|
Lunyu
The ''Analects'', also known as the ''Sayings of Confucius'', is an ancient Chinese philosophical text composed of sayings and ideas attributed to Confucius and his contemporaries, traditionally believed to have been compiled by his followers. The consensus among scholars is that large portions of the text were composed during the Warring States period (475–221 BC), and that the work achieved its final form during the mid-Han dynasty (206 BC220 AD). During the early Han, the ''Analects'' was merely considered to be a commentary on the Five Classics. However, by the dynasty's end the status of the ''Analects'' had grown to being among the central texts of Confucianism. During the late Song dynasty (960–1279 AD) the importance of the ''Analects'' as a Chinese philosophy work was raised above that of the older Five Classics, and it was recognized as one of the "Four Books". The ''Analects'' has been one of the most widely read and studied books in China f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De (Chinese)
(; zh, c=德, p=dé), also written as , is a key concept in Chinese philosophy, usually translated "inherent character; inner power; integrity" in Taoism, "moral character; virtue; morality" in Confucianism and other contexts, and "quality; virtue" () or "merit; virtuous deeds" () in Chinese Buddhism. The word Chinese is an ancient word with complexities across several subfields of linguistics: namely in its semantics, orthography, and etymology. Meanings The ''Hanyu Da Zidian'', provides twenty meanings for , translatable as # Rise, go up, climb, ascend. [] # Morals, morality, virtue, personal conduct, moral integrity, honor. [] # Denoting a wise/enlightened person with moral character. [] # Kindness, favor, grace, graciousness. [] # Grateful, gratefulness, thankful, indebted. [] # Benevolent rule, good government, good instruction. [] # Objective regulations/rules. [] # Quality, nature, basic character, characteristi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junzi
The word junzi ( or "Son of the Vassal, or Monarch") is a Chinese philosophical term often translated as "gentleman", "superior person",Sometimes "exemplary person". Paul R. Goldin translates it "noble man" in an attempt to capture both its early political and later moral meaning. Cf.Confucian Key Terms: Junzi". or "noble man". Since the characters are overtly gendered, the term is frequently translated as "gentleman"; gentry and distinguished/moral person are common gender-neutral translations. Traditionally referring to the "aristocratic nobility of the Zhou", ''Junzi'' is employed in the Book of Changes to mean a superior man, and by Confucius in his works to describe a virtuous person with noble characters. In Confucianism In Confucianism, the ideal personality is the 聖 ''shèng'', translated as saint or sage. However, since sagehood is unattainable for most people, Confucius articulated a less demanding ideal of a cultured and moral life, using the term ''junzi''—or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anhui University Bamboo Strips
The Anhui University Bamboo Strips 安徽大學竹簡 (also known as 安大簡) is a corpus of manuscripts purchased by the Anhui University in 2015, and currently under publication. Since the corpus comes from illegal excavations, specifics about its recovery are lost. Through radiocarbon dating analysis conducted at Peking University, the material has been dated to the Warring States period. It is yet another discovery that enriches scholarly understanding of this ancient era, alongside other recoveries, such as the Guodian collection, the Shanghai Museum Collection, and the Tsinghua corpus. Overview According to preliminary publications, the corpus includes 1167 strips, in fairly good conditions, with length ranging from 21.3 to 48.5 cm. The editors in charge of curating and publishing the collection divided the material into four groups. # A manuscript version of partial content in the Book of Odes 詩經. This is the first one published by the editor, in the first volume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
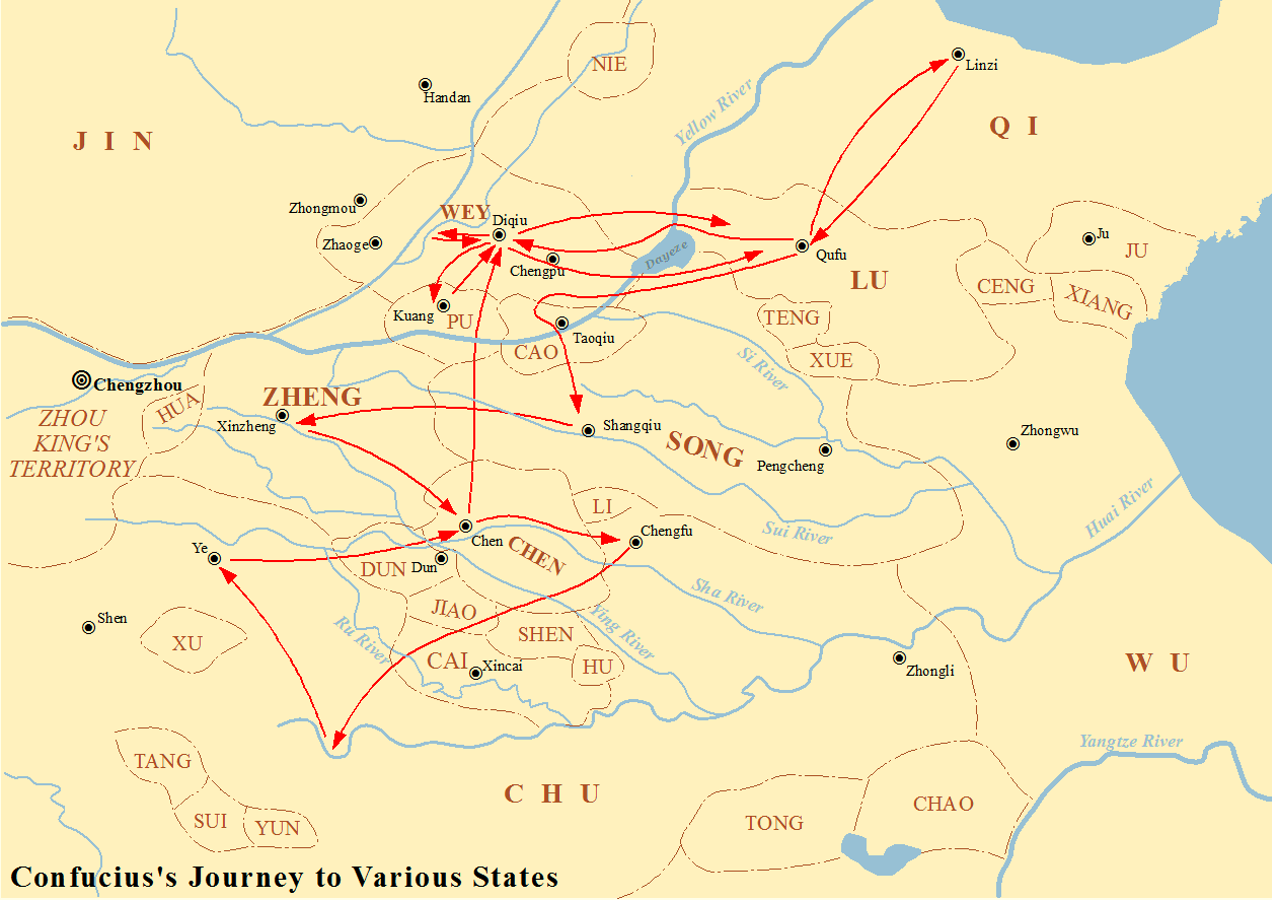
Confucius
Confucius (; pinyin: ; ; ), born Kong Qiu (), was a Chinese philosopher of the Spring and Autumn period who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. Much of the shared cultural heritage of the Sinosphere originates in the philosophy and teachings of Confucius. His philosophical teachings, called Confucianism, emphasized personal and governmental morality, harmonious social relationships, righteousness, kindness, sincerity, and a ruler's responsibilities to lead by virtue. Confucius considered himself a transmitter for the values of Ancient China, earlier periods which he claimed had been abandoned in his time. He advocated for filial piety, endorsing strong family loyalty, Ancestor veneration in China, ancestor veneration, the respect of elders by their children and of husbands by their wives. Confucius recommended a robust family unit as the cornerstone for an ideal government. He championed the Silver Rule, or a negative form of the Golden Rule, advising, "Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simplified Chinese Characters
Simplified Chinese characters are one of two standardized Chinese characters, character sets widely used to write the Chinese language, with the other being traditional characters. Their mass standardization during the 20th century was part of an initiative by the People's Republic of China (PRC) to promote literacy, and their use in ordinary circumstances on the mainland has been encouraged by the Chinese government since the 1950s. They are the official forms used in mainland China, Malaysia, and Singapore, while traditional characters are officially used in Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan. Simplification of a component—either a character or a sub-component called a Radical (Chinese characters), radical—usually involves either a reduction in its total number of Chinese character strokes, strokes, or an apparent streamlining of which strokes are chosen in what places—for example, the radical used in the traditional character is simplified to to form the simplified charac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seal Script
Seal script or sigillary script () is a Chinese script styles, style of writing Chinese characters that was common throughout the latter half of the 1st millennium BC. It evolved organically out of bronze script during the Zhou dynasty (1046–256 BC). The variant of seal script used in the state of Qin eventually became comparatively standardized, and was adopted as the formal script across all of China during the Qin dynasty (221–206 BC). It was still widely used for decorative engraving and seal (East Asia), seals during the Han dynasty (202 BC220 AD). The literal translation given above was coined during the Han dynasty, and reflects the role of the script being reduced to ceremonial inscriptions. Types The term ''seal script'' may refer to several distinct varieties, including the large seal script and the small seal script. Without qualification, ''seal script'' usually refers to the small seal script—that is, the lineage which evolved with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lu (state)
Lu (; 249 BC) was a vassal Ancient Chinese states, state during the Zhou dynasty of History of China#Ancient China, ancient China located around modern Shandong. Founded in the 11th century BC, its rulers were from a cadet branch of the Jī, House of Ji () that ruled the Zhou dynasty. The first duke was Boqin, a son of the Duke of Zhou, who was brother of King Wu of Zhou and regent to King Cheng of Zhou. Lu was the home state of Confucius as well as Mozi, and, as such, has an outsized cultural influence among the states of the Eastern Zhou and in history. The ''Annals of Spring and Autumn'', for instance, was written with the Lu rulers' years as their basis. Another great work of Chinese history, the ''Zuo Zhuan'' or ''Commentary of Zuo'', was traditionally considered to have been written in Lu by Zuo Qiuming. Geography The state's capital was in Qufu and its territory mainly covered the central and southwest regions of what is now Shandong Province. It was borde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu Xiang (scholar)
Liu Xiang (77–6BCE), born Liu Gengsheng and bearing the courtesy name Zizheng, was a Chinese astronomer, historian, librarian, poet, politician, and writer of the Western Han dynasty. Among his polymathic scholarly specialties were history, literary bibliography, and astronomy. He is particularly well known for his bibliographic work in cataloging and editing the extensive imperial library. Life Liu Gengsheng was born in Xuzhou. Being a distant relative of Liu Bang, the founder of the Han dynasty, he was a member of the ruling dynastic clan (the Liu family). Liu Xiang's father ranked as a marquess. Liu Xiang's son, Liu Xin, would continue the scholarly tradition of his father and his relative Liu An (the Prince of Huainan). By the beginning of Emperor Yuan's reign, Liu Xiang was a member of a group of Confucian officials, including Xiao Wangzhi, who wished to limit the power of the emperor's female family members relatives' clans, the Shi and the Xu. He ended up on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mencius
Mencius (孟子, ''Mèngzǐ'', ; ) was a Chinese Confucian philosopher, often described as the Second Sage () to reflect his traditional esteem relative to Confucius himself. He was part of Confucius's fourth generation of disciples, inheriting his ideology and developing it further. Living during the Warring States period, he is said to have spent much of his life travelling around the states offering counsel to different rulers. Conversations with these rulers form the basis of the ''Mencius (book), Mencius'', which would later be canonised as a Confucian classic. One primary principle of his work is that human nature is righteous and humane. The responses of citizens to the policies of rulers embodies this principle, and a state with righteous and humane policies will flourish by nature. The citizens, with freedom from good rule, will then allocate time to caring for their wives, brothers, elders, and children, and be educated with rites and naturally become better citizens. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wang Chong
Wang Chong (; 27 – c. 97 AD), courtesy name Zhongren (仲任), was a Chinese astronomer, meteorologist, naturalist, philosopher, and writer active during the Eastern Han dynasty. He developed a rational, secular, naturalistic and mechanistic account of the world and of human beings and gave a materialistic explanation of the origin of the universe. His main work was the '' Lunheng'' (論衡, "Critical Essays"). This book contained many theories involving early sciences of astronomy and meteorology, and Wang Chong was even the first in Chinese history to mention the use of the square-pallet chain pump, which became common in irrigation and public works in China thereafter.Needham, Volume 4, Part 2, 344 Wang also accurately described the process of the water cycle. Unlike most of the Chinese philosophers of his period, Wang spent much of his life in non-self-inflicted poverty. He was said to have studied by standing at bookstalls, and had a superb memory, which allowed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Chinese
Classical Chinese is the language in which the classics of Chinese literature were written, from . For millennia thereafter, the written Chinese used in these works was imitated and iterated upon by scholars in a form now called Literary Chinese, which was used for almost all formal writing in China until the early 20th century. Each written character corresponds to a single spoken syllable, and almost always to a single independent word. As a result, the characteristic style of the language is comparatively terse. Starting in the 2nd century CE, use of Literary Chinese spread to the countries surrounding China, including Vietnam, Korea, Japan, and the Ryukyu Islands, where it represented the only known form of writing. Literary Chinese was adopted as the language of civil administration in these countries, creating what is known as the Sinosphere. Each additionally developed systems of readings and annotations that enabled non-Chinese speakers to interpret Literary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |