|
Lesser Sac
The lesser sac, also known as the omental bursa, is a part of the peritoneal cavity that is formed by the lesser omentum, lesser and greater omentum. Usually found in mammals, it is connected with the greater sac via the omental foramen or ''Foramen of Winslow''. In mammals, it is common for the lesser sac to contain considerable amounts of fat. Anatomic margins ;Anterior margin: listed from the top-to-bottom margin: Caudate lobe of the liver, lesser omentum, stomach, gastrocolic ligament ;Lateral margin: listed from the most anterior to the most posterior margin: Gastrosplenic ligament, spleen, Lienorenal ligament ;Posterior margin: Left kidney and adrenal gland, pancreas ;Inferior margin: Greater omentum ;Superior margin: Liver If any of the marginal structures rupture their contents could leak into the lesser sac. If the stomach were to rupture on its anterior side though the leak would collect in the greater sac. The lesser sac is formed during embryogenesis from an inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Sac
In human anatomy, the greater sac, also known as the general cavity (of the abdomen) or peritoneum of the peritoneal cavity proper, is the cavity in the abdomen that is inside the peritoneum but outside the lesser sac. It is connected with the lesser sac via the omental foramen, also known as the ''foramen of Winslow'' or ''epiploic foramen'', which is anteriorly bounded by the portal triad – portal vein, hepatic artery, and common bile duct. Additional images File:Gray989.png, Schematic figure of the bursa omentalis, etc. Human embryo of eight weeks. File:Gray990.png, Diagrams to illustrate the development of the greater omentum and transverse mesocolon. See also * Coelom * Greater omentum * Lesser omentum * Omental bursa (Lesser sac) * Omental foramen (Epiploic foramen, Foramen of Winslow) * Peritoneum The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancreas
The pancreas (plural pancreases, or pancreata) is an Organ (anatomy), organ of the Digestion, digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity, abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e., it has both an endocrine and a digestive exocrine function. Ninety-nine percent of the pancreas is exocrine and 1% is endocrine. As an endocrine gland, it functions mostly to regulate blood sugar levels, secreting the hormones insulin, glucagon, somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide. As a part of the digestive system, it functions as an exocrine gland secreting pancreatic juice into the duodenum through the pancreatic duct. This juice contains bicarbonate, which neutralizes acid entering the duodenum from the stomach; and digestive enzymes, which break down carbohydrates, proteins and lipids, fats in food entering the duodenum from the stomach. Inflammation of the pancreas is kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
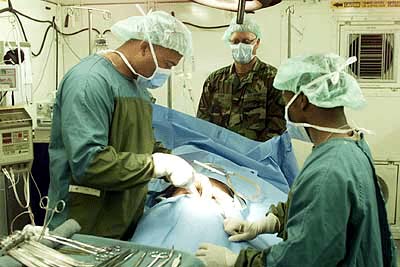
General Surgery
General surgery is a Surgical specialties, surgical specialty that focuses on alimentary canal and Abdomen, abdominal contents including the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, Appendix (anatomy), appendix and bile ducts, and often the thyroid gland. General surgeons also deal with diseases involving the human skin, skin, breast, soft tissue, trauma (medicine), trauma, peripheral artery disease and hernias and perform endoscopic as such as gastroscopy, colonoscopy and laparoscopic procedures. Scope General surgeons may sub-specialise into one or more of the following disciplines: Trauma surgery In many parts of the world including North America, Australia and the UK, United Kingdom, the overall responsibility for major trauma, trauma care falls under the auspices of general surgery. Some general surgeons obtain advanced training in this field (most commonly surgical critical care) and specialty certification surgical critical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) was an American Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1892, incorporated in the New York (state), state of New York and headquartered in Boston. Over the years, the company had multiple divisions, including GE Aerospace, aerospace, GE Power, energy, GE HealthCare, healthcare, lighting, locomotives, appliances, and GE Capital, finance. In 2020, GE ranked among the Fortune 500, ''Fortune'' 500 as the 33rd largest firm in the United States by gross revenue. In 2023, the company was ranked 64th in the Forbes Global 2000, ''Forbes'' Global 2000. In 2011, GE ranked among the Fortune 20 as the 14th most profitable company, but later very severely underperformed the market (by about 75%) as its profitability collapsed. Two employees of GE—Irving Langmuir (1932) and Ivar Giaever (1973)—have been awarded the Nobel Prize. From 1986 until 2013, GE was the owner of the NBC television network through its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mesothelium supported by a thin layer of connective tissue. This peritoneal lining of the cavity supports many of the abdomen#Contents, abdominal organs and serves as a conduit for their blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves. The abdominal cavity (the space bounded by the vertebrae, abdominal muscles, Thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm, and pelvic floor) is different from the intraperitoneal space (located within the abdominal cavity but wrapped in peritoneum). The structures within the intraperitoneal space are called "intraperitoneal" (e.g., the stomach and intestines), the structures in the abdominal cavity that are located behind the intraperitoneal space are called "retroperitoneal" (e.g., the kidneys), and those structures below the intrape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Omentum
The lesser omentum (small omentum or gastrohepatic omentum) is the double layer of peritoneum that extends from the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach, and to the first part of the duodenum. The lesser omentum is usually divided into these two connecting parts: the hepatogastric ligament, and the hepatoduodenal ligament. Structure The lesser omentum is extremely thin, and is continuous with the two layers of peritoneum which cover respectively the antero-superior and postero-inferior surfaces of the stomach and first part of the duodenum. When these two layers reach the lesser curvature of the stomach and the upper border of the duodenum, they join and ascend as a double fold to the porta hepatis. To the left of the porta, the fold is attached to the bottom of the fossa for the ductus venosus, along which it is carried to the diaphragm, where the two layers separate to embrace the end of the esophagus. At the right border of the lesser omentum, the two layer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foramen Of Winslow
In human anatomy, the omental foramen (epiploic foramen, foramen of Winslow after the anatomist Jacob B. Winslow, or uncommonly aditus; ) is the passage of communication, or foramen, between the greater sac, and the lesser sac of the peritoneal cavity. Borders It has the following borders: * ''anterior'': the free border of the lesser omentum, known as the hepatoduodenal ligament. This has two layers and within these layers are the common bile duct, hepatic artery, and hepatic portal vein. * ''posterior'': the peritoneum covering the inferior vena cava * ''superior'': the peritoneum covering the caudate lobe of the liver * ''inferior'': the peritoneum covering the commencement of the duodenum and the hepatic artery, the latter passing forward below the foramen before ascending between the two layers of the lesser omentum. * ''left lateral'': gastrosplenic ligament and splenorenal ligament As the portal vein is the most posterior structure in the hepatoduodenal ligament, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Sac
In human anatomy, the greater sac, also known as the general cavity (of the abdomen) or peritoneum of the peritoneal cavity proper, is the cavity in the abdomen that is inside the peritoneum but outside the lesser sac. It is connected with the lesser sac via the omental foramen, also known as the ''foramen of Winslow'' or ''epiploic foramen'', which is anteriorly bounded by the portal triad – portal vein, hepatic artery, and common bile duct. Additional images File:Gray989.png, Schematic figure of the bursa omentalis, etc. Human embryo of eight weeks. File:Gray990.png, Diagrams to illustrate the development of the greater omentum and transverse mesocolon. See also * Coelom * Greater omentum * Lesser omentum * Omental bursa (Lesser sac) * Omental foramen (Epiploic foramen, Foramen of Winslow) * Peritoneum The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terms For Anatomical Location
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek language, Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes, axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether a vertebrate is a biped or a quadruped, due to the difference in the neuraxis, or if an invertebrate is a non-bilaterian. A non-bilaterian has no anterior or posterior surface for example but can still have a descriptor used such as proximal or distal in relation to a body part that is nearest to, or furthest from its middle. International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standards for subdisciplines of anatomy. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryogenesis
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell. The resulting fusion of these two cells produces a single-celled zygote that undergoes many cell divisions that produce cells known as blastomeres. The blastomeres (4-cell stage) are arranged as a solid ball that when reaching a certain size, called a morula, (16-cell stage) takes in fluid to create a cavity called a blastocoel. The structure is then termed a blastula, or a blastocyst in mammals. The mammalian blastocyst hatches before implantating into the endometrial lining of the womb. Once implanted the embryo will continue its development through the next stages of gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis. Gastrulation is the formation of the three germ layers that will form all of the different parts o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |