|
Kalybe (temple)
A kalybe (; ) is a type of temple found in the eastern Roman Empire dating from the 1st century and after. They were intended to serve as a "public facade or stage-setting, solely for the display of statuary." "[T]hey were essentially stage-sets for ritual enacted ''in front'' of them." The kalybe has been associated with the Roman imperial cult. The first kalybe to be identified as a distinct type was in Umm Iz-Zetun (or Zetum),For one modern spelling of the toponym. described by Eugène-Melchior de Vogüé in 1867. Together with the temple he found two Greek inscriptions describing the structure as a "kalybe." Other than these, the only occurrence of the term is in a lexicon of Hesychius of Alexandria from the 5th century; since that time more than seven similar temples have been identified in Roman Syria. In addition to Umm Iz-Zetum these include Shaqqa (''Saccaea''), Il-Haiyat, Shahba (''Philippopolis'') (built around 245 by the Emperor Philip the Arab), Qanawat (''Kanatha'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalybe Umm Iz Zetum
Calybe (Ancient Greek: Καλυβη means "rustic hut") may refer to the two distinct characters from Greek mythology: * Calybe, a nymph who was a wife of the Trojan king Laomedon and the mother of Bucolion. * Calybe, one of the follower of Dionysus In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, myth, Dionysus (; ) is the god of wine-making, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, festivity, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, and theatre. He was also known as Bacchus ( or ; ... in the India, Indian War.Nonnus, 29.270 Notes References * Bibliotheca (Pseudo-Apollodorus), (Pseudo-)Apollodorus, ''The Library'', with an English translation by Sir James George Frazer (1921). 2 volumes. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press; London: William Heinemann Ltd. . *English translationavailable at the Perseus Digital Library. *Greek textavailable from the same website. * *English translationavailable at the Topos Text Project. *Greek text available at the Perseus Dig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
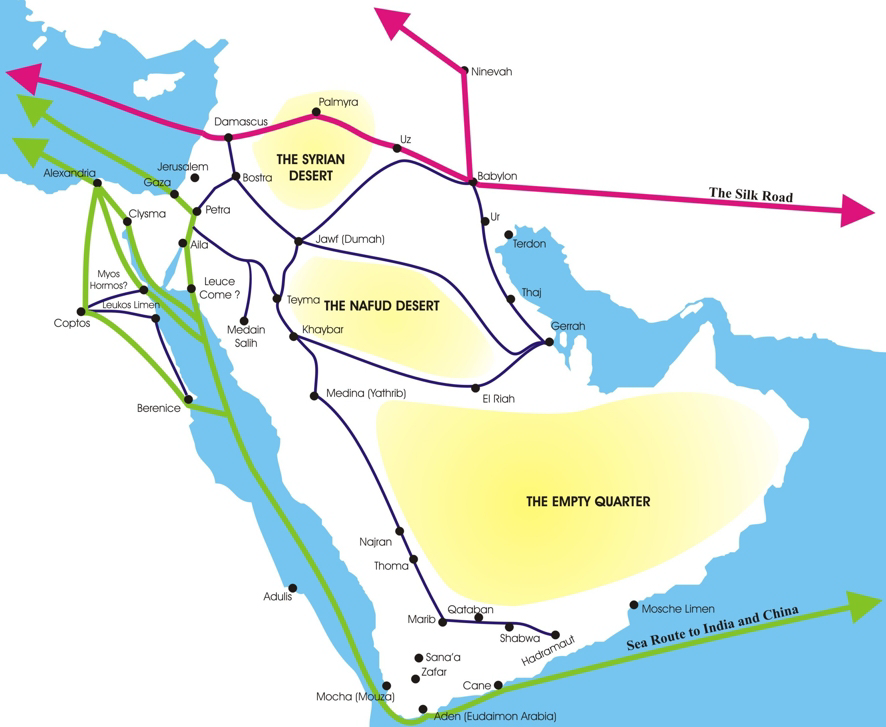
Bosra
Bosra (), formerly Bostra () and officially called Busra al-Sham (), is a town in southern Syria, administratively belonging to the Daraa District of the Daraa Governorate and geographically part of the Hauran region. Bosra is an ancient city mentioned in 14th century BC Egyptian sources. A key Nabatean city, it became the prosperous provincial capital of the Roman province of Arabia Petraea following the dissolvement of the Nabatean kingdom. With the advent of Christianity, Bostra flourished as a Metropolitan Archbishopric, under the jurisdiction of Eastern Orthodox Patriarchate of Antioch and All the East. It also became a Latin Catholic titular see and the episcopal see of a Melkite Catholic Archeparchy. Throughout its history under various Muslim rulers, the city maintained its strategic importance as Syria's southern gateway. It attracted attention from Damascus' rulers and was governed by various lords, serving as a hub for Islamic learning and endowments. However, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Roman Buildings And Structures
Ancient history is a time period from the History of writing, beginning of writing and recorded human history through late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the development of Sumerian language, Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500, ending with the Early Muslim conquests, expansion of Islam in late antiquity. The three-age system periodises ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages vary between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was Exponential growth, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
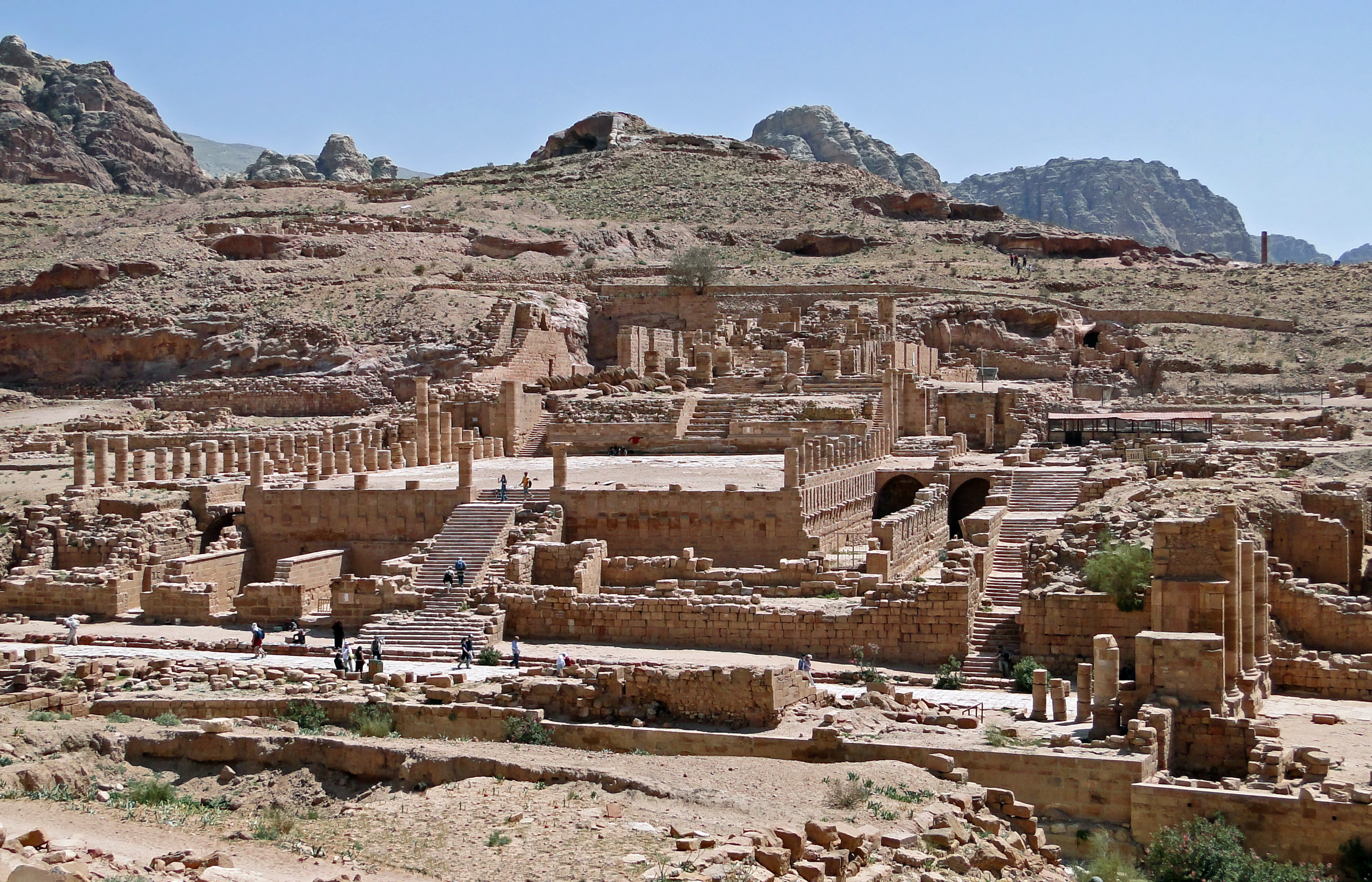
Petra
Petra (; "Rock"), originally known to its inhabitants as Raqmu (Nabataean Aramaic, Nabataean: or , *''Raqēmō''), is an ancient city and archaeological site in southern Jordan. Famous for its rock-cut architecture and water conduit systems, Petra is also called the "Rose City" because of the colour of the sandstone from which it is carved. The city is one of the New 7 Wonders of the World and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The area around Petra has been inhabited from as early as 7000 BC, and was settled by the Nabataeans, a nomadic Arab people, in the 4th century BC. Petra would later become the capital city of the Nabataean Kingdom in the second century BC. The Nabataeans invested in Petra's proximity to the incense trade routes by establishing it as a major regional trading hub, which gained them considerable revenue. Unlike their enemies, the Nabataeans were accustomed to living in the barren deserts and thus were able to defend their kingdom. They were particularly sk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabbel II Soter
Rabbel II Soter ( Nabataean Aramaic: ''Rabʾēl dī ʾaḥyēy wa-šēzīb ʿammeh'', "Rabbel, who gave life and deliverance to his people") was the last ruler of the Nabataean Kingdom, ruling from 70 to 106. His name as transcribed in Arabic is '. After the death of his father, Malichus II, Rabbel still a child, ascended to the throne. His mother, Shaqilath II, assumed the regency of the Nabataean Kingdom, during the minority of her son Rabel II in 70-76 AD. His sister Gamilath became queen of the Nabataeans. Rabbel gave himself the Greek title " Soter",Taylor (2001), pp.73-74 meaning "Savior". He reigned with his first wife Queen Gamilath and his second wife Queen Hagaru. Gamilat was a queen in 76–102 AD and Hagru was a queen in 102–106. After his death in 106, the Roman emperor Trajan Trajan ( ; born Marcus Ulpius Traianus, 18 September 53) was a Roman emperor from AD 98 to 117, remembered as the second of the Five Good Emperors of the Nerva–Anto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabataean Kingdom
The Nabataean Kingdom (Nabataean Aramaic: 𐢕𐢃𐢋𐢈 ''Nabāṭū''), also named Nabatea () was a political state of the Nabataeans during classical antiquity. The Nabataean Kingdom controlled many of the trade routes of the region, amassing large wealth and drawing the envy of its neighbors. It stretched south along the Tihamah into the Hejaz, up as far north as Damascus, which it controlled for a short period (85–71 BC). Nabataea remained an independent political entity from the mid-3rd century BC until it was annexed in AD 106 by the Roman Empire, which renamed it to Arabia Petraea. History Nabataeans The Nabataeans were one among several formerly Bedouin, nomadic Arab tribes that roamed (later settled) the Arabian Desert and moved with their herds to wherever they could find pasture and water. They became familiar with their area as seasons passed, and they struggled to survive during bad years when seasonal rainfall diminished. The origin of the specific tribe of Arab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabataean Architecture
Nabatean architecture (Arabic: اَلْعِمَارَةُ النَّبَطِيَّةُ; al-ʿimarah al-nabatiyyah) refers to the building traditions of the Nabateans ( /ˌnæbəˈtiːənz/; Nabataean Aramaic: 𐢕𐢃𐢋𐢈 ''Nabāṭū''; Arabic: ٱلْأَنْبَاط ''al-ʾAnbāṭ''; compare Akkadian: 𒈾𒁀𒌅 ''Nabātu''; Ancient Greek: Ναβαταῖος; Latin: ''Nabataeus''), an ancient Arab people who inhabited northern Arabia and the southern Levant. Their settlements—most prominently the assumed capital city of Raqmu (present-day Petra, Jordan)—gave the name ''Nabatene'' (Ancient Greek: Ναβατηνή, ''Nabatēnḗ'') to the Arabian borderland that stretched from the Euphrates to the Red Sea. Their architectural style is notable for its temples and tombs, most famously the ones found in Petra. The style appears to be a mix of Mesopotamian, Phoenician, Hellenistic, and South Arabian influences modified to suit the Arab architectural taste. Petra, the ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippos, Israel
Hippos () or Sussita (Aramaic, ) is an ancient city and archaeological site located on a hill 2 km east of the Sea of Galilee, attached by a topographical saddle to the western slopes of the Golan Heights. Hippos was a Hellenistic city in the northern Jordan Valley, and a long-time member of the Decapolis, a group of ten cities more closely tied to the Greco-Roman culture than to the local Semitic-speaking population. Later, Hippos became a predominantly Christian city, which declined towards the end of the Byzantine period and throughout the Early Muslim period, and was abandoned after the 749 earthquake. Geography Hippos was built on a flat-topped foothill east of and above the Sea of Galilee, above sea level, near Ein Gev. Besides the fortified city itself, Hippos had two harbor on the Sea of Galilee and a large area of the surrounding hinterlandHippos' Territorium. Etymology The city was founded in the mid-second century BCE as ''Antioch of Hippos'' () Hippos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amman
Amman ( , ; , ) is the capital and the largest city of Jordan, and the country's economic, political, and cultural center. With a population of four million as of 2021, Amman is Jordan's primate city and is the largest city in the Levant region, the fifth-largest city in the Arab world, and the tenth-largest metropolitan area in the Middle East. The earliest evidence of settlement in Amman dates to the 8th millennium BC in 'Ain Ghazal, home to the world's oldest statues of the human form. During the Iron Age, the city was known as ''Rabat Aman'', the capital of the Ammonite Kingdom. In the 3rd century BC, the city was renamed ''Philadelphia'' and became one of the ten Greco-Roman cities of the Decapolis. Later, in the 7th century AD, the Rashidun Caliphate renamed the city Amman. Throughout most of the Islamic era, the city alternated between periods of devastation and periods of relative prosperity. Amman was largely abandoned during the Ottoman period from the 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qanawat
Qanawat () is a village in Syria, located 7 km north-east of al-Suwayda. It stands at an elevation of about 1,200 m, near a river and surrounded by woods. Its inhabitants are entirely from the Druze community. According to the Central Bureau of Statistics (Syria), Syria Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS), Qanawat had a population of 8,324 in the 2004 census. History Qanawat is one of the earliest cities in the Bashan and Hauran areas. It is probably evidenced in the Hebrew Bible as Kenath (Hebrew: קְנָת, , ). Possible earlier evidence, is from Ancient Egyptian documents like the execration texts (second group) of the 20th-19th century BC, and the Amarna letters of the 14th century BC (as Qanu, in EA 204). Hellenistic and Roman history The ancient Hellenistic-Roman city of Canatha (also Kanatha, Κάναθα in Ancient Greek), is mentioned for the first time in the reign of Herod the Great (1st century BC), when Nabatean Arab forces defeated a Jewish army. It r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a place of worship, a building used for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. By convention, the specially built places of worship of some religions are commonly called "temples" in English, while those of other religions are not, even though they fulfill very similar functions. The religions for which the terms are used include the great majority of ancient religions that are now extinct, such as the Ancient Egyptian religion and the Ancient Greek religion. Among religions still active: Hinduism (whose temples are called Mandir or Kovil), Buddhism (whose temples are called Vihar), Sikhism (whose temples are called gurudwara), Jainism (whose temples are sometimes called derasar), Zoroastrianism (whose temples are sometimes called Agiary), the Baháʼí Faith (which are often simply referred to as Baháʼí House of Worship), Taoism (which are sometimes called Daoguan), Shinto (which are often called Jinja), C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip The Arab
Philip I (; – September 249), commonly known as Philip the Arab, was Roman emperor from 244 to 249. After the death of Gordian III in February 244, Philip, who had been Praetorian prefect, rose to power. He quickly negotiated peace with the Sasanian Empire and returned to Rome to be confirmed by the Roman Senate, Senate. According to many historians, he was possibly the first Christian Roman Emperor. Although his reign lasted only five years, it marks an unusually stable period in a century that is otherwise known for having been turbulent. Near the end of his rule, Philip commemorated Ab urbe condita#Use, Rome's first millennium. In September 249 he was killed during or shortly after the Battle of Verona (249), Battle of Verona against the usurper Decius, Trajan Decius, who was subsequently recognized by the Senate as his successor. Born in modern-day Shahba#Roman history, Shahba, Syria, in what was then Arabia Petraea, Philip's ethnicity was most likely Arabs, Arab. While h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |