|
Levitation (physics)
Levitation (from Latin ', ) is the process by which an object is held aloft in a stable position, without mechanical support via any physical contact. Levitation is accomplished by providing an upward force that counteracts the pull of gravitation, gravity (in relation to gravity on earth), plus a smaller stabilizing force that pushes the object toward a home position whenever it is a small distance away from that home position. The force can be a fundamental force such as magnetic or electrostatic, or it can be a reactive force such as optical, buoyant, aerodynamic, or hydrodynamic. Levitation excludes Buoyancy, floating at the surface of a liquid because the liquid provides direct mechanical support. Levitation excludes hovering flight by insects, hummingbirds, helicopters, rockets, and balloons because the object provides its own counter-gravity force. Physics Levitation (on Earth or any planetoid) requires an upward force that cancels out the weight of the object, so that th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnet 4
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, steel, nickel, cobalt, etc. and attracts or repels other magnets. A permanent magnet is an object made from a material that is magnetized and creates its own persistent magnetic field. An everyday example is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. Materials that can be magnetized, which are also the ones that are strongly attracted to a magnet, are called Ferromagnetism, ferromagnetic (or ferrimagnetic). These include the elements iron, nickel and cobalt and their alloys, some alloys of rare-earth element, rare-earth metals, and some naturally occurring minerals such as lodestone. Although ferromagnetic (and ferrimagnetic) materials are the only ones attracted to a magnet strongly enough to be commonly considered magnetic, all oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Field
An electric field (sometimes called E-field) is a field (physics), physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles such as electrons. In classical electromagnetism, the electric field of a single charge (or group of charges) describes their capacity to exert attractive or repulsive forces on another charged object. Charged particles exert attractive forces on each other when the sign of their charges are opposite, one being positive while the other is negative, and repel each other when the signs of the charges are the same. Because these forces are exerted mutually, two charges must be present for the forces to take place. These forces are described by Coulomb's law, which says that the greater the magnitude of the charges, the greater the force, and the greater the distance between them, the weaker the force. Informally, the greater the charge of an object, the stronger its electric field. Similarly, an electric field is stronger nearer charged objects and weaker f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenon
Xenon is a chemical element; it has symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the formation of xenon hexafluoroplatinate, the first noble gas compound to be synthesized. Xenon is used in flash lamps and arc lamps, and as a general anesthetic. The first excimer laser design used a xenon dimer molecule (Xe2) as the lasing medium, and the earliest laser designs used xenon flash lamps as pumps. Xenon is also used to search for hypothetical weakly interacting massive particles and as a propellant for ion thrusters in spacecraft. Naturally occurring xenon consists of seven stable isotopes and two long-lived radioactive isotopes. More than 40 unstable xenon isotopes undergo radioactive decay, and the isotope ratios of xenon are an important tool for studying the early history of the Solar System. Radioactive xe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noble Gas
The noble gases (historically the inert gases, sometimes referred to as aerogens) are the members of Group (periodic table), group 18 of the periodic table: helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), radon (Rn) and, in some cases, oganesson (Og). Under Standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions, the first six of these Chemical element, elements are odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low chemical reactivity and cryogenics, cryogenic boiling points. The properties of oganesson are uncertain. The intermolecular force between noble gas atoms is the very weak London dispersion force, so their boiling points are all cryogenic, below . The noble gases' Chemically inert, inertness, or tendency not to Chemical reaction, react with other chemical substances, results from their electron configuration: their Electron shell, outer shell of valence electrons is "full", giving them little tendency to participate in chemical reactions. Only a few hun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is the force exerted by a fluid opposing the weight of a partially or fully immersed object (which may be also be a parcel of fluid). In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus, the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. The pressure difference results in a net upward force on the object. The magnitude of the force is proportional to the pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the submerged volume of the object, i.e. the Displacement (fluid), displaced fluid. For this reason, an object with average density greater than the surrounding fluid tends to sink because its weight is greater than the weight of the fluid it displaces. If the objec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buoyant Levitation
Levitation, Levitate, or Levitating may refer to: Concepts *Levitation (illusion), an illusion where a magician appears to levitate a person or object *Levitation (paranormal), the claimed paranormal phenomenon of levitation, occurring without any scientific explanation *Levitation (physics), the process by which an object is suspended against gravity, in a stable position without solid physical contact *Levitation of saints, a mystical phenomenon attributed to some saints Music Albums * ''Levitation'' (Hawkwind album) *Levitation (Flamingods album) * ''Levitate'' (Bruce Hornsby album) * ''Levitate'' (The Fall album) Songs * "Levitating" (song), by Dua Lipa * "Levitate" (Hadouken! song) * "Levitate" (Hollywood Undead song) * "Levitate" (Imagine Dragons song) *"Levitation", song by Beach House from ''Depression Cherry'' *"Levitation", song by Circa Zero from ''Circus Hero'' *"The Levitated", song by Scale the Summit from '' The Collective'' *"Levitate", song by Imelda May from ''L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
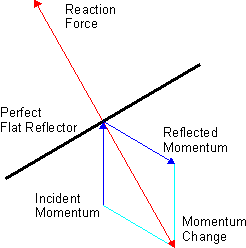
Radiation Pressure
Radiation pressure (also known as light pressure) is mechanical pressure exerted upon a surface due to the exchange of momentum between the object and the electromagnetic field. This includes the momentum of light or electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength that is Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbed, Reflection (physics), reflected, or otherwise emitted (e.g. black-body radiation) by matter on any scale (from macroscopic objects to dust particles to gas molecules). The associated force is called the radiation pressure force, or sometimes just the force of light. The forces generated by radiation pressure are generally too small to be noticed under everyday circumstances; however, they are important in some physical processes and technologies. This particularly includes objects in outer space, where it is usually the main force acting on objects besides gravity, and where the net effect of a tiny force may have a large cumulative effect over long periods of time. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Momentum
In Newtonian mechanics, momentum (: momenta or momentums; more specifically linear momentum or translational momentum) is the product of the mass and velocity of an object. It is a vector quantity, possessing a magnitude and a direction. If is an object's mass and is its velocity (also a vector quantity), then the object's momentum (from Latin '' pellere'' "push, drive") is: \mathbf = m \mathbf. In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of measurement of momentum is the kilogram metre per second (kg⋅m/s), which is dimensionally equivalent to the newton-second. Newton's second law of motion states that the rate of change of a body's momentum is equal to the net force acting on it. Momentum depends on the frame of reference, but in any inertial frame of reference, it is a ''conserved'' quantity, meaning that if a closed system is not affected by external forces, its total momentum does not change. Momentum is also conserved in special relativity (with a mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can move no faster than the speed of light measured in vacuum. The photon belongs to the class of boson particles. As with other elementary particles, photons are best explained by quantum mechanics and exhibit wave–particle duality, their behavior featuring properties of both waves and particles. The modern photon concept originated during the first two decades of the 20th century with the work of Albert Einstein, who built upon the research of Max Planck. While Planck was trying to explain how matter and electromagnetic radiation could be in thermal equilibrium with one another, he proposed that the energy stored within a material object should be regarded as composed of an integer number of discrete, equal-sized parts. To explain the pho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hovercraft
A hovercraft (: hovercraft), also known as an air-cushion vehicle or ACV, is an amphibious craft capable of travelling over land, water, mud, ice, and various other surfaces. Hovercraft use blowers to produce a large volume of air below the Hull (watercraft), hull, or air cushion, that is slightly above atmospheric pressure. The pressure difference between the higher-pressure air below the hull and lower pressure ambient air above it produces lift, which causes the hull to float above the running surface. For stability reasons, the air is typically blown through slots or holes around the outside of a disk- or oval-shaped platform, giving most hovercraft a characteristic rounded-rectangle shape. The first practical design for hovercraft was derived from a British invention in the 1950s. They are now used throughout the world as specialised transports in disaster relief, coastguard, military and survey applications, as well as for sport or passenger service. Very large version ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Hockey
Air hockey is a tabletop sport where two opposing players try to score goals against each other on a low-friction table using two hand-held discs (mallets/pushers) and a lightweight plastic puck. The air hockey table has raised edges that allow the puck to reflect off horizontally, and a very smooth, slippery surface that further reduces friction by suspending the puck on a thin cushion of air ejected from tiny vent holes built inside the surface. This causes the puck to hover and move easily across the table with little loss of velocity, which simulates the lubricated sliding of an ice hockey puck across a well polished rink, hence the name of the game. Federations * United States Air Hockey Association (USAA) – 1978 * Air Hockey Players Association (AHPA) – 2015 * North Carolina Air Hockey Player Association (NCAHP) – 2016 Air hockey tables A typical air hockey table consists of a large smooth playing surface designed to minimize friction, a surrounding rail to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porous
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measure the "accessible void", the total amount of void space accessible from the surface (cf. closed-cell foam). There are many ways to test porosity in a substance or part, such as industrial CT scanning. The term porosity is used in multiple fields including pharmaceutics, ceramics, metallurgy, materials, manufacturing, petrophysics, hydrology, earth sciences, soil mechanics, rock mechanics, and engineering. Void fraction in two-phase flow In gas-liquid two-phase flow, the void fraction is defined as the fraction of the flow-channel volume that is occupied by the gas phase or, alternatively, as the fraction of the cross-sectional area of the channel that is occupied by the gas phase. Void fraction usually varies from location to loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |