|
Joystick
A joystick, sometimes called a flight stick, is an input device consisting of a stick that pivots on a base and reports its angle or direction to the device it is controlling. Also known as the control column, it is the principal control device in the cockpit of many civilian and military aircraft, either as a centre stick or side-stick. It has various switches to control functions of the aircraft controlled by the Pilot and First Officer of the flight. Joysticks are often used to control video games, and usually have push-buttons whose state can be read by the computer. A popular variation of the joystick used on modern video game consoles is the analog stick. Joysticks are also used for controlling machines such as cranes, trucks, underwater unmanned vehicles, wheelchairs, surveillance cameras, and Zero-turn mower, zero turning radius lawn mowers. Miniature finger-operated joysticks have been adopted as input devices for smaller electronic equipment such as mobile phones. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Stick
An analog stick (analogue stick in British English), also known as a control stick, thumbstick or joystick, is an input method designed for video games that translates thumb movement into directional control. It consists of a protruding stick mounted on a pivot, with movement registered through continuous electrical signals rather than discrete switches, allowing for greater nuance than traditional digital inputs. Unlike D-pads, which rely on fixed electrical contacts, analog sticks use potentiometers to measure their position across a full range of motion. Many models allow the stick to be pressed down like a button, allowing users to execute commands without removing their thumb from the stick. Since its introduction, the analog stick has largely replaced the D-pad as the primary directional input in modern game controllers. Usage in video games The initial prevalence of analog sticks was as peripherals for flight simulator games, to better reflect the subtleties of control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Game Console
A video game console is an electronic device that Input/output, outputs a video signal or image to display a video game that can typically be played with a game controller. These may be home video game console, home consoles, which are generally placed in a permanent location connected to a television or other display devices and controlled with a separate game controller, or handheld game console, handheld consoles, which include their own display unit and controller functions built into the unit and which can be played anywhere. Hybrid consoles combine elements of both home and handheld consoles. Video game consoles are a specialized form of home computer geared towards video game playing, designed with affordability and accessibility to the general public in mind, but lacking in raw computing power and customization. Simplicity is achieved in part through the use of game cartridges or other simplified methods of distribution, easing the effort of launching a game. However, thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Input Device
In computing, an input device is a piece of equipment used to provide data and control signals to an information processing system, such as a computer or information appliance. Examples of input devices include keyboards, computer mice, scanners, cameras, joysticks, and microphones. Input devices can be categorized based on: * modality of output (e.g., mechanical motion, audio, visual, etc.) * whether the output is discrete (e.g., pressing of key) or continuous (e.g., a mouse's position, though digitized into a discrete quantity, is fast enough to be considered continuous) * the number of degrees of freedom involved (e.g., two-dimensional traditional mice, or three-dimensional navigators designed for CAD applications) Keyboard A keyboard is a human interface device which is represented as a matrix of buttons. Each button, or key, can be used to either input an alphanumeric character to a computer, or to call upon a particular function of the computer. It acts as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wasserfall Missile
The ("Waterfall remote-controlled anti-aircraft rocket") was a German guided supersonic surface-to-air missile project of World War II. Development was not completed before the end of the war and it was not used operationally. The system was based on many of the technologies developed for the V-2 rocket program, including the rocket itself, which was essentially a much scaled-down version of the V-2 airframe. Significant additional development was required, including design and test of an effective guidance system to allow interception of an air target, adoption of hypergolic fuels to allow the missile to stand ready for launch for days or weeks, and the development of a reliable Proximity Fuse. :234 Technical characteristics was essentially an anti-aircraft development of the V-2 rocket, sharing the same general layout and shaping. Since the missile had to fly only to the altitudes of the attacking bombers, and needed a far smaller warhead to destroy these, it could be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Blériot
Louis Charles Joseph Blériot ( , also , ; 1 July 1872 – 1 August 1936) was a French aviator, inventor, and engineer. He developed the first practical headlamp for cars and established a profitable business manufacturing them, using much of the money he made to finance his attempts to build a successful aircraft. Blériot was the first to use the combination of hand-operated joystick and foot-operated rudder control as used to the present day to operate the aircraft flight control system, aircraft control surfaces. Blériot was also the first to make a working, powered, piloted monoplane.Gibbs-Smith 1953, p. 239 In 1909 he became world-famous for making the first aeroplane flight across the English Channel, winning the prize of £1,000 offered by the ''Daily Mail'' newspaper. He was the founder of Blériot Aéronautique, a successful aircraft manufacturing company. Early years Born at No.17h rue de l'Arbre à Poires (now rue Sadi-Carnot) in Cambrai, Louis was the first of five ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aileron
An aileron (French for "little wing" or "fin") is a hinged flight control surface usually forming part of the trailing edge of each wing of a fixed-wing aircraft. Ailerons are used in pairs to control the aircraft in roll (or movement around the aircraft's longitudinal axis), which normally results in a change in flight path due to the tilting of the lift vector. Movement around this axis is called rolling or banking. Considerable controversy exists over credit for the invention of the aileron. The Wright brothers and Glenn Curtiss fought a years-long legal battle over the Wright patent of 1906, which described a method of wing-warping to achieve lateral control. The brothers prevailed in several court decisions which found that Curtiss's use of ailerons violated the Wright patent. Ultimately, the First World War compelled the U.S. Government to legislate a legal resolution. A much earlier aileron concept was patented in 1868 by British scientist Matthew Piers Watt Boul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azon
AZON (or Azon), from "azimuth only", was one of the world's first guided weapons, deployed by the Allies and contemporary with the German Fritz X. Officially designated VB-1 ("Vertical Bomb 1"), it was invented by Major Henry J. Rand and Thomas J. O'Donnell during the latter stages of World War II as the answer to the difficult problem of destroying the narrow wooden bridges that supported much of the Burma Railway. AZON was essentially a general-purpose AN-M65 bomb with a quadrilateral 4-fin style radio controlled tail fin design as part of a "tail package" to give the desired guidance capability, allowing adjustment of the vertical trajectory in the yaw axis, giving the Azon unit a lateral steering capability (meaning it could only steer left and right, and could not alter its pitch or rate of fall). This lack of any pitch control meant that the bombardier still had to accurately release it with a bombsight to ensure it could not fall short of or beyond the target. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Esnault-Pelterie
Robert Albert Charles Esnault-Pelterie (8 November 1881 – 6 December 1957) was a French aircraft designer and spaceflight theorist. He is referred to as being one of the founders of modern rocketry and astronautics, along with the Russian Konstantin Tsiolkovsky, the Germans Hermann Oberth, Wernher von Braun and the American Robert H. Goddard. Biography He was born on 8 November 1881 in Paris to a textile industrialist. He was educated at the ''Faculté des Sciences'', studying engineering at the University of Paris, Sorbonne. He served in World War I and was made an ''Officier de la Légion d'Honneur''. In November 1928, on board the ''SS Ile de France, Ile de France'' while sailing to New York City, he was married to Carmen Bernaldo de Quirós, the daughter of Don Antonio and Yvonne Cabarrus, and granddaughter of General Marquis of Santiago, Grandee of Spain, Head of the Military Household of Queen Isabella II of Spain, Isabella II. He died on 6 December 1957 in Nice, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Loraine
Robert Bilcliffe Loraine (14 January 1876 – 23 December 1935) was a successful London and Broadway British stage actor, actor-manager, and soldier who later enjoyed a side career as a pioneer aviator. Born in New Brighton, his father was Henry Loraine and mother Edith Kingsley (born Mary Ellen Bayliss). Robert made his first stage appearance in the English provinces in 1889, prior to serving in the Second Boer War. He introduced the George Bernard Shaw play '' Man and Superman'' to Broadway in 1905. Theatrical career Loraine was a versatile actor and was successful both in serious plays and in popular works of light entertainment. He was particularly associated with the works of George Bernard Shaw, taking over the role of John Tanner from Harley Granville Barker in the fourth run of '' Man and Superman'' at the Royal Court Theatre. He also won critical acclaim for performances in plays by William Shakespeare and August Strindberg. Aviation In 1909 Loraine took up the new t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
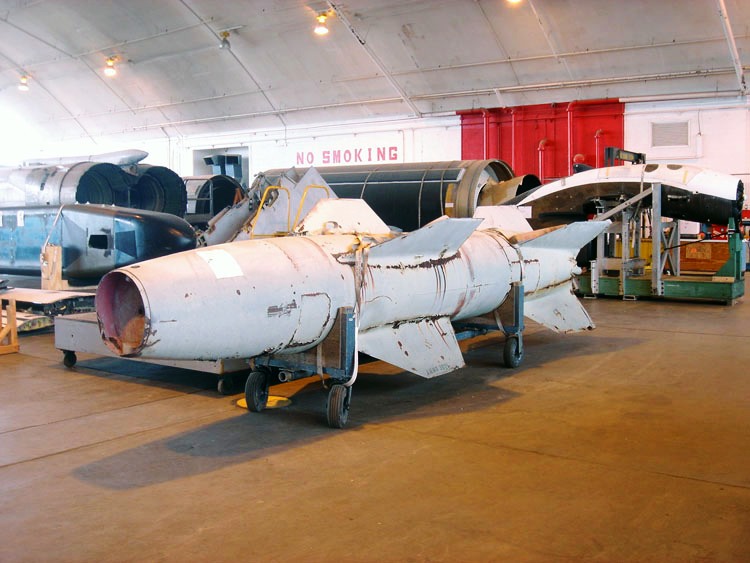
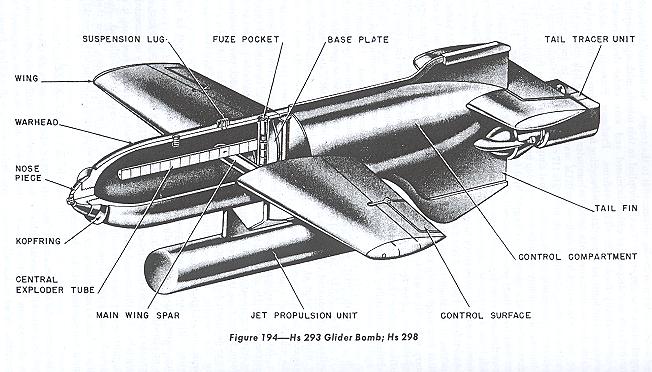
Henschel Hs 293
The Henschel Hs 293 was a World War II Nazi Germany, German Command guidance, radio-guided glide bomb. It is the first operational anti-shipping missile, first used unsuccessfully on 25 August 1943 and then with increasing success over the next year, damaging or sinking at least 25 ships. Allied efforts to jam the radio control link were increasingly successful despite German efforts to counter them. The weapon remained in use through 1944 when it was also used as an air-to-ground weapon to attack bridges to prevent the Allied breakout after D-Day, but proved almost useless in this role. Development The Hs 293 project started in 1940, based on the "Gustav Schwartz Propellerwerke" pure glide bomb designed in 1939. The Schwartz design did not have a terminal guidance system; instead, it used an autopilot to maintain a straight course. It was intended to be launched from a bomber at sufficient distance to keep the aircraft out of range of anti-aircraft artillery, anti-aircraft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cockpit
A cockpit or flight deck is the area, on the front part of an aircraft, spacecraft, or submersible, from which a pilot controls the vehicle. The cockpit of an aircraft contains flight instruments on an instrument panel, and the controls that enable the pilot to fly the aircraft. In most airliners, a door separates the cockpit from the aircraft cabin. After the September 11, 2001 attacks, all major airlines fortified their cockpits against access by hijackers. Etymology The word cockpit seems to have been used as a nautical term in the 17th century, without reference to cock fighting. It referred to an area in the rear of a ship where the cockswain's station was located, the cockswain being the pilot of a smaller "boat" that could be dispatched from the ship to board another ship or to bring people ashore. The word "cockswain" in turn derives from the old English terms for "boat-servant" (''coque'' is the French word for "shell"; and ''swain'' was old English for boy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centre Stick
A centre stick (or center stick in the United States), or simply control stick, is an aircraft cockpit arrangement where the control column (or joystick) is located in the center of the cockpit either between the pilot's legs or between the pilots' positions. Since the throttle controls are typically located to the left of the pilot, the right hand is used for the stick, although left-hand or both-hands operation is possible if required.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', page 132. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. . The centre stick is a part of an aircraft's flight control system and is typically linked to its ailerons and elevators, or alternatively to its elevons, by control rods or control cables on basic aircraft. On heavier, faster, more advanced aircraft the centre stick may also control power-assist modules. Modern aircraft centre sticks are also usually equipped with a number of electrical control switches within easy finger reach, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |