areas in the United Kingdom, metropolitan area is the fifth largest in the United Kingdom, with a population of 2.24 million. On the eastern side of the Mersey Estuary, Liverpool historically lay within the ancient Hundred (county division), hundred of West Derby (hundred), West Derby in the county of Lancashire. It became a Borough status in the United Kingdom, borough in 1207, a City status in the United Kingdom, city in 1880, and a county borough independent of the newly-created Lancashire County Council in 1889. Its Port of Liverpool, growth as a major port was paralleled by the expansion of the city throughout the Industrial Revolution. Along with general cargo, freight, and raw materials such as coal and cotton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. Comprising the westernmost peninsulas of Eurasia, it shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south and Asia to the east. Europe is commonly considered to be separated from Asia by the watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea and the waterways of the Turkish Straits. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and Europe ... is formed by the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, and the Blac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)