|
Levocetirizine
Levocetirizine, sold under the brand name Xyzal, among others, is a second-generation antihistamine used for the treatment of allergic rhinitis (hay fever) and long-term hives of unclear cause. It is less sedating than older antihistamines. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include sleepiness, dry mouth, cough, vomiting, and diarrhea. Use in pregnancy appears safe but has not been well studied and use when breastfeeding is of unclear safety. It is classified as a second-generation antihistamine and works by blocking histamine H1-receptors. Levocetirizine was approved for medical use in the United States in 2007, and is available as a generic medication. In 2022, it was the 152nd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 3million prescriptions. Medical uses Levocetirizine is used for allergic rhinitis. This includes allergy symptoms such as watery eyes, runny nose, sneezing, hives, and itching. Side effects Levocetirizine is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cetirizine
Cetirizine is a second-generation antihistamine, second-generation Peripherally selective antihistamine used to treat allergic rhinitis (hay fever), dermatitis, and urticaria (hives). It is taken by mouth. Effects generally begin within thirty minutes and last for about a day. The degree of benefit is similar to other antihistamines such as diphenhydramine, which is a first-generation antihistamine. Common side effects include sleepiness, dry mouth, headache, and abdominal pain. The degree of sleepiness that occurs is generally less than with first-generation antihistamines because second-generation antihistamines are more selective for the Histamine H1 receptor, H1 receptor. Compared to other second-generation antihistamines, cetirizine can cause drowsiness. Among second-generation antihistamines, cetirizine is more likely than fexofenadine and loratadine to cause drowsiness. Use in pregnancy appears safe, but use during breastfeeding is not recommended. The medication works ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UCB (company)
UCB (Union Chimique Belge) is a multinational biopharmaceutical company headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. UCB is an international company with revenue of €4.178 billion in 2016 which focuses primarily on research and development, specifically involving medications centered on epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, and Crohn's disease. The company's efforts are focused on treatments for severe diseases treated by specialists, particularly in the fields of central nervous system (CNS) disorders (including epilepsy), inflammatory disorders (including allergy), and oncology. Every three years, the company presents the UCB Award under the patronage of the Queen Elisabeth Medical Foundation to promote neuroscience research. The winner of this award is selected by an independent scientific committee. History UCB was founded on 18 January 1928 by Emmanuel Janssen, a Belgian businessman. Initially focused on industrial chemicals (it was one of the first companies to distill ammonia fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Generation Antihistamines
H1 antagonists, also called H1 blockers, are a class of medications that block the action of histamine at the H1 receptor, helping to relieve allergic reactions. Agents where the main therapeutic effect is mediated by negative modulation of histamine receptors are termed antihistamines; other agents may have antihistaminergic action but are not true antihistamines. In common use, the term "antihistamine" refers only to H1-antihistamines. Virtually all H1-antihistamines function as inverse agonists at the histamine H1-receptor, as opposed to neutral antagonists, as was previously believed. Medical uses H1-antihistamines are used clinically to treat histamine-mediated allergic conditions. These indications may include:Rossi S (Ed.) (2004). ''Australian Medicines Handbook 2004''. Adelaide: Australian Medicines Handbook. * Allergic rhinitis * Allergic conjunctivitis * Allergic dermatological conditions (contact dermatitis) * Rhinorrhea (runny nose) * Urticaria * Angioedema * Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palpitations
Palpitations occur when a person becomes aware of their heartbeat. The heartbeat may feel hard, fast, or uneven in their chest. Symptoms include a very fast or irregular heartbeat. Palpitations are a sensory symptom. They are often described as a skipped beat, a rapid flutter, or a pounding in the chest or neck. Palpitations are not always the result of a physical problem with the heart and can be linked to anxiety. However, they may signal a arrhythmia, fast or irregular heartbeat. Palpitations can be brief or long-lasting. They can be intermittent or continuous. Other symptoms can include dizziness, shortness of breath, sweating, headaches, and chest pain. There are a variety of causes of palpitations not limited to the following: Palpitation may be associated with coronary artery disease, coronary heart disease, perimenopause, hyperthyroidism, adult heart muscle diseases like hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, congenital heart diseases like atrial septal defects, diseases causing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lightheadedness
Lightheadedness is a common and typically unpleasant sensation of dizziness or a feeling that one may faint. The sensation of lightheadedness can be short-lived, prolonged, or, rarely, recurring. In addition to dizziness, the individual may feel as though their head is weightless. The individual may also feel as though the room is "spinning" or moving (vertigo). Most causes of lightheadedness are not serious and either cure themselves quickly or are easily treated. Keeping a sense of balance requires the brain to process a variety of information received from the eyes, the nervous system, and the inner ears. If the brain is unable to process these signals, such as when the messages are contradictory, or if the sensory systems are improperly functioning, an individual may experience lightheadedness or dizziness. Lightheadedness is very similar to pre-syncope. Pre-syncope is the immediate stage before syncope (fainting), particularly in cases of temporary visual field loss (i.e. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration whereby a substance is taken through the Human mouth, mouth, swallowed, and then processed via the digestive system. This is a common route of administration for many medications. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes of administration, such as Injection (medicine), injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth". The expression is used in medicine to describe a treatment that is taken orally (but not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphenylmethylpiperazine
Diphenylmethylpiperazine, also known as benzhydrylpiperazine, is a chemical compound and piperazine derivative. It features a piperazine ring with a benzhydryl (diphenylmethyl) group bound to one of the nitrogens. Cyclizine, an antihistamine and anticholinergic Anticholinergics (anticholinergic agents) are substances that block the action of the acetylcholine (ACh) neurotransmitter at synapses in the central nervous system, central and peripheral nervous system. These agents inhibit the parasympatheti ... drug used to treat motion sickness, is the methylated derivative of diphenylmethylpiperazine. References 1-Piperazinyl compounds {{organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enantiomer
In chemistry, an enantiomer (Help:IPA/English, /ɪˈnænti.əmər, ɛ-, -oʊ-/ Help:Pronunciation respelling key, ''ih-NAN-tee-ə-mər''), also known as an optical isomer, antipode, or optical antipode, is one of a pair of molecular entities which are mirror images of each other and non-superposable. Enantiomer molecules are like right and left hands: one cannot be superposed onto the other without first being converted to its mirror image. It is solely a relationship of chirality (chemistry), chirality and the permanent three-dimensional relationships among molecules or other chemical structures: no amount of re-orientation of a molecule as a whole or conformational isomerism, conformational change converts one chemical into its enantiomer. Chemical structures with chirality rotate plane-polarized light. A mixture of equal amounts of each enantiomer, a ''racemic mixture'' or a ''racemate'', does not rotate light. Stereoisomers include both enantiomers and diastereomers. Diaste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distomer
The eudysmic ratio (also spelled eudismic ratio) represents the difference in pharmacologic activity between the two enantiomers of a drug. In most cases where a chiral compound is biologically active, one enantiomer is more active than the other. The eudysmic ratio is the ratio of activity between the two. A eudysmic ratio significantly differing from 1 means that they are statistically different in activity. Eudysmic ratio (ER) reflects the degree of enantioselectivity of the biological systems. For example, (S)-propranolol has ER = 130, meaning that (S)-propranolol is 130 times more active than its (R)-enantiomer. Terminology The eutomer is the enantiomer having the desired pharmacological activity, e.g., as an active ingredient in a drug. The distomer, on the other hand, is the enantiomer of the eutomer which may have undesired bioactivity or may be bio-inert. A racemic mixture is an equal mixture of both enantiomers, which may be easier to manufacture than a single enant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiral Switch
A chiral switch is a chiral drug that has already approved as racemate but has been re-developed as a single enantiomer. The term chiral switching was introduced by Agranat and Caner in 1999 to describe the development of single enantiomers from racemate drugs. For example, levofloxacin is a chiral switch of racemic ofloxacin. It is important to understand that chiral switches are treated as a Selection Invention, selection invention. A selection invention is an invention that selects a group of new members from a previously known class on the basis of superior properties. Description The essential principle of a chiral switch is that there is a change in the status of chirality. In general, the term chiral switch is preferred over racemic switch because the switch is usually happening from a racemic drug to the corresponding single enantiomer. To express the pharmacological activities of each of the chiral twins of a racemic drug, two technical terms have been coined: ''eut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
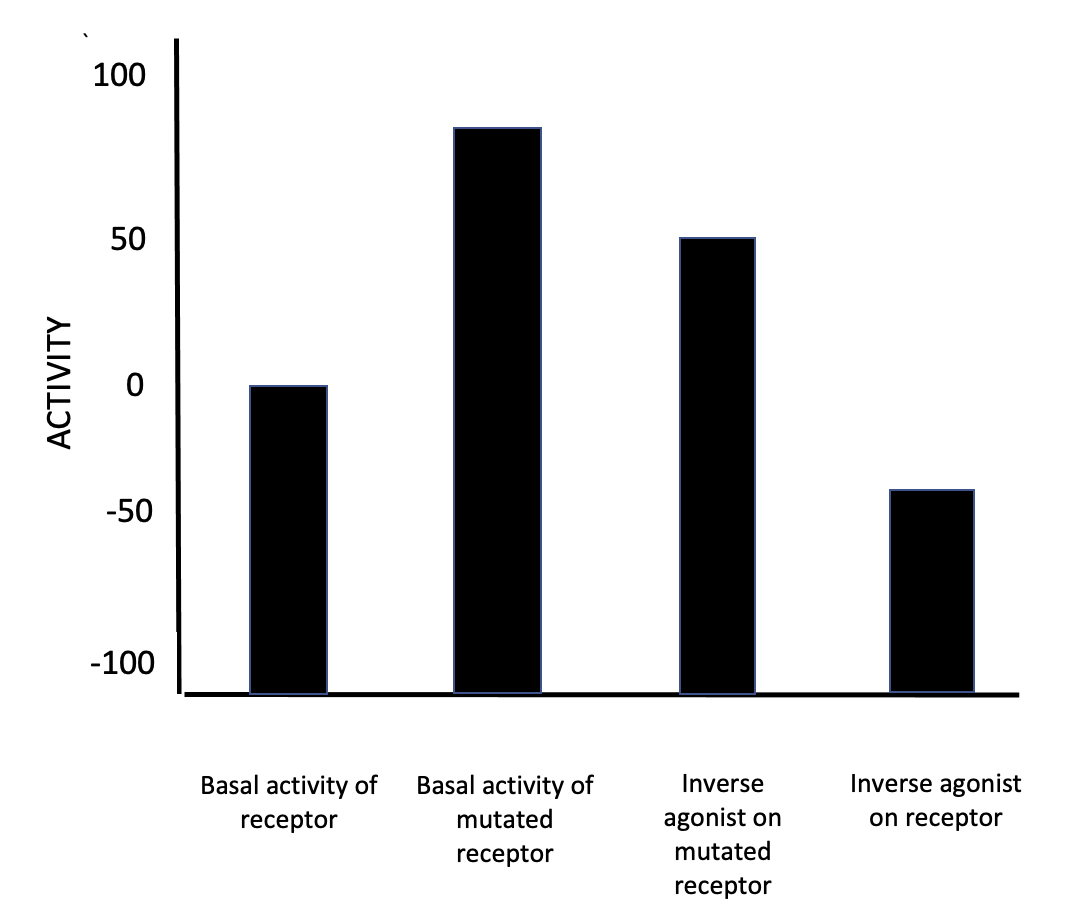
Inverse Agonist
In pharmacology, an inverse agonist is a drug that binds to the same receptor as an agonist but induces a pharmacological response opposite to that of the agonist. A neutral antagonist has no activity in the absence of an agonist or inverse agonist but can block the activity of either; they are in fact sometimes called ''blockers'' (examples include alpha blockers, beta blockers, and calcium channel blockers). Inverse agonists have opposite actions to those of agonists but the effects of both of these can be blocked by antagonists. A prerequisite for an inverse agonist response is that the receptor must have a constitutive (also known as intrinsic or basal) level of activity in the absence of any ligand. An agonist increases the activity of a receptor above its basal level, whereas an inverse agonist decreases the activity below the basal level. The efficacy of a full agonist is by definition 100%, a neutral antagonist has 0% efficacy, and an inverse agonist has < 0% (i.e., n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |