|
Kinetics (physics)
In physics and engineering, kinetics is the branch of classical mechanics that is concerned with the relationship between the motion In physics, motion is when an object changes its position with respect to a reference point in a given time. Motion is mathematically described in terms of displacement, distance, velocity, acceleration, speed, and frame of reference to an o ... and its causes, specifically, forces and torques. Since the mid-20th century, the term "Dynamics (mechanics), dynamics" (or "analytical dynamics") has largely superseded "kinetics" in physics textbooks, though the term is still used in engineering. In Plasma (physics), plasma physics, kinetics refers to the study of Continuum mechanics, continua in velocity space. This is usually in the context of non-thermal (Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution#Physical applications, non-Maxwellian) velocity distributions, or processes that Perturbation theory (quantum mechanics), perturb thermal distributions. These ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." It is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics. (...) You will come to see physics as a towering achievement of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
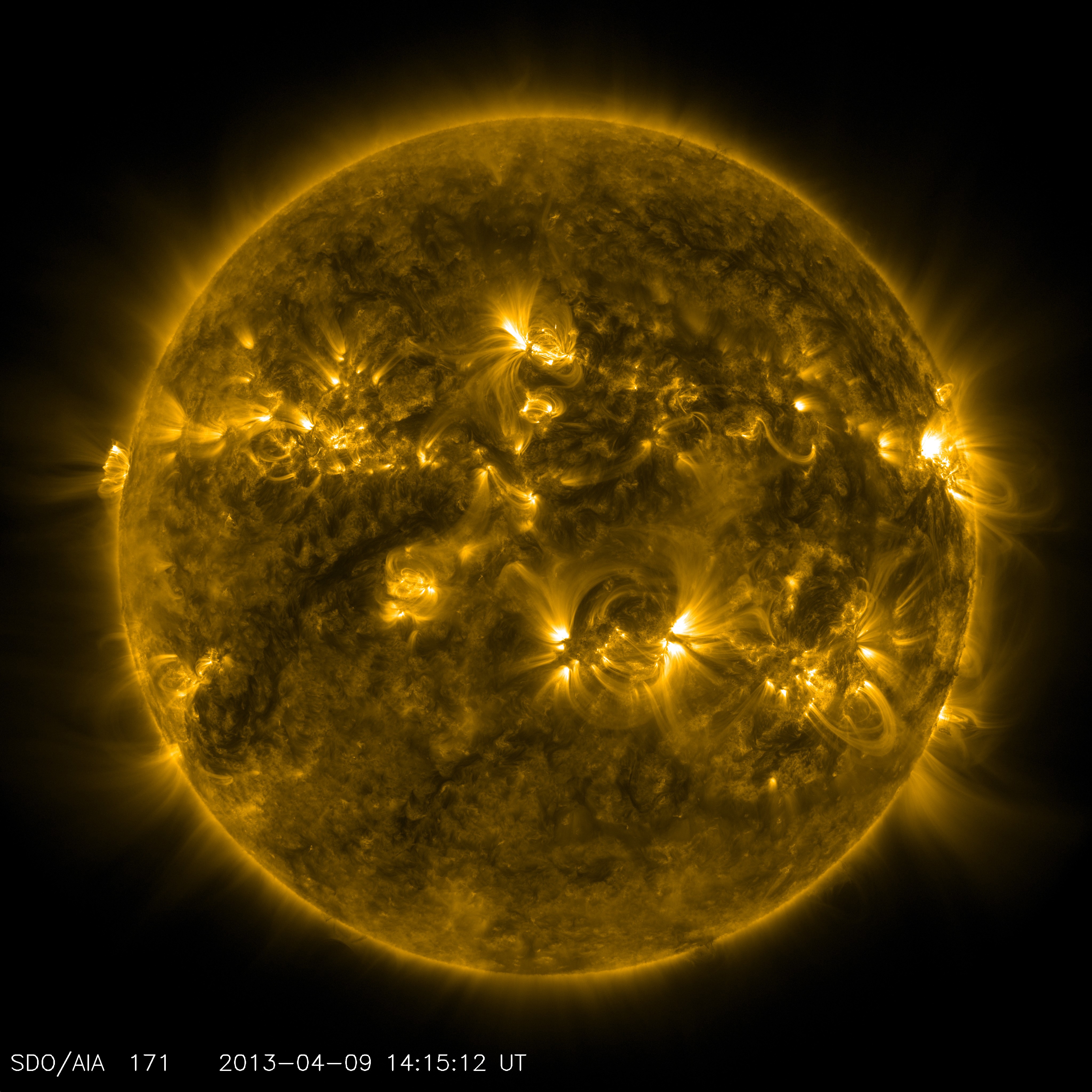
Plasma (physics)
Plasma () is a state of matter characterized by the presence of a significant portion of charged particles in any combination of ions or electrons. It is the most abundant form of ordinary matter in the universe, mostly in stars (including the Sun), but also dominating the rarefied intracluster medium and Outer space#Intergalactic space, intergalactic medium. Plasma can be artificially generated, for example, by heating a neutral gas or subjecting it to a strong electromagnetic field. The presence of charged particles makes plasma electrically conductive, with the dynamics of individual particles and macroscopic plasma motion governed by collective electromagnetic fields and very sensitive to externally applied fields. The response of plasma to electromagnetic fields is used in many modern devices and technologies, such as plasma display, plasma televisions or plasma etching. Depending on temperature and density, a certain number of neutral particles may also be present, in wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Physics
Chemical physics is a branch of physics that studies chemical processes from a physical point of view. It focuses on understanding the physical properties and behavior of chemical systems, using principles from both physics and chemistry. This field investigates physicochemical phenomena using techniques from atomic and molecular physics and condensed matter physics. The United States Department of Education defines chemical physics as "A program that focuses on the scientific study of structural phenomena combining the disciplines of physical chemistry and atomic/molecular physics. Includes instruction in heterogeneous structures, alignment and surface phenomena, quantum theory, mathematical physics, statistical and classical mechanics, chemical kinetics, and laser physics." Distinction between chemical physics and physical chemistry While at the interface of physics and chemistry, chemical physics is distinct from physical chemistry as it focuses more on using physical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Kinetics
Chemical kinetics, also known as reaction kinetics, is the branch of physical chemistry that is concerned with understanding the rates of chemical reactions. It is different from chemical thermodynamics, which deals with the direction in which a reaction occurs but in itself tells nothing about its rate. Chemical kinetics includes investigations of how experimental conditions influence the speed of a chemical reaction and yield information about the reaction's mechanism and transition states, as well as the construction of mathematical models that also can describe the characteristics of a chemical reaction. History The pioneering work of chemical kinetics was done by German chemist Ludwig Wilhelmy in 1850. He experimentally studied the rate of inversion of sucrose and he used integrated rate law for the determination of the reaction kinetics of this reaction. His work was noticed 34 years later by Wilhelm Ostwald. In 1864, Peter Waage and Cato Guldberg published the law ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetohydrodynamics
In physics and engineering, magnetohydrodynamics (MHD; also called magneto-fluid dynamics or hydromagnetics) is a model of electrically conducting fluids that treats all interpenetrating particle species together as a single Continuum mechanics, continuous medium. It is primarily concerned with the low-frequency, large-scale, magnetic behavior in Plasma (physics), plasmas and liquid metals and has applications in multiple fields including space physics, geophysics, astrophysics, and engineering. The word ''magnetohydrodynamics'' is derived from ' meaning magnetic field, ' meaning water, and ' meaning movement. The field of MHD was initiated by Hannes Alfvén, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1970. History The MHD description of electrically conducting fluids was first developed by Hannes Alfvén in a 1942 paper published in Nature (journal), ''Nature'' titled "Existence of Electromagnetic–Hydrodynamic Waves" which outlined his discovery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perturbation Theory (quantum Mechanics)
In quantum mechanics, perturbation theory is a set of approximation schemes directly related to mathematical perturbation for describing a complicated quantum system in terms of a simpler one. The idea is to start with a simple system for which a mathematical solution is known, and add an additional "perturbing" Hamiltonian representing a weak disturbance to the system. If the disturbance is not too large, the various physical quantities associated with the perturbed system (e.g. its energy levels and eigenstates) can be expressed as "corrections" to those of the simple system. These corrections, being small compared to the size of the quantities themselves, can be calculated using approximate methods such as asymptotic series. The complicated system can therefore be studied based on knowledge of the simpler one. In effect, it is describing a complicated unsolved system using a simple, solvable system. Approximate Hamiltonians Perturbation theory is an important tool for de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxwell–Boltzmann Distribution
In physics (in particular in statistical mechanics), the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution, or Maxwell(ian) distribution, is a particular probability distribution named after James Clerk Maxwell and Ludwig Boltzmann. It was first defined and used for describing particle speeds in ideal gas, idealized gases, where the particles move freely inside a stationary container without interacting with one another, except for very brief collisions in which they exchange energy and momentum with each other or with their thermal environment. The term "particle" in this context refers to gaseous particles only (atoms or molecules), and the system of particles is assumed to have reached thermodynamic equilibrium. The energies of such particles follow what is known as Maxwell–Boltzmann statistics, and the statistical distribution of speeds is derived by equating particle energies with kinetic energy. Mathematically, the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution is the chi distribution with three degre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velocity
Velocity is a measurement of speed in a certain direction of motion. It is a fundamental concept in kinematics, the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of physical objects. Velocity is a vector (geometry), vector Physical quantity, quantity, meaning that both magnitude and direction are needed to define it. The Scalar (physics), scalar absolute value (Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude) of velocity is called , being a coherent derived unit whose quantity is measured in the International System of Units, SI (metric system) as metres per second (m/s or m⋅s−1). For example, "5 metres per second" is a scalar, whereas "5 metres per second east" is a vector. If there is a change in speed, direction or both, then the object is said to be undergoing an ''acceleration''. Definition Average velocity The average velocity of an object over a period of time is its Displacement (geometry), change in position, \Delta s, divided by the duration of the period, \Delt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuum Mechanics
Continuum mechanics is a branch of mechanics that deals with the deformation of and transmission of forces through materials modeled as a ''continuous medium'' (also called a ''continuum'') rather than as discrete particles. Continuum mechanics deals with ''deformable bodies'', as opposed to rigid bodies. A continuum model assumes that the substance of the object completely fills the space it occupies. While ignoring the fact that matter is made of atoms, this provides a sufficiently accurate description of matter on length scales much greater than that of inter-atomic distances. The concept of a continuous medium allows for intuitive analysis of bulk matter by using differential equations that describe the behavior of such matter according to physical laws, such as mass conservation, momentum conservation, and energy conservation. Information about the specific material is expressed in constitutive relationships. Continuum mechanics treats the physical properties of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analytical Dynamics
In theoretical physics and mathematical physics, analytical mechanics, or theoretical mechanics is a collection of closely related formulations of classical mechanics. Analytical mechanics uses '' scalar'' properties of motion representing the system as a whole—usually its kinetic energy and potential energy. The equations of motion are derived from the scalar quantity by some underlying principle about the scalar's variation. Analytical mechanics was developed by many scientists and mathematicians during the 18th century and onward, after Newtonian mechanics. Newtonian mechanics considers vector quantities of motion, particularly accelerations, momenta, forces, of the constituents of the system; it can also be called ''vectorial mechanics''. A scalar is a quantity, whereas a vector is represented by quantity and direction. The results of these two different approaches are equivalent, but the analytical mechanics approach has many advantages for complex problems. Analytical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engineering
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, systems. Modern engineering comprises many subfields which include designing and improving infrastructure, machinery, vehicles, electronics, Materials engineering, materials, and energy systems. The Academic discipline, discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more Academic specialization, specialized fields of engineering, each with a more specific emphasis for applications of applied mathematics, mathematics and applied science, science. See glossary of engineering. The word '':wikt:engineering, engineering'' is derived from the Latin . Definition The American Engineers' Council for Professional Development (the predecessor of the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology aka ABET) has defined "engineering" as: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analytical Dynamics
In theoretical physics and mathematical physics, analytical mechanics, or theoretical mechanics is a collection of closely related formulations of classical mechanics. Analytical mechanics uses '' scalar'' properties of motion representing the system as a whole—usually its kinetic energy and potential energy. The equations of motion are derived from the scalar quantity by some underlying principle about the scalar's variation. Analytical mechanics was developed by many scientists and mathematicians during the 18th century and onward, after Newtonian mechanics. Newtonian mechanics considers vector quantities of motion, particularly accelerations, momenta, forces, of the constituents of the system; it can also be called ''vectorial mechanics''. A scalar is a quantity, whereas a vector is represented by quantity and direction. The results of these two different approaches are equivalent, but the analytical mechanics approach has many advantages for complex problems. Analytical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |