|
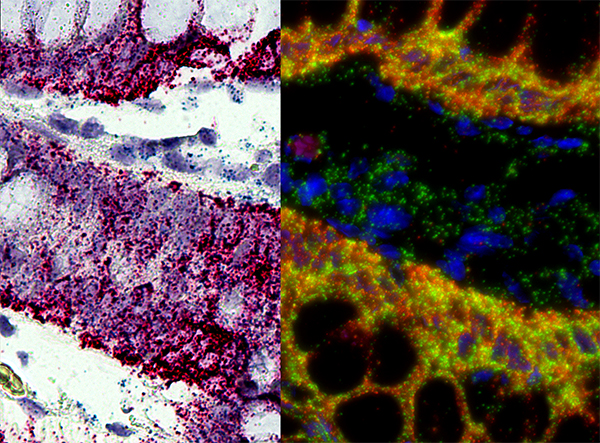
Koilocytosis
A koilocyte is a squamous epithelial cell that has undergone a number of structural changes, which occur as a result of infection of the cell by human papillomavirus (HPV). Identification of these cells by pathologists can be useful in diagnosing various HPV-associated lesions. History With the advent of the PAP smear in 1941 for the diagnosis of cervical lesions numerous cytological observations were made over a short period of time. In 1951, Canadian gynaecologist/ cytologist Dr J. Earnest Ayre described and illustrated halo cells while working in Miami. He described these squamous cells of the uterine cervix to be having a perinuclear clearing, mono or bi-nucleate with poor keratinizing features and hyperchromatic atypical nuclei. He also proposed that these vacuolated cells were pre-cancerous and being always found in association with chronic inflammatory cells, must be caused by a long standing inflammation of infection either viral or otherwise. He said that the presence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HPV-positive Oropharyngeal Cancer
Human papillomavirus-positive oropharyngeal cancer (HPV-positive OPC or HPV+OPC), is a cancer (squamous cell carcinoma) of the throat caused by the human papillomavirus type 16 virus (HPV16). In the past, cancer of the oropharynx (throat) was associated with the use of alcohol or tobacco or both, but the majority of cases are now associated with the HPV virus, acquired by having oral contact with the genitals ( oral-genital sex) of a person who has a genital HPV infection. Risk factors include having a large number of sexual partners, a history of oral-genital sex or anal–oral sex, having a female partner with a history of either an abnormal Pap smear or cervical dysplasia, having chronic periodontitis, and, among men, younger age at first intercourse and a history of genital warts. HPV-positive OPC is considered a separate disease from HPV-negative oropharyngeal cancer (also called HPV negative-OPC and HPV-OPC). HPV-positive OPC presents in one of four ways: as an asymptomat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ThinPrep Pap Smear HPV
Liquid-based cytology is a method of preparing samples for examination in cytopathology. The sample is collected, normally by a small brush, in the same way as for a conventional smear test, but rather than the smear being transferred directly to a microscope slide, the sample is deposited into a small bottle of preservative liquid. At the laboratory, the liquid is treated to remove other elements such as mucus before a layer of cells is placed on a slide. History For many years, efforts have been made to develop methods that would enhance the sensitivity and specificity of the Papanicolaou smear (also called Pap smear). Emphasis has been placed on creating automated screening machines whose success depends on a representative sampling of cells on standardized slides containing a monolayer of well-stained, well-preserved cells. From this research and development, liquid-based gynecologic specimen collection has evolved. Its proponents argue that liquid-based preparations outper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papanicolaou Stain
Papanicolaou stain (also Papanicolaou's stain and Pap stain) is a multichromatic (multicolored) cytological staining technique developed by George Papanicolaou in 1942. The Papanicolaou stain is one of the most widely used stains in cytology, where it is used to aid pathologists in making a diagnosis. Although most notable for its use in the detection of cervical cancer in the Pap test or Pap smear, it is also used to stain non- gynecological specimen preparations from a variety of bodily secretions and from small needle biopsies of organs and tissues. Papanicolaou published three formulations of this stain in 1942, 1954, and 1960. Usage Pap staining is used to differentiate cells in smear preparations (in which samples are spread or smeared onto a glass microscope slide) from various bodily secretions and needle biopsies; the specimens may include gynecological smears (Pap smears), sputum, brushings, washings, urine, cerebrospinal fluid, abdominal fluid, pleural fluid, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Situ Hybridization
''In situ'' hybridization (ISH) is a type of Hybridisation (molecular biology), hybridization that uses a labeled complementary DNA, RNA or modified nucleic acid strand (i.e., a Hybridization probe, probe) to localize a specific DNA or RNA sequence in a portion or section of tissue (biology), tissue (''in situ'') or if the tissue is small enough (e.g., plant seeds, ''Drosophila'' embryos), in the entire tissue (whole mount ISH), in cells, and in circulating tumor cells (CTCs). This is distinct from immunohistochemistry, which usually localizes proteins in tissue sections. In situ hybridization is used to reveal the location of specific nucleic acid sequences on chromosomes or in tissues, a crucial step for understanding the organization, regulation, and function of genes. The key techniques currently in use include ''in situ'' hybridization to mRNA with oligonucleotide and RNA probes (both radio-labeled and hapten-labeled), analysis with light and electron microscopes, whole mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymerase Chain Reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to make millions to billions of copies of a specific DNA sample rapidly, allowing scientists to amplify a very small sample of DNA (or a part of it) sufficiently to enable detailed study. PCR was invented in 1983 by American biochemist Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation. Mullis and biochemist Michael Smith (chemist), Michael Smith, who had developed other essential ways of manipulating DNA, were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993. PCR is fundamental to many of the procedures used in genetic testing and research, including analysis of Ancient DNA, ancient samples of DNA and identification of infectious agents. Using PCR, copies of very small amounts of DNA sequences are exponentially amplified in a series of cycles of temperature changes. PCR is now a common and often indispensable technique used in medical laboratory research for a broad variety of applications including biomedical research and forensic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISSN (identifier)
An International Standard Serial Number (ISSN) is an eight-digit to uniquely identify a periodical publication (periodical), such as a magazine. The ISSN is especially helpful in distinguishing between serials with the same title. ISSNs are used in ordering, cataloging, interlibrary loans, and other practices in connection with serial literature. The ISSN system was first drafted as an International Organization for Standardization (ISO) international standard in 1971 and published as ISO 3297 in 1975. ISO subcommittee TC 46/SC 9 is responsible for maintaining the standard. When a serial with the same content is published in more than one media type, a different ISSN is assigned to each media type. For example, many serials are published both in print and electronic media. The ISSN system refers to these types as print ISSN (p-ISSN) and electronic ISSN (e-ISSN). Consequently, as defined in ISO 3297:2007, every serial in the ISSN system is also assigned a linking ISSN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doi (identifier)
A digital object identifier (DOI) is a persistent identifier or handle used to uniquely identify various objects, standardized by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). DOIs are an implementation of the Handle System; they also fit within the URI system (Uniform Resource Identifier). They are widely used to identify academic, professional, and government information, such as journal articles, research reports, data sets, and official publications. A DOI aims to resolve to its target, the information object to which the DOI refers. This is achieved by binding the DOI to metadata about the object, such as a URL where the object is located. Thus, by being actionable and interoperable, a DOI differs from ISBNs or ISRCs which are identifiers only. The DOI system uses the indecs Content Model to represent metadata. The DOI for a document remains fixed over the lifetime of the document, whereas its location and other metadata may change. Referring to an onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
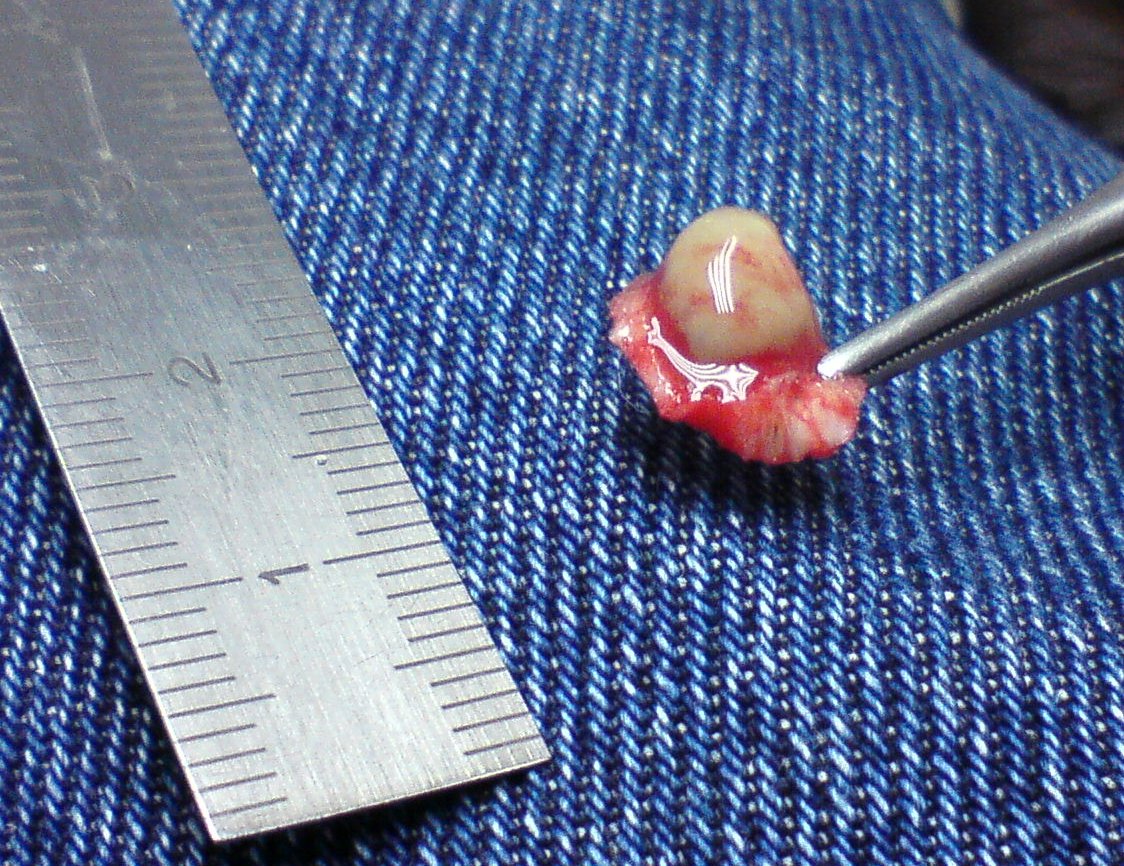
Verruca Vulgaris
A plantar wart is a wart occurring on the bottom of the foot or toes. Its color is typically similar to that of the skin. Small black dots often occur on the surface. One or more may occur in an area. They may result in pain with pressure such that walking is difficult. They are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). A break in the skin is required for infection to occur. Risk factors include use of communal showers, having had prior warts, and poor immune function. Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms. Treatment is only needed if it is causing symptoms. This may include salicylic acid, cryotherapy, chemo-based fluorouracil or bleomycin, and surgical removal. The skin atop the lesion should generally be removed before treatment. In about a third to two-thirds of cases, they go away without specific treatment, but this may take a few years. Plantar warts are common. Children and young adults are most often affected. Signs and symptoms Their colors are typically simil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LSIL
The Bethesda system (TBS), officially called The Bethesda System for Reporting Cervical Cytology, is a system for reporting cervical or vaginal cytologic diagnoses, used for reporting Pap smear results. It was introduced in 1988 and revised in 1991, 2001, and 2014. The name comes from the location (Bethesda, Maryland) of the conference, sponsored by the National Institutes of Health, that established the system. Since 2010, there is also a Bethesda system used for cytopathology of thyroid nodules, which is called The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology (TBSRTC or BSRTC). Like TBS, it was the result of a conference sponsored by the NIH and is published in book editions (currently by Springer). Mentions of "the Bethesda system" without further specification usually refer to the cervical system, unless the thyroid context of a discussion is implicit. Cervix Abnormal results include: * Atypical squamous cells ** Atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (AS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrum Of SIL Cervical Dysplasia (4445758838)
A spectrum (: spectra or spectrums) is a set of related ideas, objects, or properties whose features overlap such that they blend to form a continuum. The word ''spectrum'' was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light after passing through a prism. In the optical spectrum, light wavelength is viewed as continuous, and spectral colors are seen to blend into one another smoothly when organized in order of their corresponding wavelengths. As scientific understanding of light advanced, the term came to apply to the entire electromagnetic spectrum, including radiation not visible to the human eye. ''Spectrum'' has since been applied by analogy to topics outside optics. Thus, one might talk about the " spectrum of political opinion", or the "spectrum of activity" of a drug, or the "autism spectrum". In these uses, values within a spectrum may not be associated with precisely quantifiable numbers or definitions. Such uses imply a broad ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASC-US
The Bethesda system (TBS), officially called The Bethesda System for Reporting Cervical Cytology, is a system for reporting cervical or vaginal cytologic diagnoses, used for reporting Pap smear results. It was introduced in 1988 and revised in 1991, 2001, and 2014. The name comes from the location (Bethesda, Maryland) of the conference, sponsored by the National Institutes of Health, that established the system. Since 2010, there is also a Bethesda system used for cytopathology of thyroid nodules, which is called The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology (TBSRTC or BSRTC). Like TBS, it was the result of a conference sponsored by the NIH and is published in book editions (currently by Springer). Mentions of "the Bethesda system" without further specification usually refer to the cervical system, unless the thyroid context of a discussion is implicit. Cervix Abnormal results include: * Atypical squamous cells ** Atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (AS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anal Intraepithelial Neoplasia
Intraepithelial neoplasia (IEN) is the development of a benign neoplasia or high-grade dysplasia in an epithelium. The exact dividing line between dysplasia and neoplasia has been very difficult to draw throughout the era of medical science. It varies between persons. In the localizations shown below, the term ''intraepithelial neoplasia'' is used to describe more accurately what was historically referred to as epithelial dysplasia. IEN is not cancer, but it is associated with higher risk for developing cancer in future. It is thus sometimes a precancerous condition A precancerous condition is a condition, tumor or lesion involving abnormal cells which are associated with an increased risk of developing into cancer. Clinically, precancerous conditions encompass a variety of abnormal tissues with an increase .... Localizations References Lesions {{oncology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |