|
Kingdom Of Dali
The Dali Kingdom, also known as the Dali State (; Bai language, Bai: Dablit Guaif), was a Bai people, Bai dynastic state situated in modern Yunnan province, China, from 937 to 1253. In 1253, it was Mongol conquest of China, conquered by the Mongols. However, descendants of its ruling house continued to administer the area as ''tusi'' chiefs under the Yuan dynasty rule until Ming conquest of Yunnan in 1382.. The former capital of the Dali Kingdom remains known as Dali City, Dali in modern Yunnan Province today. Name The Dali Kingdom takes its name from Dali City. Famed for its high quality marble, Dali (dàlǐ 大理) literally means "marble" in Chinese. History Origins Nanzhao was overthrown in 902 and three dynasties ruling successor kingdoms called Great Changhe (903-927), Great Tianxing (927-928), and Great Yining (928-937) followed in quick succession before Duan Siping seized power in 937, establishing himself at Dali City, Dali. The Duan clan professed to have Han Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Song Dynasty
The Song dynasty ( ) was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period#Ten Kingdoms, Ten Kingdoms, ending the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. The Song frequently came into conflict with the contemporaneous Liao dynasty, Liao, Western Xia and Jin dynasty (1115–1234), Jin dynasties in northern China. After retreating to southern China following attacks by the Jin dynasty, the Song was eventually conquered by the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The History of the Song dynasty, dynasty's history is divided into two periods: during the Northern Song (; 960–1127), the capital was in the northern city of Bianjing (now Kaifeng) and the dynasty controlled most of what is now East China. The #Southern Song, 1127–1279, Southern Song (; 1127–1279) comprise the period following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myanmar
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has a population of about 55 million. It is bordered by India and Bangladesh to its northwest, China to its northeast, Laos and Thailand to its east and southeast, and the Andaman Sea and the Bay of Bengal to its south and southwest. The country's capital city is Naypyidaw, and its largest city is Yangon (formerly Rangoon). Early civilisations in the area included the Tibeto-Burman-speaking Pyu city-states in Upper Myanmar and the Mon kingdoms in Lower Myanmar. In the 9th century, the Bamar people entered the upper Irrawaddy River, Irrawaddy valley, and following the establishment of the Pagan Kingdom in the 1050s, the Burmese language and Culture of Myanmar, culture and Buddhism in Myanmar, Theravada Buddhism slowly became dominant in the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
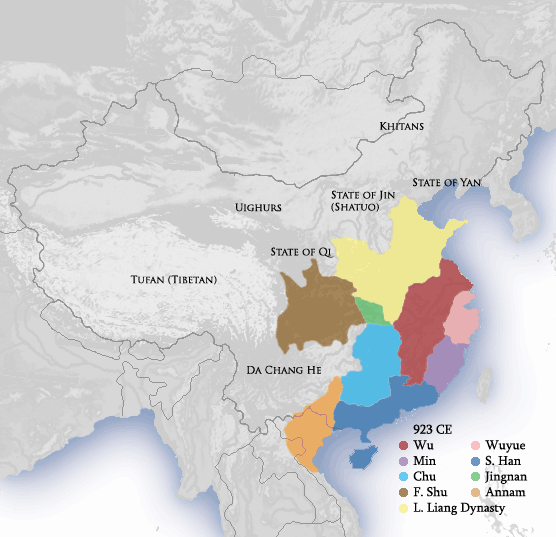
Former Shu
Great Shu ( zh, c=大蜀, p=Dàshǔ), known in historiography as the Former Shu ( zh, c=前蜀, p=Qiánshǔ, links=no) or occasionally Wang Shu (王蜀), was a dynastic state of China and one of the Ten Kingdoms during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. It existed from 907 to 925 CE. The country's name changed from "Shu" to "Han" ( zh, t=漢, p=Hàn, links=no) in 917–918, which is not to be confused with another contemporaneous kingdom during the same Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period, the Southern Han Southern Han ( zh , t = 南漢 , p = Nán Hàn , j=Naam4 Hon3; 917–971), officially Han ( zh , t = 漢 , links=no), originally Yue ( zh , c = 越 , links=no), was a dynastic state of China and one of the Ten Kingdoms that existed during the ... ( zh, t=南漢, s=南汉, first=t, p=Nán Hàn, links=no), 917–971 CE. Rulers See also * Later Shu References * Further reading * {{DEFAULTSORT:Shu Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Forme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese, alternatively the Han people, are an East Asian people, East Asian ethnic group native to Greater China. With a global population of over 1.4 billion, the Han Chinese are the list of contemporary ethnic groups, world's largest ethnic group, making up about 17.5% of the world population. The Han Chinese represent 91.11% of the population in China and 97% of the population in Taiwan. Han Chinese are also a significant Overseas Chinese, diasporic group in Southeast Asian countries such as Thailand, Malaysia, and Indonesia. In Singapore, people of Han Chinese or Chinese descent make up around 75% of the country's population. The Han Chinese have exerted a primary formative influence in the development and growth of Chinese civilization. Originating from Zhongyuan, the Han Chinese trace their ancestry to the Huaxia people, a confederation of agricultural tribes that lived along the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River in the north central plains of Chin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanzhao
Nanzhao ( zh, t=南詔, s=南诏, p=Nánzhào), also spelled Nanchao, , Yi language: ꂷꏂꌅ, ''Mashynzy'') was a dynastic kingdom that flourished in what is now southwestern China and northern Southeast Asia during the 8th and 9th centuries, during the mid/late Tang dynasty. It was centered on present-day Yunnan in China, with its capitals in modern-day Dali City. The kingdom was officially called Dameng (大蒙) from 738 to 859 AD, Dali (大禮) from 859 to 877 and Dafengmin (大封民) from 877 to 902. History Origins Nanzhao encompassed many ethnic and linguistic groups. Some historians believe that the majority of the population were the Bai people (then known as the "White Man") and the Yi people (then known as the "Black Man"), but that the elite spoke a variant of Nuosu (also called ''Yi''), a Northern Loloish language. Scriptures unearthed from Nanzhao were written in the Bai language. The Cuanman people came to power in Yunnan during Zhuge Liang's Sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ming Conquest Of Yunnan
The Ming conquest of Yunnan was the final phase in the Ming dynasty expulsion of Mongol-led Yuan dynasty rule from China proper in the 1380s. Background The Hongwu Emperor had sent envoys to Yunnan in 1369, 1370, 1372, 1374, and 1375 to request for its submission. Some of the envoys were killed and this was the pretext under which an invasion was launched against the regime in Yunnan, then still loyal to the Northern Yuan. War Some 250,000 to 300,000 Han and Hui Muslim troops were mobilized to crush the remaining Yuan-held territory in Yunnan in 1381. The Ming General Fu Youde led the attack on the Mongol and Muslim forces of the Northern Yuan. Also fighting on the Ming side were Generals Mu Ying and Lan Yu, who led Ming loyalist Muslim troops against Yuan loyalist Muslims. The Prince of Liang, Basalawarmi, committed suicide on January 6, 1382, as the Ming dynasty Muslim troops overwhelmed the Northern Yuan's Mongol and Muslim forces. Mu Ying and his Muslim troops were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan Dynasty
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=元朝, p=Yuáncháo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Division of the Mongol Empire, its division. It was established by Kublai (Emperor Shizu or Setsen Khan), the fifth khagan-emperor of the Mongol Empire from the Borjigin clan, and lasted from 1271 to 1368. In Chinese history, the Yuan dynasty followed the Song dynasty and preceded the Ming dynasty. Although Genghis Khan's enthronement as Khagan in 1206 was described in Chinese language, Chinese as the Han Chinese, Han-style title of Emperor of China, Emperor and the Mongol Empire had ruled territories including modern-day northern China for decades, it was not until 1271 that Kublai Khan officially proclaimed the dynasty in the traditional Han style, and the conquest was not complete until 1279 when the Southern Song dynasty was defeated in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tusi
''Tusi'', often translated as "headmen" or "chieftains", were hereditary tribal leaders recognized as imperial officials by the Yuan, Ming, and Qing dynasties of China, and the Later Lê and Nguyễn dynasties of Vietnam. They ruled certain ethnic minorities in central China, western China, southwestern China, and the Indochinese peninsula nominally on behalf of the central government. As succession to the ''Tusi'' position was hereditary, these regimes effectively formed numerous autonomous petty dynasties under the suzerainty of the central court. This arrangement is known as the ''Tusi System'' or the ''Native Chieftain System'' ( zh, c=, p=Tǔsī Zhìdù). It should not be confused with the Chinese tributary system or the Jimi system. ''Tusi'' regimes were located primarily in Yunnan, Guizhou, Tibet, Sichuan, Chongqing, the Xiangxi Prefecture of Hunan, and the Enshi Prefecture of Hubei. ''Tusi'' entities were also established in the historical dependencies and fronti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol Conquest Of China
The Mongol conquest of China was a series of major military efforts by the Mongol Empire to conquer various empires ruling over China for 74 years (1205–1279). It spanned over seven decades in the 13th century and involved the defeat of the Jin dynasty, Western Liao, Western Xia, Tibet, the Dali Kingdom, the Southern Song, and the Eastern Xia. The Mongol Empire under Genghis Khan started the conquest with small-scale raids into Western Xia in 1205 and 1207. In 1279, the Mongol ruler Kublai Khan formally established the Yuan dynasty in the Chinese tradition, having crushed the last Song resistance, marking the reunification of China under Mongol rule, the first time that non- Han people had ruled the entire country. It was the first time that Tibet was unified with the rest of China. Conquest of Western Xia In the early 1200s, Temujin, soon to be known as Genghis Khan, began consolidating his power in Mongolia. Following the death of the Kerait leader Ong Khan to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yunnan
Yunnan; is an inland Provinces of China, province in Southwestern China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 47.2 million (as of 2020). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the Chinese provinces of Guizhou, Sichuan, Autonomous regions of China, autonomous regions of Guangxi and Tibet Autonomous Region, Tibet, as well as Southeast Asian countries Myanmar (Burma), Vietnam, and Laos. Yunnan is China's fourth least developed province based on disposable income per capita in 2014. Yunnan is situated in a mountainous area, with high elevations in the Northwest and low elevations in the Southeast. Most of the population lives in the eastern part of the province. In the west, the altitude can vary from the mountain peaks to river valleys as much as . Yunnan is rich in natural resources and has the largest diversity of plant life in China. Of the approximately 30,000 species of Vascular plant, higher plants in China, Yunnan has perhaps 17, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bai People
The Bai or Pai (Bai language, Bai: , ; zh, c=白族, p=Báizú), are an East Asian people, East Asian ethnic group native to the Dali Bai Autonomous Prefecture of Yunnan, Yunnan Province, Bijie area of Guizhou, Guizhou Province, and Sangzhi County, Sangzhi area of Hunan, Hunan Province. The Bai constitute one of the 56 List of ethnic groups in China, ethnic groups officially recognized by China, with a population of 2,091,543 (2020 Chinese census, as of 2020). Names The Bai people hold the colour white in high esteem and call themselves "Baipzix" (', Baizi, 白子), "Bai'ho" (', Baihuo, 白伙), "Bai yinl" (', Baini, 白尼), or "Miep jiax". ''Bai'' means "white" in Chinese. Because of their strong preference for white, in 1956 the Chinese authorities named this ethnic group the Bai nationality. The Bai were previously named the Minjia (民家) by the Chinese from the 14th century to 1949. Modern identity The Bai people are one of the most sinicized minorities in China. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |