|
Karakkaze
Karakkaze (空っ風、からっかぜ) refers to a kind of strong, dry wind that occurs in the Kantō region of Japan. Overview Karakkaze is formed when wind gusts cross atop the mountains in the Jōetsu region and experience a drop in both temperature and atmospheric pressure. Water vapor in the air falls as rain or snow on the mountain, so the wind that then crosses over the mountain becomes dry. Gunma Prefecture is famous for its karakkaze in winter. Other names include Jōmō Karakkaze (Jōmō is an old name for Gunma) and Akagi Oroshi (karakkaze that blows down from Mt. Akagi). In Jomo Karuta, karakkaze is featured on the 'ra' card. Besides Gunma, Nasunohara in Tochigi Prefecture and Hamamatsu in Shizuoka Prefecture both are famous for karakkaze; there it is called Nasu and Enshu Karakkaze respectively. Effects A phenomenon known as foehn wind A Foehn, or Föhn (, , , ), is a type of dry, relatively warm downslope wind in the lee of a mountain range. It is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunma Prefecture
is a landlocked Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Kantō region of Honshu. Gunma Prefecture has a population of 1,937,626 (1 October 2019) and has a geographic area of . Gunma Prefecture borders Niigata Prefecture and Fukushima Prefecture to the north, Nagano Prefecture to the southwest, Saitama Prefecture to the south, and Tochigi Prefecture to the east. Maebashi is the capital and Takasaki is the largest city of Gunma Prefecture, with other major cities including Ōta, Gunma, Ōta, Isesaki, Gunma, Isesaki, and Kiryū, Gunma, Kiryū. Gunma Prefecture is one of only eight landlocked prefectures, located on the northwestern corner of the Kantō Plain with 14% of its total land being designated as List of national parks of Japan, natural parks. History The ancient province of Gunma was a center of horse breeding and trading activities for the newly immigrated continental peoples (or Toraijin). The arrival of horses and the remains of horse tackle coinci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kantō Region
The is a geography, geographical region of Honshu, the largest island of Japan. In a common definition, the region includes the Greater Tokyo Area and encompasses seven prefectures of Japan, prefectures: Chiba Prefecture, Chiba, Gunma Prefecture, Gunma, Ibaraki Prefecture, Ibaraki, Kanagawa Prefecture, Kanagawa, Saitama Prefecture, Saitama, Tochigi Prefecture, Tochigi, and Tokyo. Slightly more than 45 percent of the land area within its boundaries is the Kantō Plain. The rest consists of the hills and mountains that form land borders with other list of regions of Japan, regions of Japan. As the Kantō region contains Tokyo, the capital and largest city of Japan, the region is considered the center of Japan's politics and economy. According to the official census on October 1, 2010 by the Statistics Bureau (Japan), Statistics Bureau of Japan, the population was 42,607,376, amounting to approximately one third of the total population of Japan. Other definitions The assemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jōetsu Region
is a geographical region within Niigata Prefecture, Japan Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea .... It includes of the cities of Jōetsu, Itoigawa and Myōkō. History The historical Jōetsu region is in the area of the old provinces of Kōzuke and Echigo. The region is traditionally known as a less developed area of Japan. The Joetsu area is a strategic hub in the larger regional transport network. ; retrieved 2012-4-17. References External links * Niigata JET[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Akagi
is a stratovolcano in Gunma Prefecture, Japan. The broad, low dominantly andesitic stratovolcano rises above the northern end of the Kanto Plain. It contains an elliptical, summit caldera with post-caldera lava domes arranged along a NW–SE line. Lake Ono is located at the NE end of the caldera. An older stratovolcano was partially destroyed by edifice collapse, producing a debris-avalanche deposit along the south flank. A series of large plinian eruptions accompanied growth of a second stratovolcano during the Pleistocene. Construction of the central cone in the late-Pleistocene summit caldera began following the last of the plinian eruptions about 31,000 years ago. During historical time unusual activity was recorded on several occasions during the 9th century, but reported eruptions in 1251 and 1938 are considered uncertain. Mount Akagi, along with Mount Myōgi and Mount Haruna, is one of the , and the cold north winds which blow down from it are called or . The ''Ama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jomo Karuta
are Japanese playing cards. Playing cards were introduced to Japan by Portuguese traders during the mid-16th century. These early decks were used for trick-taking games. The earliest indigenous ''karuta'' was invented in the town of Miike in Chikugo Province at around the end of the 16th century. The Miike karuta Memorial Hall located in Ōmuta, Fukuoka, is the only municipal museum in Japan dedicated specifically to the history of ''karuta''. ''Karuta'' packs are classified into two groups, those that are descended from Portuguese-suited playing cards and those from '' e-awase''. ''E-awase'' originally derived from '' kai-awase'', which was played with shells but were converted to card format during the early 17th century. The basic idea of any ''e-awase karuta'' game is to be able to quickly determine which card out of an array of cards is required and then to grab the card before it is grabbed by an opponent. It is often played by children at elementary school and junio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tochigi Prefecture
is a landlocked Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Kantō region of Honshu. Tochigi Prefecture has a population of 1,897,649 (1 June 2023) and has a geographic area of 6,408 Square kilometre, km2 (2,474 Square mile, sq mi). Tochigi Prefecture borders Fukushima Prefecture to the north, Gunma Prefecture to the west, Saitama Prefecture to the south, and Ibaraki Prefecture to the southeast. Utsunomiya is the capital and largest city of Tochigi Prefecture, with other major cities including Oyama, Tochigi, Oyama, Tochigi, Tochigi, Tochigi, and Ashikaga, Tochigi, Ashikaga. Tochigi Prefecture is one of only eight landlocked prefectures and its mountainous northern region is a popular tourist region in Japan. The Nasu District, Tochigi, Nasu area is known for its onsens, local sake, and Skiing, ski resorts, the villa of the Imperial House of Japan, Imperial Family, and the station of the Shinkansen railway line. The city of Nikkō, Tochigi, Nikkō, with its ancien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shizuoka Prefecture
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Chūbu region of Honshu. Shizuoka Prefecture has a population of 3,555,818 and has a geographic area of . Shizuoka Prefecture borders Kanagawa Prefecture to the east, Yamanashi Prefecture to the northeast, Nagano Prefecture to the north, and Aichi Prefecture to the west. Shizuoka (city), Shizuoka is the capital and Hamamatsu is the largest city in Shizuoka Prefecture, with other major cities including Fuji, Shizuoka, Fuji, Numazu, and Iwata, Shizuoka, Iwata. Shizuoka Prefecture is located on Japan's Pacific Ocean coast and features Suruga Bay formed by the Izu Peninsula, and Lake Hamana which is considered to be one of Japan's largest lakes. Mount Fuji, the tallest volcano in Japan and cultural icon of the country, is partially located in Shizuoka Prefecture on the border with Yamanashi Prefecture. Shizuoka Prefecture has a significant Motor vehicle, motoring heritage as the founding location of Honda, Suzuki Motor C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
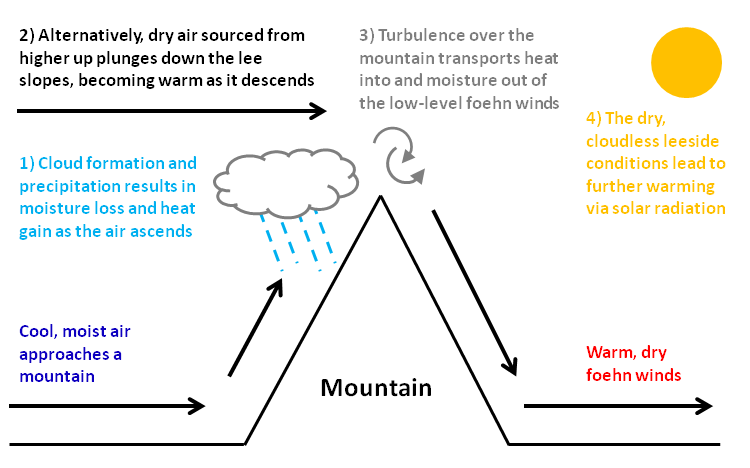
Foehn Wind
A Foehn, or Föhn (, , , ), is a type of dry, relatively warm downslope wind in the lee of a mountain range. It is a rain shadow wind that results from the subsequent adiabatic warming of air that has dropped most of its moisture on windward slopes (see orographic lift). As a consequence of the different adiabatic lapse rates of moist and dry air, the air on the leeward slopes becomes warmer than equivalent elevations on the windward slopes. Foehn winds can raise temperatures by as much as in just a matter of hours. Switzerland, southern Germany, and Austria have a warmer climate due to the Foehn, as moist winds off the Mediterranean Sea blow over the Alps. Etymology The name ''Foehn'' (, ) arose in the Alpine region. Originating from Latin , a mild west wind of which Favonius was the Roman personification and probably transmitted by or just , the term was adopted as . In the Southern Alps, the phenomenon is known as but also and in Serbo-Croatian and Slovene. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ōta, Gunma
is a city located in Gunma Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 224,358 in 109,541 households, and a population density of 1300 persons per km2. The total area of the city is . Geography Ōta is located in the extreme southeastern portion of Gunma Prefecture in the northern Kantō Plains, bordered by Tochigi Prefecture to the east and Saitama Prefecture to the south. The city is located northwest of Tokyo between the Tone and Watarase rivers. It is located about 80 kilometers northwest of central Tokyo, about 30 kilometers east of the prefectural capital at Maebashi, about 40 kilometers east of Takasaki. The elevation of the city ranges from 30–40 meters in lowland in the south, southwest, northeast, and east, to 40–70 meters in the northwest. Surrounding municipalities Gunma Prefecture * Isesaki * Kiryū * Midori * Ōizumi * Ōra Tochigi Prefecture * Ashikaga Saitama Prefecture * Fukaya * Kumagaya Climate Ōta has a Humid continental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashikaga, Tochigi
is a Cities of Japan, city located in Tochigi Prefecture of Honshu, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 140,036, in 62,123 households and a population density of 788 persons per km2. The total area of the city is . Geography Ashikaga is located in the northern Kanto plain in the far southwestern corner of Tochigi Prefecture, bordering on Gunma Prefecture to the north, west and south. The Watarase River flows through the center of the city. It is located approximately 80 km north of Tokyo. Surrounding municipalities Gunma Prefecture * Kiryū, Gunma, Kiryū * Ōra, Gunma, Ōra * Ōta, Gunma, Ōta * Tatebayashi, Gunma, Tatebayashi Tochigi Prefecture * Sano, Tochigi, Sano Climate Ashikaga has a Humid continental climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') characterized by warm summers. The average annual temperature in Ashikaga is 14.2 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1280 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winds
Wind is the natural movement of atmosphere of Earth, air or other gases relative to a planetary surface, planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hours, to global winds resulting from the difference in absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption of solar energy between the climate zones on Earth. The study of wind is called anemology. The two main causes of large-scale atmospheric circulation are the differential heating between the equator and the poles, and the rotation of the planet (Coriolis effect). Within the tropics and subtropics, thermal low circulations over terrain and high plateaus can drive monsoon circulations. In coastal areas the sea breeze/land breeze cycle can define local winds; in areas that have variable terrain, mountain and valley breezes can prevail. Winds are commonly classified by their scale (spatial), spatial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |