|
Lithium Iodide
Lithium iodide, or LiI, is a compound of lithium and iodine. When exposed to air, it becomes yellow in color, due to the oxidation of iodide to iodine. It crystallizes in the NaCl motif. It can participate in various hydrates.Wietelmann, Ulrich and Bauer, Richard J. (2005) "Lithium and Lithium Compounds" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', Wiley-VCH: Weinheim. . Applications Lithium iodide is used as a solid-state electrolyte for high-temperature batteries. It is also the standard electrolyte in artificial pacemakers due to the long cycle life it enables. The solid is used as a phosphor for neutron detection. It is also used, in a complex with Iodine, in the electrolyte of dye-sensitized solar cells. In organic synthesis, LiI is useful for cleaving C-O bonds. For example, it can be used to convert methyl esters to carboxylic acids: : Similar reactions apply to epoxides and aziridines. Lithium iodide was used as a radiocontrast agent for CT scans. Its use was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Lithium
Lithium (from , , ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive and flammable, and must be stored in vacuum, inert atmosphere, or inert liquid such as purified kerosene or mineral oil. It exhibits a metallic luster (mineralogy), luster. It corrosion, corrodes quickly in air to a dull silvery gray, then black tarnish. It does not occur freely in nature, but occurs mainly as pegmatite, pegmatitic minerals, which were once the main source of lithium. Due to its solubility as an ion, it is present in ocean water and is commonly obtained from brines. Lithium metal is isolated electrolysis, electrolytically from a mixture of lithium chloride and potassium chloride. The Atomic nucleus, nucleus of the lithiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Iodine
Iodine is a chemical element; it has symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists at standard conditions as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a violet gas at . The element was discovered by the French chemist Bernard Courtois in 1811 and was named two years later by Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac, after the Ancient Greek , meaning 'violet'. Iodine occurs in many oxidation states, including iodide (I−), iodate (), and the various periodate anions. As the heaviest essential mineral nutrient, iodine is required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. Iodine deficiency affects about two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disabilities. The dominant producers of iodine today are Chile and Japan. Due to its high atomic number and ease of attachment to organic compounds, it has also found favour as a non-toxic radiocontrast material. Because of the spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Epoxide
In organic chemistry, an epoxide is a cyclic ether, where the ether forms a three-atom ring: two atoms of carbon and one atom of oxygen. This triangular structure has substantial ring strain, making epoxides highly reactive, more so than other ethers. They are produced on a large scale for many applications. In general, low molecular weight epoxides are colourless and nonpolar, and often volatile. Nomenclature A compound containing the epoxide functional group can be called an epoxy, epoxide, oxirane, and ethoxyline. Simple epoxides are often referred to as oxides. Thus, the epoxide of ethylene (C2H4) is ethylene oxide (C2H4O). Many compounds have trivial names; for instance, ethylene oxide is called "oxirane". Some names emphasize the presence of the epoxide functional group, as in the compound ''1,2-epoxyheptane'', which can also be called ''1,2-heptene oxide''. A polymer formed from epoxide precursors is called an ''epoxy''. However, few if any of the epoxy groups i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Carboxylic Acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an Substituent, R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl group (e.g., alkyl, alkenyl, aryl), or hydrogen, or other groups. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion. Examples and nomenclature Carboxylic acids are commonly identified by their trivial names. They often have the suffix ''-ic acid''. IUPAC-recommended names also exist; in this system, carboxylic acids have an ''-oic acid'' suffix. For example, butyric acid () is butanoic acid by IUPAC guidelines. For nomenclature of complex molecules containing a carboxylic acid, the carboxyl can be considered position one of the parent chain even if there are other substituents, such as 3-chloropropanoic acid. Alternately, it can be named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Organic Synthesis
Organic synthesis is a branch of chemical synthesis concerned with the construction of organic compounds. Organic compounds are molecules consisting of combinations of covalently-linked hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms. Within the general subject of organic synthesis, there are many different types of synthetic routes that can be completed including total synthesis, Enantioselective synthesis, stereoselective synthesis, automated synthesis, and many more. Additionally, in understanding organic synthesis it is necessary to be familiar with the methodology, techniques, and applications of the subject. Total synthesis A total synthesis refers to the complete chemical synthesis of molecules from simple, Precursor (chemistry), natural precursors. Total synthesis is accomplished either via a linear or convergent approach. In a Linear synthesis, ''linear'' synthesis—often adequate for simple structures—several steps are performed sequentially until the molecule is com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Dye-sensitized Solar Cell
A dye-sensitized solar cell (DSSC, DSC, DYSC or Grätzel cell) is a low-cost solar cell belonging to the group of thin film solar cells. It is based on a semiconductor formed between a photo-sensitized anode and an electrolyte, a '' photoelectrochemical'' system. The modern version of a dye solar cell, also known as the Grätzel cell, was originally co-invented in 1988 by Brian O'Regan and Michael Grätzel at UC Berkeley and this work was later developed by the aforementioned scientists at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) until the publication of the first high efficiency DSSC in 1991. Michael Grätzel has been awarded the 2010 Millennium Technology Prize for this invention. The DSSC has a number of attractive features; it is simple to make using conventional roll-printing techniques, is semi-flexible and semi-transparent which offers a variety of uses not applicable to glass-based systems, and most of the materials used are low-cost. In practice it has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Electrolyte
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions, but not through the movement of electrons. This includes most soluble Salt (chemistry), salts, acids, and Base (chemistry), bases, dissolved in a polar solvent like water. Upon dissolving, the substance separates into cations and anions, which disperse uniformly throughout the solvent. Solid-state electrolytes also exist. In medicine and sometimes in chemistry, the term electrolyte refers to the substance that is dissolved. Electrically, such a solution is neutral. If an electric potential is applied to such a solution, the cations of the solution are drawn to the electrode that has an abundance of electrons, while the anions are drawn to the electrode that has a deficit of electrons. The movement of anions and cations in opposite directions within the solution amounts to a current. Some gases, such as hydrogen chloride (HCl), under conditions of high temperature or low pressure can also functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , that has no electric charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. The Discovery of the neutron, neutron was discovered by James Chadwick in 1932, leading to the discovery of nuclear fission in 1938, the first self-sustaining nuclear reactor (Chicago Pile-1, 1942) and the first nuclear weapon (Trinity (nuclear test), Trinity, 1945). Neutrons are found, together with a similar number of protons in the atomic nucleus, nuclei of atoms. Atoms of a chemical element that differ only in neutron number are called isotopes. Free neutrons are produced copiously in nuclear fission and nuclear fusion, fusion. They are a primary contributor to the nucleosynthesis of chemical elements within stars through fission, fusion, and neutron capture processes. Neutron stars, formed from massive collapsing stars, consist of neutrons at the density of atomic nuclei but a total mass more than the Sun. Neutron properties and interactions ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Phosphor
A phosphor is a substance that exhibits the phenomenon of luminescence; it emits light when exposed to some type of radiant energy. The term is used both for fluorescent or phosphorescent substances which glow on exposure to ultraviolet or visible light, and cathodoluminescent substances which glow when struck by an electron beam ( cathode rays) in a cathode-ray tube. When a phosphor is exposed to radiation, the orbital electrons in its molecules are excited to a higher energy level; when they return to their former level they emit the energy as light of a certain color. Phosphors can be classified into two categories: fluorescent substances which emit the energy immediately and stop glowing when the exciting radiation is turned off, and phosphorescent substances which emit the energy after a delay, so they keep glowing after the radiation is turned off, decaying in brightness over a period of milliseconds to days. Fluorescent materials are used in applications in wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Artificial Pacemaker
A pacemaker, also known as an artificial cardiac pacemaker, is an Implant (medicine), implanted medical device that generates Pulse (signal processing), electrical pulses delivered by electrodes to one or more of the Heart chamber, chambers of the heart. Each pulse causes the targeted chamber(s) to muscle contraction, contract and pump blood, thus regulating the function of the electrical conduction system of the heart. The primary purpose of a pacemaker is to maintain an even heart rate, either because the heart's natural cardiac pacemaker provides an inadequate or irregular heartbeat, or because there is a heart block, block in the heart's electrical conduction system. Modern pacemakers are externally programmable and allow a cardiologist to select the optimal pacing modes for individual patients. Most pacemakers are on demand, in which the stimulation of the heart is based on the dynamic demand of the circulatory system. Others send out a fixed rate of impulses. A specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
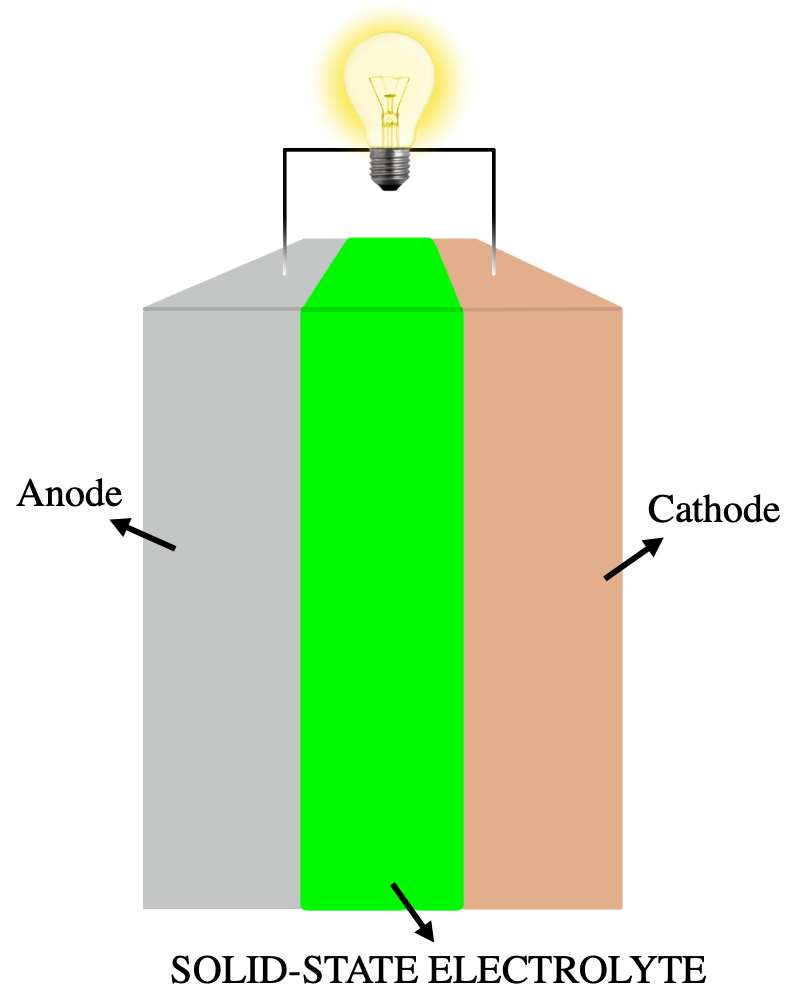 |
Solid-state Electrolyte
A solid-state electrolyte (SSE) is a solid Ionic conductivity (solid state), ionic conductor and electron-insulating electrolyte, material and it is the characteristic component of the solid-state battery. It is useful for applications in electrical energy storage in substitution of the liquid electrolytes found in particular in the lithium-ion battery. Their main advantages are their absolute safety, no issues of leakages of toxic organic solvents, low flammability, non-volatility, mechanical and thermal stability, easy processability, low self-discharge, higher achievable power density and cyclability. This makes possible, for example, the use of a lithium metal anode in a practical device, without the intrinsic limitations of a liquid electrolyte thanks to the property of lithium Dendrite (crystal), dendrite suppression in the presence of a solid-state electrolyte membrane. The use of a high-capacity and low reduction potential anode, like lithium with a specific capacity of 386 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |