|
Magnesium-28
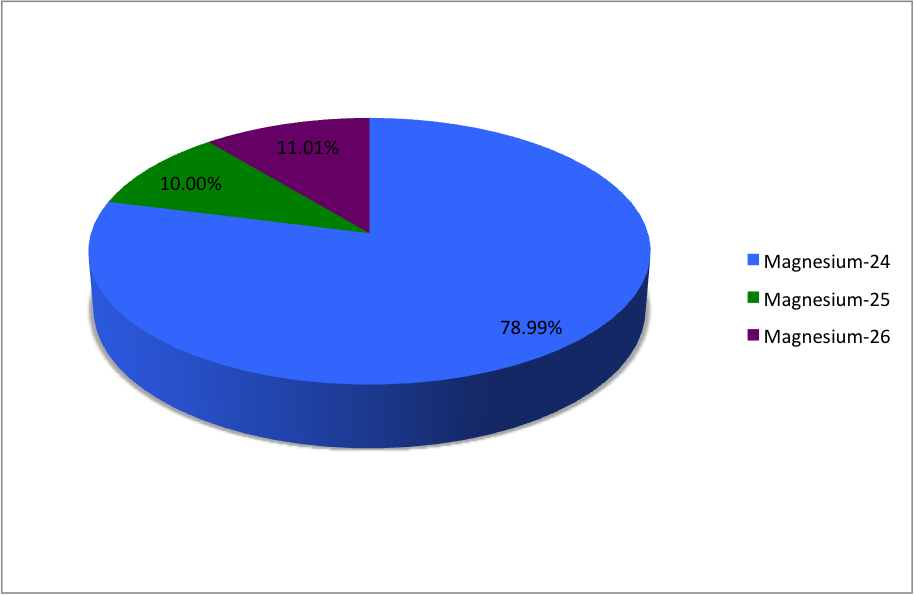
Magnesium (12Mg) naturally occurs in three stable isotopes: , , and . There are 19 radioisotopes that have been discovered, ranging from to (with the exception of ). The longest-lived radioisotope is with a half-life of . The lighter isotopes mostly decay to isotopes of sodium while the heavier isotopes decay to isotopes of aluminium. The shortest-lived is proton-unbound with a half-life of . A precise measurement of the neutron-rich 40Mg in 2019 showed the unexpected difference in its nuclear structure, compared to the lighter neighboring isotopes. List of isotopes , -id=Magnesium-18 , , style="text-align:right" , 12 , style="text-align:right" , 6 , , , 2p , , 0+ , , , -id=Magnesium-19 , , style="text-align:right" , 12 , style="text-align:right" , 7 , , , 2p , , 1/2−# , , , - , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2 style="text-align:right" , 12 , rowspan=2 style="text-align:right" , 8 , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2, , β+ () , , rowsp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic table), it occurs naturally only in combination with other elements and almost always has an oxidation state of +2. It reacts readily with air to form a thin Passivation (chemistry), passivation coating of magnesium oxide that inhibits further corrosion of the metal. The free metal burns with a brilliant-white light. The metal is obtained mainly by electrolysis of magnesium Salt (chemistry), salts obtained from brine. It is less dense than aluminium and is used primarily as a component in strong and lightweight magnesium alloy, alloys that contain aluminium. In the cosmos, magnesium is produced in large, aging stars by the sequential addition of three Helium nucleus, helium nuclei to a carbon nucleus. When such stars explo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium-27
Magnesium (12Mg) naturally occurs in three stable isotopes: , , and . There are 19 radioisotopes that have been discovered, ranging from to (with the exception of ). The longest-lived radioisotope is with a half-life of . The lighter isotopes mostly decay to isotopes of sodium while the heavier isotopes decay to isotopes of aluminium. The shortest-lived is proton-unbound with a half-life of . A precise measurement of the neutron-rich 40Mg in 2019 showed the unexpected difference in its nuclear structure, compared to the lighter neighboring isotopes. List of isotopes , -id=Magnesium-18 , , style="text-align:right" , 12 , style="text-align:right" , 6 , , , 2p , , 0+ , , , -id=Magnesium-19 , , style="text-align:right" , 12 , style="text-align:right" , 7 , , , 2p , , 1/2−# , , , - , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2 style="text-align:right" , 12 , rowspan=2 style="text-align:right" , 8 , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2, , β+ () , , rowsp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Error
In statistics and optimization, errors and residuals are two closely related and easily confused measures of the deviation of an observed value of an element of a statistical sample from its "true value" (not necessarily observable). The error of an observation is the deviation of the observed value from the true value of a quantity of interest (for example, a population mean). The residual is the difference between the observed value and the '' estimated'' value of the quantity of interest (for example, a sample mean). The distinction is most important in regression analysis, where the concepts are sometimes called the regression errors and regression residuals and where they lead to the concept of studentized residuals. In econometrics, "errors" are also called disturbances. Introduction Suppose there is a series of observations from a univariate distribution and we want to estimate the mean of that distribution (the so-called location model (statistics), location model). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium-38
Magnesium (12Mg) naturally occurs in three stable isotopes: , , and . There are 19 radioisotopes that have been discovered, ranging from to (with the exception of ). The longest-lived radioisotope is with a half-life of . The lighter isotopes mostly decay to isotopes of sodium while the heavier isotopes decay to isotopes of aluminium. The shortest-lived is proton-unbound with a half-life of . A precise measurement of the neutron-rich 40Mg in 2019 showed the unexpected difference in its nuclear structure, compared to the lighter neighboring isotopes. List of isotopes , -id=Magnesium-18 , , style="text-align:right" , 12 , style="text-align:right" , 6 , , , 2p , , 0+ , , , -id=Magnesium-19 , , style="text-align:right" , 12 , style="text-align:right" , 7 , , , 2p , , 1/2−# , , , - , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2 style="text-align:right" , 12 , rowspan=2 style="text-align:right" , 8 , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2, , β+ () , , rowsp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Emission
Neutron emission is a mode of radioactive decay in which one or more neutrons are ejected from a Atomic nucleus, nucleus. It occurs in the most neutron-rich/proton-deficient nuclides, and also from excited states of other nuclides as in photodisintegration, photoneutron emission and beta-delayed neutron emission. As only a neutron is lost by this process the number of protons remains unchanged, and an atom does not become an atom of a different element, but a different isotope of the same element. Neutrons are also produced in the spontaneous fission, spontaneous and nuclear fission, induced fission of certain heavy nuclides. Spontaneous neutron emission As a consequence of the Pauli exclusion principle, nuclei with an excess of protons or neutrons have a higher average energy per nucleon. Nuclei with a sufficient excess of neutrons have a greater energy than the combination of a free neutron and a nucleus with one less neutron, and therefore can decay by neutron emission. Nuclei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |