|
Majority Voting
In social choice theory, the majority rule (MR) is a social choice rule which says that, when comparing two options (such as bills or candidates), the option preferred by more than half of the voters (a ''majority'') should win. In political philosophy, the ''majority rule'' is one of two major competing notions of democracy. The most common alternative is given by the utilitarian rule (or other welfarist rules), which identify the spirit of liberal democracy with the equal consideration of interests.Ball, Terence and Antis Loizides"James Mill" The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Winter 2020 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.). Although the two rules can disagree in theory, political philosophers beginning with James Mill have argued the two can be reconciled in practice, with majority rule being a valid approximation to the utilitarian rule whenever voters share similarly-strong preferences. This position has found strong support in many social choice models, where the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Choice Theory
Social choice theory is a branch of welfare economics that extends the Decision theory, theory of rational choice to collective decision-making. Social choice studies the behavior of different mathematical procedures (social welfare function, social welfare functions) used to combine individual preferences into a coherent whole.Amartya Sen (2008). "Social Choice". ''The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics'', 2nd EditionAbstract & TOC./ref> It contrasts with political science in that it is a Normative economics, normative field that studies how a society can make good decisions, whereas political science is a Positive economics, descriptive field that observes how societies actually do make decisions. While social choice began as a branch of economics and decision theory, it has since received substantial contributions from mathematics, philosophy, political science, and game theory. Real-world examples of social choice rules include constitution, constitutions and Parliamentary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandatory Referendum
A mandatory referendum, also known as an obligatory referendum, is a referendum that is legally required to be held under specific circumstances. This is in contrast to an optional referendum, which comes from either by public or legislative request. The actions that require mandatory referendums are set by law and normally concern major governmental actions or matters of large public significance. The most commonly found example worldwide of a mandatory referendum is a required referendum to adopt or amend a national constitution, which exists in many countries. Austria In Austria, a mandatory referendum at the federal level is provided for in the event of an overall amendment to the federal constitution (Art. 44 para. 3 B-VG). An overall amendment to the constitution occurs when one or more of the construction principles of the constitution (democratic, federal, rule of law, separation of powers or liberal construction principle) are seriously changed. It is controversial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supermajority
A supermajority is a requirement for a proposal to gain a specified level of support which is greater than the threshold of one-half used for a simple majority. Supermajority rules in a democracy can help to prevent a majority from eroding fundamental rights of a minority, but can also hamper efforts to respond to problems and encourage corrupt compromises at times when action is taken. Changes to constitutions, especially those with entrenched clauses, commonly require supermajority support in a legislature. In consensus democracy the supermajority rule is applied in most cases. __TOC__ History The first known use of a supermajority rule was in juries during the 100s BC in ancient Rome. In some cases, two thirds of jurors had to confirm they were ready to take a decision before the matter went to a simple majority vote. Pope Alexander III introduced the use of supermajority rule for papal elections at the Third Lateran Council in 1179. In the Democratic Party of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Center Squeeze
A center squeeze is a kind of spoiler effect shared by rules like the two-round system, plurality-with-primaries, and instant-runoff voting (IRV). In a center squeeze, the Majority-preferred candidate, majority-preferred and Social utility efficiency, socially optimal candidate is eliminated in favor of a more Extremism, extreme alternative before having a chance to face another candidate in a one-on-one race. Systems with center-squeeze are sometimes called centrifugal ("center-fleeing") because they encourage political polarization. Candidates focused on appealing to a small Political base, base of Core support, core supporters can "squeeze" broadly-popular candidates trapped between them out of the race, by splitting the First-preference votes, first-round vote needed to survive earlier rounds. This effect was first predicted by Social choice theory, social choice theorists in the 1940s and 50s, and has since been documented in various countries using Plurality-rule family, pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
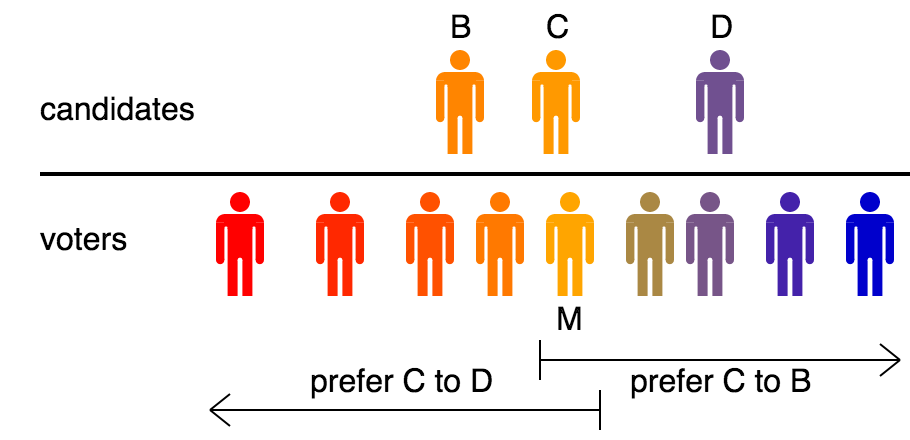
Median Voter Theorem
In political science and social choice theory, social choice, Black's median voter theorem says that if voters and candidates are distributed along a political spectrum, any voting method Condorcet criterion, compatible with majority-rule will elect the candidate preferred by the median voter. The median voter theorem thus shows that under a realistic model of voter behavior, Arrow's impossibility theorem, Arrow's theorem does not apply, and Decision theory, rational choice is possible for societies. The theorem was first derived by Duncan Black in 1948, and independently by Kenneth Arrow. Voting rules without this median voter property, like Instant-runoff voting, ranked choice voting, Plurality voting, plurality, and plurality-with-primaries have a Center-squeeze, center-squeeze effect that encourages candidates to take more extreme positions than the population would prefer. Similar median voter theorems exist for rules like score voting and approval voting when voters are either ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intensity Of Preference
In economics, a cardinal utility expresses not only which of two outcomes is preferred, but also the intensity of preferences, i.e. ''how much'' better or worse one outcome is compared to another. In Consumer choice, consumer choice theory, economists originally attempted to replace cardinal utility with the apparently weaker concept of ordinal utility. Cardinal utility appears to impose the assumption that interval scale, levels of absolute satisfaction exist, so magnitudes of increments to satisfaction can be compared across different situations. However, economists in the 1940s proved that under mild conditions, ordinal utilities imply cardinal utilities. This result is now known as the von Neumann–Morgenstern utility theorem; many similar utility representation theorems exist in other contexts. History In 1738, Daniel Bernoulli was the first to theorize about the marginal value of money. He assumed that the value of an additional amount is inversely proportional to the pecu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preference (economics)
In economics, and in other social sciences, preference refers to an order by which an Agent (economics), agent, while in search of an "optimal choice", ranks alternatives based on their respective utility. ''Preferences'' are evaluations that concern matters of value, in relation to practical reasoning. Individual preferences are determined by taste, need, ..., as opposed to price, availability or personal income. Classical economics assumes that people act in their best (rational) interest. In this context, rationality would dictate that, when given a choice, an individual will select an option that maximizes their self-interest. But preferences are not always transitive relation, transitive, both because real humans are far from always being rational and because in some situations preferences can form cycle (graph theory), cycles, in which case there exists no well-defined optimal choice. An example of this is Efron dice. The concept of preference plays a key role in many discip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rated Voting
Rated, evaluative, graded, or cardinal voting rules are a class of voting methods that allow voters to state how strongly they support a candidate, by giving each one a grade on a separate scale. The distribution of ratings for each candidate—i.e. the percentage of voters who assign them a particular score—is called their merit profile. For example, if candidates are graded on a 4-point scale, one candidate's merit profile may be 25% on every possible rating (1, 2, 3, and 4), while a perfect candidate would have a merit profile where 100% of voters assign them a score of 4. Since rated methods allow the voters to express how strongly they support a candidate, these methods are not covered by Arrow's impossibility theorem, and their resistance to the spoiler effect becomes a more complex matter. Some rated methods are immune to the spoiler effect when every voter rates the candidates on an absolute scale, but they are not when the voters' rating scales change based on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First-preference Plurality
First-past-the-post (FPTP)—also called choose-one, first-preference plurality (FPP), or simply plurality—is a single-winner voting rule. Voters mark one candidate as their favorite, or first-preference, and the candidate with more first-preference votes than any other candidate (a ''plurality'') is elected, even if they do not have more than half of votes (a ''majority''). FPP has been used to elect part of the British House of Commons since the Middle Ages before spreading throughout the British Empire. Throughout the 20th century, many countries that previously used FPP have abandoned it in favor of other electoral systems, including the former British colonies of Australia and New Zealand. FPP is still officially used in the majority of US states for most elections. However, the combination of partisan primaries and a two-party system in these jurisdictions means that most American elections behave effectively like two-round systems, in which the first round choose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-round Plurality
The two-round system (TRS or 2RS), sometimes called ballotage, top-two runoff, or two-round plurality, is a single-winner electoral system which aims to elect a member who has support of the majority of voters. The two-round system involves one or two rounds of choose-one voting, where the voter marks a single favorite candidate in each round. If no one has a majority of votes in the first round, the two candidates with the most votes in the first round move on to a second election (a second round of voting). The two-round system is in the family of plurality voting systems that also includes single-round plurality (FPP). Like instant-runoff (ranked-choice) voting and first past the post, it elects one winner. The two-round system first emerged in France and has since become the most common single-winner electoral system worldwide. Despite this, runoff-based rules like the two-round system and RCV have faced criticism from social choice theorists as a result of their suscep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instant-runoff Voting
Instant-runoff voting (IRV; ranked-choice voting (RCV), preferential voting, alternative vote) is a single-winner ranked voting election system where Sequential loser method, one or more eliminations are used to simulate Runoff (election), runoff elections. When no candidate has a majority of the votes in the first round of counting, each following round eliminates the candidate with the fewest First-preference votes, first-preferences (among the remaining candidates) and transfers their votes if possible. This continues until one candidate accumulates a majority of the votes still in play. Instant-runoff voting falls under the plurality-based voting-rule family, in that under certain conditions the candidate with the least votes is eliminated, making use of secondary rankings as contingency votes. Thus it is related to the Runoff election, two-round runoff system and the exhaustive ballot. IRV could also be seen as a single-winner equivalent of Single transferable vote, sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plurality-rule Family
In social choice theory, the majority rule (MR) is a social choice rule which says that, when comparing two options (such as Bill (law), bills or Candidate, candidates), the option preferred by more than half of the voters (a ''majority'') should win. In political philosophy, the ''majority rule'' is one of two major competing notions of democracy. The most common alternative is given by the utilitarian rule (or other welfarist rules), which identify the spirit of liberal democracy with the equal consideration of interests.Ball, Terence and Antis Loizides"James Mill" The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Winter 2020 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.). Although the two rules can disagree in theory, political philosophers beginning with James Mill have argued the two can be reconciled in practice, with majority rule being a valid approximation to the utilitarian rule whenever voters share similarly-strong preferences. This position has found strong support in many Social choice the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |