|
Karakoa
''Karakoa'' were large outrigger warships from the Philippines. They were used by native Filipinos, notably the Kapampangans and the Visayans, during seasonal sea raids. ''Karakoa'' were distinct from other traditional Philippine sailing vessels in that they were equipped with platforms for transporting warriors and for fighting at sea. During peacetime, they were also used as trading ships. Large ''karakoa'', which could carry hundreds of rowers and warriors, were known as ''joangas'' (also spelled '' juangas'') by the Spanish. Panday Piray of Pampanga, Philippines, was also known for forging heavy bronze lantaka to be mounted on Lakan's (Naval Chief/Commander) ships called 'caracoas' doing battle against the Spanish invaders and cannons were also commissioned by Rajah Sulayman for the fortification of Maynila. By the end of the 16th century, the Spanish denounced ''karakoa'' ship-building and its usage. It later led to a total ban of the ship and the traditions assigned to i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burulan
Burulan is a Visayan term referring to fighting platforms on the traditional large trimaran warships (''balangay'') of the Philippines. They were made from bamboo and were distinctively raised from the deck. They carried the warrior-nobility of the Visayans and other passengers during travel, naval warfare, and seasonal coastal raids ('' mangayaw''), so as to avoid interfering with the paddlers. This platform can be covered by an awning of woven palm leaves (, Spanish: ) during hot days or when it rains, protecting the crew and cargo. In very large ships, the ''burulan'' can be augmented by a pair of fighting platforms mounted directly on the cross-wise supports (''batangan'') of the outriggers (''katig''). These were known as . They differed from the '' daramba'', which were also platforms mounted on the outriggers, in that the latter were mounted on the water and were used by commoner warriors ('' horo-han'') primarily for paddling, and occasionally for fighting. See also *Out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juanga (ship)
A juanga or joanga refers to large-sized ''Kora kora, kora-kora'', ''karakoa'' and ''lanong''.Mallari (1989). p. 424. They are used all throughout the Philippines and Eastern Indonesia, in Maluku Islands, Maluku smaller versions were popular and are still used to this day (Kora-kora). They are propelled by oars but are not used for carrying cargo.Poesponegoro (1981). p. 114. Etymology The word juanga and joanga are cognates with "Junk (ship), junk", which refers to several types of ships in Asia. Retana and Pastells considered the name derived from Hokkien , which means boat. Paul Pelliot and Waruno Mahdi reject the Chinese origin of the word "junk". Instead, it may be derived from "jong" (transliterated as joṅ) in Old Javanese which means ship. The first record of Old Javanese ''jong'' comes from an inscription in Bali dating to the 11th century CE. It was first recorded in the Malay language, Malay and Chinese language by the 15th century, when a Chinese word list identified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balangay
A balangay, or barangay, is a type of lashed-lug boat built by joining planks edge-to-edge using pins, dowels, and fiber lashings. They are found throughout the Philippines and were used largely as trading ships up until the colonial era. The oldest known balangay are the eleven Butuan boats, which have been carbon-dated individually from 689 to 988 CE and were recovered from several sites in Butuan, Agusan del Norte. The Butuan boats are the single largest concentration of lashed-lug boat remains of the Austronesian vessels, Austronesian boatbuilding traditions. They are found in association with large amounts of trade goods from East Asia, Southeast Asia, and as far as Persia, indicating they traded as far as the Middle East. Balangay were the first wooden watercraft excavated in Southeast Asia. Balangay are celebrated annually in the Balanghai Festival of Butuan. Names ''Balangay'' was one of the Pigafetta's dictionary#Some List of Words, first native words the Europeans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kora Kora
A kora-kora or kora kora or coracora is a traditional canoe from the Maluku (Moluccas) Islands, Indonesia. They are naval boat for carrying men on raids for plunder or for slaves. In Maritime Southeast Asia, raiding for slaves was an honourable way of making a living, and the kora kora was needed for defence against raids as well as for forays. Large kora-kora is called juanga or joanga. Etymology The origin of the name is unknown, but it has been proposed that it may have been derived from the Arabic "قُرقور" ''qorqora'', the plural of ''qarâqir,'' meaning "large merchant ship". It is also likely that the origin of the names are native, with the meaning lost through time, as other Austronesian vessels with no contact with Arab traders also bear similar names like the Ivatan '' karakuhan'' and the Marshallese '' korkor''. The term may also comes from Spanish or Portuguese '' carraca'', but in the oldest Portuguese and Spanish accounts of the Moluccas reports ''caraco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivatan People
The Ivatan people are an Austronesian ethnolinguistic group native to the Batanes and Babuyan Islands of the northernmost Philippines. They are genetically closely related to other ethnic groups in Northern Luzon, but also share close linguistic and cultural affinities with the Tao people of Orchid Island in Taiwan. The culture of the Ivatans is partly influenced by the environmental conditions of Batanes. Unlike the old-type nipa huts common in the Philippines, Ivatans have adopted their now-famous stone houses made of coral and limestone, designed to protect against the hostile climate. Origins A 2011 genetic study has concluded that it is likely that the Batanes Islands were initially only used as "stepping stones" during the early stages of the maritime Austronesian expansion from Taiwan into the Philippine Islands (c. 3000 BCE). It was later re-colonized by Austronesians from northern Luzon at around 1200 BCE, which became the ancestors of the Ivatan people. Archaeol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lashed-lug
Lashed-lug boats are ancient boat-building techniques of the Austronesian peoples. It is characterized by the use of raised lugs (also called "cleats") on the inner face of hull planks. These lugs have holes drilled in them so that other hull components such as ribs, thwarts or other structural components can be tied to them with natural fiber ropes (hence "lashed"). This allows a structure to be put together without any metal fastenings. The planks are further stitched together edge-to-edge by sewing or using dowels ("treenails") unto a dugout keel and the solid carved wood pieces that form the caps for the prow and stern. Characteristically, the shell of the boat is created first, prior to being lashed unto ribs. The seams between planks are also sealed with absorbent tapa bark and fiber that expands when wet or caulked with resin-based preparations. Lashed-lug construction has been used on a wide size range of vessels, from small craft, such as logboats that have had planks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loanword
A loanword (also a loan word, loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language (the recipient or target language), through the process of borrowing. Borrowing is a metaphorical term that is well established in the linguistic field despite its acknowledged descriptive flaws: nothing is taken away from the donor language and there is no expectation of returning anything (i.e., the loanword). Loanwords may be contrasted with calques, in which a word is borrowed into the recipient language by being directly translated from the donor language rather than being adopted in (an approximation of) its original form. They must also be distinguished from cognates, which are words in two or more related languages that are similar because they share an etymological origin in the ancestral language, rather than because one borrowed the word from the other. Examples and related terms A loanword is distinguished from a calque (or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malayo-Polynesian
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeast Asia (Indonesia and the Philippine Archipelago) and the Pacific Ocean, with a smaller number in continental Asia in the areas near the Malay Peninsula, with Cambodia, Vietnam and the Chinese island Hainan as the northwest geographic outlier. Malagasy, spoken on the island of Madagascar off the eastern coast of Africa in the Indian Ocean, is the furthest western outlier. Many languages of the Malayo-Polynesian family in insular Southeast Asia show the strong influence of Sanskrit, Tamil and Arabic, as the western part of the region has been a stronghold of Hinduism, Buddhism, and, later, Islam. Two morphological characteristics of the Malayo-Polynesian languages are a system of affixation and reduplication (repetition of all or part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korkor (boat)
The Walap is a traditional ocean-going sailing outrigger canoe from the Marshall Islands. It belongs to the Micronesian proa type whose main characteristics are: single main hull, outrigger-mounted float/ballast, and asymmetric hull profile. Walaps have a lee platform. Like all pacific proas, they are always sailed with the outrigger to windward; they do not tack but "shunt" (reverse direction), so both ends of the boat are identical. The distinction between bow and stern depends only on the heading of the boat. Walaps are not dugouts; only the keel is made of a single bread-fruit log when possible, and the rest are planks sewn together with coconut-fiber lashings, sealed with tree sap. There are three main types of marshallese sailing canoes: * Korkor: a small rowing/sailing canoe used for fishing and transportation in the atoll lagoons. It has a crew of one or two. Used nowadays in very popular regattas. * Tipnol: a medium-sized sailing canoe. Used for travel and fishing in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marshallese People
The Micronesians or Micronesian peoples are various closely related ethnic groups native to Micronesia, a region of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. They are a part of the Austronesian ethnolinguistic group, which has an Urheimat in Taiwan. Ethno-linguistic groups classified as Micronesian include the Carolinians (Northern Mariana Islands), Chamorros (Guam & Northern Mariana Islands), Chuukese, Mortlockese, Namonuito, Paafang, Puluwat and Pollapese ( Chuuk), I-Kiribati (Kiribati), Kosraeans (Kosrae), Marshallese (Marshall Islands), Nauruans (Nauru), Palauan, Sonsorolese, and Hatohobei (Palau), Pohnpeians, Pingelapese, Ngatikese, Mwokilese (Pohnpei), and Yapese, Ulithian, Woleian, Satawalese ( Yap). Origins Based on the current scientific consensus, the Micronesians are considered, by linguistic, archaeological, and human genetic evidence, to be a subset of the sea-migrating Austronesian people, who include the Polynesians and the Melanesians. Austronesians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motu People
The Motu are native inhabitants of Papua New Guinea, living along the southern coastal area of the country. Their indigenous language is also known as Motu, and like several other languages of the region is an Austronesian language. They and the Koitabu people are the original inhabitants and owners of the land on which Port Moresby — the national capital city — stands. The largest Motu village is Hanuabada, northwest of Port Moresby. History Friedrich Ratzel in ''The History of Mankind'' in 1896 reported the tattooing in Melanesia. Among the relatively light-skinned Motu he found tattooing in patterns similar to those of Micronesia. He also reported, among the old women, blackening the body with a kind of earth which gives a lustre like black lead. This was said to be a sign of mourning. Charles Gabriel Seligman came into contact with the Motu, in 1904. He noted that, unlike many of their neighbors in the region, the Motu did not practice exogamy. However, there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
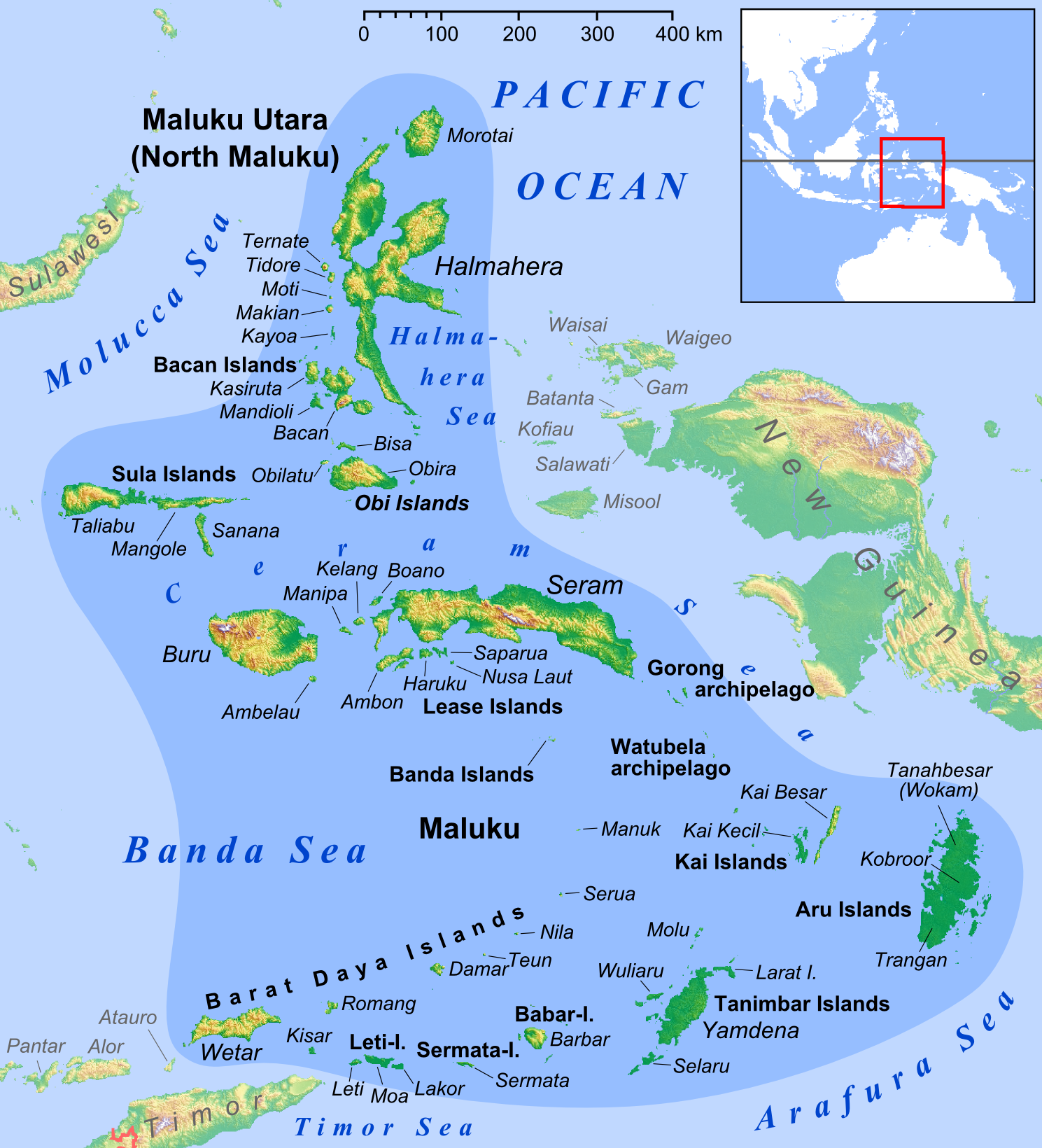
Banda Islands
The Banda Islands () are a volcanic group of ten small volcanic islands in the Banda Sea, about south of Seram Island and about east of Java (island), Java, and constitute an administrative district (''kecamatan'') within the Central Maluku Regency in the Indonesian province of Maluku (Indonesian province), Maluku. The islands rise out of deep ocean and have a total land area of approximately ; with associated maritime area this reaches . They had a population of 18,544 at the 2010 Census and 20,924 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as of mid-2023 was 21,902. Until the mid-19th century the Banda Islands were the world's only source of the spices nutmeg and mace (spice), mace, produced from the nutmeg tree. The islands are also popular destinations for scuba diving and snorkeling. The main town and administrative centre is Banda Neira, located on the island of the same name. Geography There are seven inhabited islands and several that are uninhabited. The inhabite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |