|
Mahyawa
Mahyawa or mehyawa () is an Iranian cuisine tangy sauce made out of fermented fish. Mahyawa is often sold at bakeries and by street vendors in the southern parts of Iran, especially Hormozgan, Bushehr and the southern parts of Fars province, and some of the GCC Countries, in clear bottles, showing the brown-colored sauce. Etymology The name (Mahyaweh;ماهیآوه) is derived from Mahweh (مهوه) which in Achomi language means Mah (ِمَه;mah or ماهی;mahi) for “fish” and Aweh (آوَه) or Ow (آو) for “water”. History Mahyawa (in or ) is a famous dish widely consumed in Southern Iran, the southern regions of Fars Province and Hormozgan, as well the rest of the Gulf especially the GCC countries, which has been introduced there by the it was brought by the migration of the Achums (known locally as the Huwala and Ajam communities or more commonly “Khodmooni”). They claim it was invented by Avicenna, and according to others it was prepared b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuwait
Kuwait, officially the State of Kuwait, is a country in West Asia and the geopolitical region known as the Middle East. It is situated in the northern edge of the Arabian Peninsula at the head of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to Iraq–Kuwait border, the north and Saudi Arabia to Kuwait–Saudi Arabia border, the south. With a coastline of approximately , Kuwait also shares a maritime border with Iran, across the Persian Gulf. Kuwait is a city-state, most of the country's population reside in the urban area, urban agglomeration of Kuwait City, the capital and largest city. , Kuwait has a population of 4.82 million, of which 1.53 million are Kuwaiti nationality law, Kuwaiti citizens while the remaining 3.29 million are Expatriates in Kuwait, foreign nationals from over 100 countries. Kuwait has the world's third List of sovereign states by immigrant and emigrant population, largest number of foreign nationals as a percentage of the population, where its citizens make up less th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
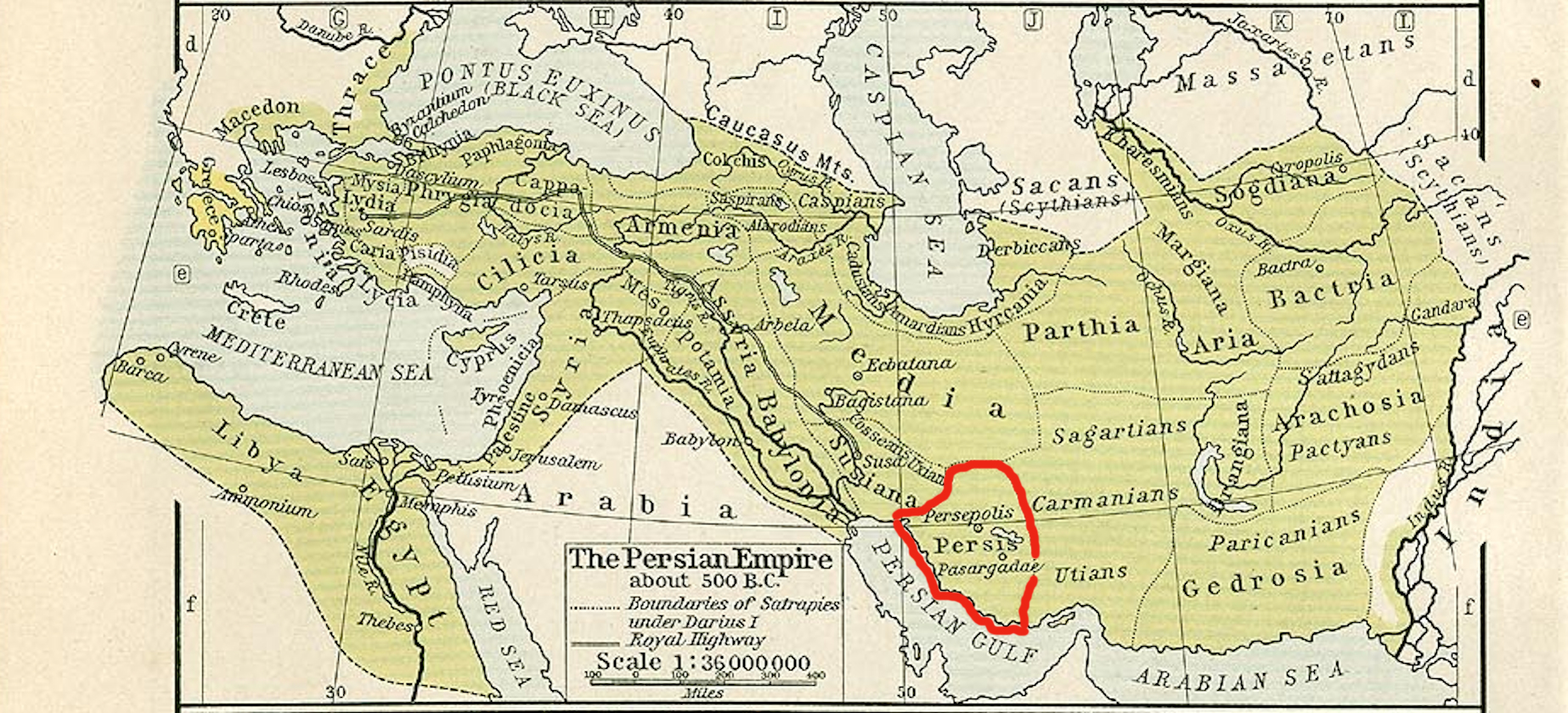
Southern Iran
Southern Iran consists of the southern mountain ranges of Zagros and Central Iranian Range, Khuzestan Plain and the northern coasts of Persian Gulf and Strait of Hormuz. Definition It includes the provinces of Fars province, Fars, Kohgiluyeh and Buyer Ahmad Province, Kohgiluyeh and Buyer Ahmad, Hormozgan and Bushehr province, Bushehr. Sometimes Khuzestan and Kerman province, Kerman are also included in this region. The major cities in the region are Shiraz, Bandarabbas, Kerman, Bam City, Rafsanjan, Sirjan, Jiroft and baft. Demographics The south of Iran is very diverse in terms of ethnicity, which includes Persians (including Kohmera, Basri, Etchmi, etc.), Arabs and Afro-Iranians, Iranians of African origin. In addition, other ethnic minorities of Iran migrated to this region for various reasons; these include Azerbaijanis, Mazanderani people, Mazandaranis, Gilaks, Talysh people, Talysh, Tat people (Iran), Tats, Kurds, and Lurs, who migrated from other regions of Iran. Clim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khosrow I
Khosrow I (also spelled Khosrau, Khusro or Chosroes; ), traditionally known by his epithet of Anushirvan ("the Immortal Soul"), was the Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 531 to 579. He was the son and successor of Kavad I (). Inheriting a reinvigorated empire at war with the Byzantines, Khosrow I signed a peace treaty with them in 532, known as the Perpetual Peace, in which the Byzantine emperor Justinian I paid 11,000 pounds of gold to the Sasanians. Khosrow then focused on consolidating his power, executing conspirators, including his uncle Bawi. Dissatisfied with the actions of the Byzantine clients and vassals, the Ghassanids, and encouraged by Ostrogoth envoys from Italy, Khosrow violated the peace treaty and declared war against the Byzantines in 540. He sacked the major city of Antioch and deported its population to Persia. In 541, he invaded Lazica and made it an Iranian protectorate, thus initiating the Lazic War. In 545, the two empires agreed to halt the wars in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
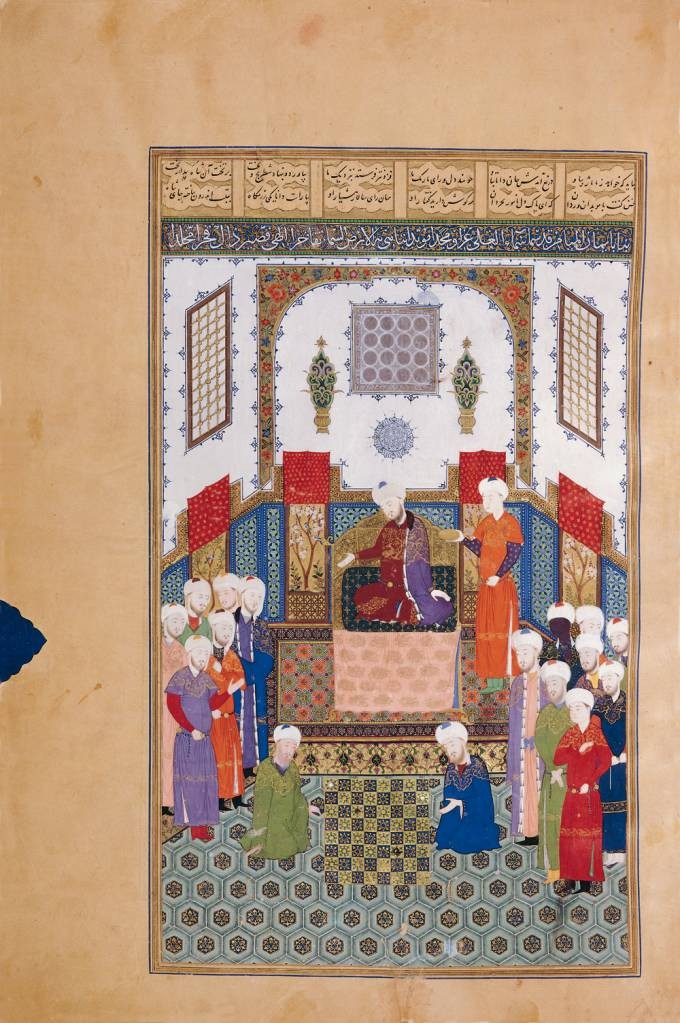
Bozorgmehr
Bozorgmehr-e Bokhtagan (Middle Persian: ''Wuzurgmihr ī Bōkhtagān''), also known as Burzmihr, Dadmihr and Dadburzmihr, was an Iranian peoples, Iranian sage and dignitary from the House of Karen, Karen family, who served as minister (''Wuzurg framadar, wuzurg framadār'') of the Sasanian Empire, Sasanian king (shah) Kavad I (), and the latter's son and successor Khosrow I (). He also served as the military commander (''spahbed'') of Khwarasan under Khosrow I and his successor Hormizd IV (). According to Persian language, Persian sources, Bozorgmehr was a man of "exceptional wisdom and sage counsels" and later became a characterisation of the expression. His name appears in several important works in Persian literature, most notably in the Shahnameh ("The Book of Kings"). The historian Arthur Christensen has suggested that Bozorgmehr was the same person as Borzuya, but historiographical studies of post-Sasanian Persian literature, as well as linguistic analysis shows otherwise. How ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avicenna
Ibn Sina ( – 22 June 1037), commonly known in the West as Avicenna ( ), was a preeminent philosopher and physician of the Muslim world, flourishing during the Islamic Golden Age, serving in the courts of various Iranian peoples, Iranian rulers. He is often described as the father of early modern medicine. His philosophy was of the Peripatetic school derived from Aristotelianism. His most famous works are ''The Book of Healing'', a philosophical and scientific encyclopedia, and ''The Canon of Medicine'', a medical encyclopedia which became a standard medical text at many medieval European University, universities and remained in use as late as 1650. Besides philosophy and medicine, Avicenna's corpus includes writings on Astronomy in medieval Islam, astronomy, Alchemy and chemistry in medieval Islam, alchemy, Geography and cartography in medieval Islam, geography and geology, Psychology in medieval Islam, psychology, Islamic theology, Logic in Islamic philosophy, logic, Mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ajam Of Bahrain
The Ajam of Bahrain (), or Demographics of Bahrain, Bahraini Persians (), are a group of ethnic communities in Bahrain, consisting of Bahraini nationality law, Bahraini citizens of Iranian peoples, Iranian ancestry and Ethnicities in Iran, Iranian background. Most families of this group are from a Shia Islam, Shia background, although there are a number of Sunni Islam, Sunni families of Achomi people, Achomi and Baloch people, Baluchi ancestry as well. This group of people is found to be predominantly bilingual. The Ajam are found in significant numbers in Manama, Muharraq, and Shia majority areas such as Saar, Diraz, and Samaheej. Both Samaheej and Diraz have their names derived from Farsi, Persian. Terms explained The terms “Ajam”, “Persian” and “Iranian” are still debatable: * Persians, Persian: The term "Persian" refers to those whose First language, mother tongue is Persian language, Persian (Farsi) and who identify as Persian. However, Iran is a mix of ethnic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huwala
Huwala (, sing. Huwali هولي) also collectively referred to as Bani Huwala, is a blanket term usually used to refer to tribal Arabs who migrated to the coast of Iran around the 13th and 14th centuries. Such migrations continued till around 19th century to the area which is now Iran's Hormozgan province and Fars province, mainly Bandar Abbas, Qishm, and the mainland near Bandar Lengeh. The Huwala follows Sunni Islam, as opposed the majority Persian Twelver Shia and similar to Sunni Peninsular Arabs. Most of the Huwala have remigrated back to the Arabian Peninsula between late 19th century and early 20th century. The imposition of restrictive economic policies by Reza Shah in the 1930s led to the migration of most of the Huwala back to the Arabian Peninsula. The term "Huwala" does not refer to Sunni Larestani Achomi families such as Kandari, Janahi, Khaloori, Zarooni, and Bastaki. It specifically refers to the actual Arab Huwalas (Arab El-Sahel), which encompasses the Qawas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achomi People
Achomi/Achami people (, , Pahlavi scripts, Inscription Parsig: 𐭠𐭰𐭬𐭭𐭩𐭠), known by their self-designated pseudonym as ''Khodmooni'' (), commonly known as ''Laris'' (), ''Larestanis'' (), or ''Garmsiris'', are an Iranian peoples, Iranic sub Ethnicity, ethnic group said to be descended of a tribe of Persians known as “Ira” (), who primarily inhabited southern Iran in a region historically known as Irahistan (presently Larestan region), in some of them migrated to Shiraz, and the Arab states of the Persian Gulf, Arab countries in the Persian Gulf region. They speak the Achomi language which has reported eight dialects and it is not intelligible with New Persian/Persian language, Farsi, (Dari, Tajik language, Tajiki, and Iranian Persian, Iranian). They are predominantly Sunni Muslims, with a Shia Islam, Shia minority. Origins The Achum/Acham people are said to be of Persian/Parsi (پارسی) descent. In the Achaemenid Empire, Achemaenid Behistun Inscription of D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, sometimes called the Arabian Gulf, is a Mediterranean seas, mediterranean sea in West Asia. The body of water is an extension of the Arabian Sea and the larger Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical NameWorking Paper No. 61, 23rd Session, Vienna, 28 March – 4 April 2006. accessed 9 October 2010 It is connected to the Gulf of Oman in the east by the Strait of Hormuz. The river delta of the Shatt al-Arab forms the northwest shoreline. The Persian Gulf has many fishing grounds, extensive reefs (mostly rocky, but also Coral reef, coral), and abundant pearl oysters, however its ecology has been damaged by industrialization and oil spills. The Persian Gulf is in the Persian Gulf Basin, which is of Cenozoic origin and related to the subduction of the Arabian plate under the Zagros Mountains. The current flooding of the basin started 15,000 years ago due to sea level rise, rising sea levels of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Persian
New Persian (), also known as Modern Persian () is the current stage of the Persian language spoken since the 8th to 9th centuries until now in Greater Iran and surroundings. It is conventionally divided into three stages: Early New Persian (8th/9th centuries), Classical Persian (10th–18th centuries), and Contemporary Persian (19th century to present). Dari is a name given to the New Persian language since the 10th century, widely used in Arabic (see Istakhri, al-Maqdisi and ibn Hawqal) and Persian texts. Since 1964, Dari has been the official name in Afghanistan for the Persian spoken there. Classification New Persian is a member of the Western Iranian group of the Iranian languages, which make up a branch of the Indo-European languages in their Indo-Iranian subdivision. The Western Iranian languages themselves are divided into two subgroups: Southwestern Iranian languages, of which Persian is the most widely spoken, and Northwestern Iranian lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Language
Persian ( ), also known by its endonym and exonym, endonym Farsi (, Fārsī ), is a Western Iranian languages, Western Iranian language belonging to the Iranian languages, Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian languages, Indo-Iranian subdivision of the Indo-European languages. Persian is a pluricentric language predominantly spoken and used officially within Iran, Afghanistan, and Tajikistan in three mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible standard language, standard varieties, respectively Iranian Persian (officially known as ''Persian''), Dari, Dari Persian (officially known as ''Dari'' since 1964), and Tajik language, Tajiki Persian (officially known as ''Tajik'' since 1999).Siddikzoda, S. "Tajik Language: Farsi or not Farsi?" in ''Media Insight Central Asia #27'', August 2002. It is also spoken natively in the Tajik variety by a significant population within Uzbekistan, as well as within other regions with a Persianate society, Persianate history in the cultural sphere o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |