|
Kiva
A kiva (also ''estufa'') is a space used by Puebloans for rites and political meetings, many of them associated with the kachina belief system. Among the modern Hopi and most other Pueblo peoples, "kiva" means a large room that is circular and underground, and used for spiritual ceremonies and a place of worship. Similar subterranean rooms are found among ruins in the Southwestern United States, indicating uses by the ancient peoples of the region including the ancestral Puebloans, the Mogollon, and the Hohokam. Those used by the ancient Pueblos of the Pueblo I Period and following, designated by the Pecos Classification system developed by archaeologists, were usually round and evolved from simpler pit-houses. For the Ancestral Puebloans, these rooms are believed to have had a variety of functions, including domestic residence along with social and ceremonial purposes. Evolution During the late 8th century, Mesa Verdeans started building square pit structures tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
False Kiva
The False Kiva is a human-made stone circle of unknown origin in a cave in a remote area of Canyonlands National Park, which is located in U.S. state of Utah. It was closed by Canyonlands National Park rangers in early August 2018, as a result of vandalism. It requires some hiking knowledge or special directions to find. It has become a popular spot for photographers capturing the Southwest, offering a unique frame for the dramatic thunderstorms or clear skies beyond. Origin While located in a naturally occurring alcove, the name ''False Kiva'' arises from the uncertainty about the circle of stones' origins and purpose, whether it is really an authentic kiva, a location used for religious purposes. Disclosure controversy Debate rages on whether to disclose the exact location of False Kiva as it enjoys a semi-protected status. Park rangers are not required to disclose the location of site, and it does not appear on official maps of the park. Because of the remoteness of the loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancestral Puebloans
The Ancestral Puebloans, also known as Ancestral Pueblo peoples or the Basketmaker-Pueblo culture, were an ancient Native American culture of Pueblo peoples spanning the present-day Four Corners region of the United States, comprising southeastern Utah, northeastern Arizona, northwestern New Mexico, and southwestern Colorado. They are believed to have developed, at least in part, from the Oshara tradition, which developed from the Picosa culture. The Ancestral Puebloans lived in a range of structures that included small family pit houses, larger structures to house clans, grand pueblos, and cliff-sited dwellings for defense. They had a complex network linking hundreds of communities and population centers across the Colorado Plateau. They held a distinct knowledge of celestial sciences that found form in their architecture. The kiva, a congregational space that was used mostly for ceremonies, was an integral part of the community structure. Archaeologists continue to d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
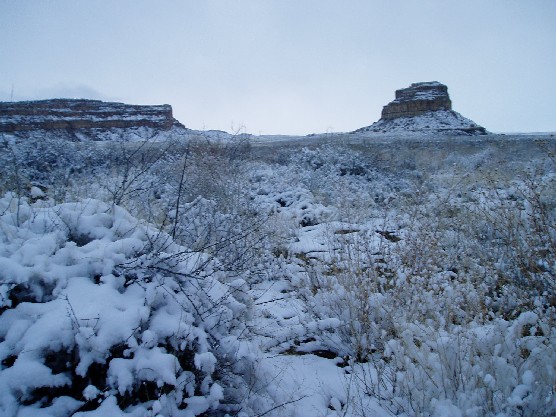
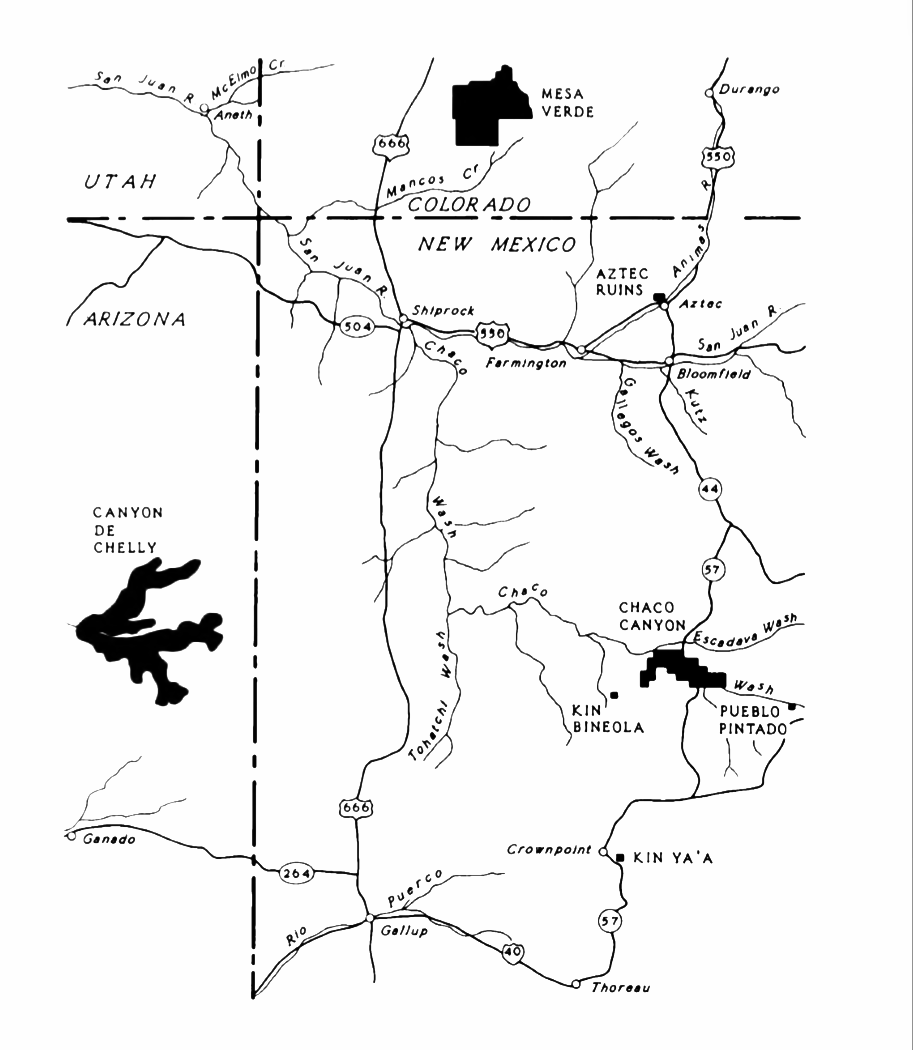
Chaco Canyon
Chaco Culture National Historical Park is a United States National Historical Park in the American Southwest hosting a large concentration of pre-Columbian indigenous ruins of pueblos. The park is located in northwestern New Mexico, between Albuquerque and Farmington, in a remote canyon cut by the Chaco Wash. Containing the most sweeping collection of ancient ruins north of Mexico, the park preserves one of the most important cultural and historical areas in the United States. Between AD 900 and 1150, Chaco Canyon was a major cultural center for the Ancestral Puebloans. Chacoans quarried sandstone blocks and hauled timber from great distances, assembling fifteen major complexes that remained the largest buildings ever built in North America until the 19th century. Evidence of archaeoastronomy at Chaco has been proposed, with the "Sun Dagger" petroglyph at Fajada Butte a popular example. Many Chacoan buildings may have been aligned to capture the solar and lunar cycles, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesa Verde National Park
Mesa Verde National Park is a national park of the United States and UNESCO World Heritage Site located in Montezuma County, Colorado, and the only World Heritage Site in Colorado. The park protects some of the best-preserved Ancestral Puebloan ancestral sites in the United States. Established by Congress and President Theodore Roosevelt in 1906, the park occupies near the Four Corners region of the American Southwest. With more than 5,000 sites, including 600 cliff dwellings, it is the largest archaeological preserve in the United States. Mesa Verde (Spanish for "green table", or more specifically "green table mountain") is best known for structures such as Cliff Palace, one of the largest cliff dwellings in North America. Starting BC Mesa Verde was seasonally inhabited by a group of nomadic Paleo-Indians known as the Foothills Mountain Complex. The variety of projectile points found in the region indicates they were influenced by surrounding areas, including the Great Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chacoan Round Room Features
Chaco Culture National Historical Park is a United States National Historical Park in the American Southwest hosting a large concentration of pre-Columbian indigenous ruins of pueblos. The park is located in northwestern New Mexico, between Albuquerque and Farmington, in a remote canyon cut by the Chaco Wash. Containing the most sweeping collection of ancient ruins north of Mexico, the park preserves one of the most important cultural and historical areas in the United States. Between AD 900 and 1150, Chaco Canyon was a major cultural center for the Ancestral Puebloans. Chacoans quarried sandstone blocks and hauled timber from great distances, assembling fifteen major complexes that remained the largest buildings ever built in North America until the 19th century. Evidence of archaeoastronomy at Chaco has been proposed, with the "Sun Dagger" petroglyph at Fajada Butte a popular example. Many Chacoan buildings may have been aligned to capture the solar and lunar cycles, requ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandelier Kiva
Bandelier National Monument is a United States National Monument near Los Alamos in Sandoval and Los Alamos counties, New Mexico. The monument preserves the homes and territory of the Ancestral Puebloans of a later era in the Southwest. Most of the pueblo structures date to two eras, dating between AD 1150 and 1600. The monument is of the Pajarito Plateau, on the slopes of the Jemez volcanic field in the Jemez Mountains. Over 70% of the monument is wilderness, with over one mile of elevation change, from about along the Rio Grande to over at the peak of Cerro Grande on the rim of the Valles Caldera, providing for a wide range of life zones and wildlife habitats. of road and more than of hiking trails are built. The monument protects Ancestral Pueblo archeological sites, a diverse and scenic landscape, and the country's largest National Park Service Civilian Conservation Corps National Landmark District. Two-thirds of the park, , is designated as the Bandelier Wildernes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puebloans
The Pueblo peoples are Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans in the Southwestern United States who share common agricultural, material, and religious practices. Among the currently inhabited Pueblos, Taos Pueblo, Taos, San Ildefonso Pueblo, San Ildefonso, Acoma Pueblo, Acoma, Zuni Pueblo, New Mexico, Zuni, and Hopi are some of the most commonly known. Pueblo people speak languages from four different Language family, language families, and each Pueblo is further divided culturally by kinship systems and agricultural practices, although all cultivate varieties of corn (maize). Pueblo peoples History of the Pueblo peoples, have lived in the American Southwest for millennia and descend from the Ancestral Puebloans, Ancestral Pueblo peoples. The term ''Anasazi'' is sometimes used to refer to Ancestral Puebloans, but it is considered derogatory and offensive. "Anasazi" is a Navajo language, Navajo adoption of a Ute Indian, Ute term that translates to ''Ancient Enem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hopi
The Hopi are Native Americans who primarily live in northeastern Arizona. The majority are enrolled in the Hopi Tribe of Arizona and live on the Hopi Reservation in northeastern Arizona; however, some Hopi people are enrolled in the Colorado River Indian Tribes of the Colorado River Indian Reservation at the border of Arizona and California. The 2010 U.S. census states that about 19,338 US citizens self-identify as being Hopi. The Hopi language belongs to the Uto-Aztecan language family. The primary meaning of the word ''Hopi'' is "behaving one, one who is mannered, civilized, peaceable, polite, who adheres to the Hopi Way." Some sources contrast this to other warring tribes that subsist on plunder.Connelly, John C., "Hopi Social Organization." In Alfonso Ortiz, vol. ed., ''Southwest'', vol. 9, in William C. Sturtevant, ed., ''Handbook of North American Indians'', Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution, 1979: 539–53, p. 551 ''Hopi'' is a concept deeply rooted in the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztec Ruins National Monument
The Aztec Ruins National Monument in northwestern New Mexico, United States, consists of preserved structures constructed by the Pueblo Indians. The national monument lies on the western bank of the Animas River in Aztec, New Mexico, about northeast of Farmington. Additional Puebloan structures can be found in Salmon Ruins and Heritage Park, south. Archaeological evidence puts the construction of the ruins in the 12th and 13th centuries. The Puebloan-built ruins were dubbed the "Aztec Ruins" by 19th century American settlers who misattributed their construction to the Aztecs. The site was declared "Aztec Ruin National Monument" on January 24, 1923. "Ruin" was changed to "Ruins" after a boundary change, on July 2, 1928. As a historical property of the National Park Service, the monument was administratively listed on the National Register of Historic Places on October 15, 1966. The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) listed the Chaco C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples Of The North American Southwest
The Indigenous peoples of the North American Southwest are those in the current states of Colorado, Arizona, New Mexico, Utah, and Nevada in the western United States, and the states of Sonora and Chihuahua in northern Mexico. An often quoted statement from Erik Reed (1666) defined the Greater Southwest culture area as extending north to south from Durango, Mexico to Durango, Colorado and east to west from Las Vegas, Nevada to Las Vegas, New Mexico.Cordell, Linda S. and Maxine E. McBrinn 2012 ''Archaeology of the Southwest'', 3rd edition. Left Coast Press, Walnut Creek Other names sometimes used to define the region include "American Southwest", "Northern Mexico", "Chichimeca", and " Oasisamerica/ Aridoamerica". This region has long been occupied by hunter-gatherers and agricultural people. Many contemporary cultural traditions exist within the Greater Southwest, including Yuman-speaking peoples inhabiting the Colorado River valley, the uplands, and Baja California, O'odham p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sipapu
A (a Hopi word) was a small hole or indentation in the floor of a (pithouse). Kivas were used by the Ancestral Puebloans and continue to be used by modern-day Puebloans. The symbolizes the portal through which their ancient ancestors first emerged to enter the present world. Hopi mythology (and similar traditions in other Pueblo cultures such as the Zuni and Acoma) states that this is the hole from which the first peoples of this world entered. As they stepped outside of the , they changed from lizard-like beings into human form. It is from this point that the "First Peoples" of the Earth began to divide and separate, becoming tribes. The original sipapu is said in Hopi and some other Uto-Aztecan Puebloan mythology to be located in the Grand Canyon The Grand Canyon is a steep-sided canyon carved by the Colorado River in Arizona, United States. The Grand Canyon is long, up to wide and attains a depth of over a mile (). The canyon and adjacent rim are contained wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |