|
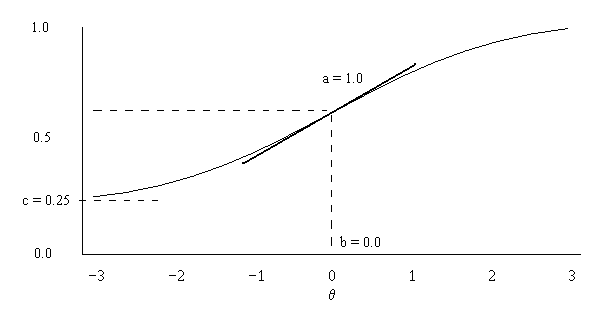
Item Response Function
In psychometrics, item response theory (IRT, also known as latent trait theory, strong true score theory, or modern mental test theory) is a paradigm for the design, analysis, and scoring of tests, questionnaires, and similar instruments measuring abilities, attitudes, or other variables. It is a theory of testing based on the relationship between individuals' performances on a test item and the test takers' levels of performance on an overall measure of the ability that item was designed to measure. Several different statistical models are used to represent both item and test taker characteristics. Unlike simpler alternatives for creating scales and evaluating questionnaire responses, it does not assume that each item is equally difficult. This distinguishes IRT from, for instance, Likert scaling, in which ''"''All items are assumed to be replications of each other or in other words items are considered to be parallel instruments". By contrast, item response theory treats the diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychometrics
Psychometrics is a field of study within psychology concerned with the theory and technique of measurement. Psychometrics generally covers specialized fields within psychology and education devoted to testing, measurement, assessment, and related activities. Psychometrics is concerned with the objective measurement of latent constructs that cannot be directly observed. Examples of latent constructs include intelligence, introversion, mental disorders, and educational achievement. The levels of individuals on nonobservable latent variables are inferred through mathematical modeling based on what is observed from individuals' responses to items on tests and scales. Practitioners are described as psychometricians, although not all who engage in psychometric research go by this title. Psychometricians usually possess specific qualifications, such as degrees or certifications, and most are psychologists with advanced graduate training in psychometrics and measurement theory. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Function
In mathematics, a function from a set (mathematics), set to a set assigns to each element of exactly one element of .; the words ''map'', ''mapping'', ''transformation'', ''correspondence'', and ''operator'' are sometimes used synonymously. The set is called the Domain of a function, domain of the function and the set is called the codomain of the function. Functions were originally the idealization of how a varying quantity depends on another quantity. For example, the position of a planet is a ''function'' of time. History of the function concept, Historically, the concept was elaborated with the infinitesimal calculus at the end of the 17th century, and, until the 19th century, the functions that were considered were differentiable function, differentiable (that is, they had a high degree of regularity). The concept of a function was formalized at the end of the 19th century in terms of set theory, and this greatly increased the possible applications of the concept. A f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PISA
Pisa ( ; ) is a city and ''comune'' (municipality) in Tuscany, Central Italy, straddling the Arno just before it empties into the Ligurian Sea. It is the capital city of the Province of Pisa. Although Pisa is known worldwide for the Leaning Tower of Pisa, the city contains more than twenty other historic churches, several medieval palaces, and bridges across the Arno. Much of the city's architecture was financed from its history as one of the Italian maritime republics. The city is also home to the University of Pisa, which has a history going back to the 12th century, the Scuola Normale Superiore di Pisa, founded by Napoleon in 1810, and its offshoot, the Sant'Anna School of Advanced Studies.Scuola Superiore Sant'Anna di Pisa Information statistics History ...
|
Margaret Wu
Margaret Wu is an Australian statistician and psychometrician who specialises in educational measurement. She is an honorary professor at the University of Melbourne. Early life Wu studied statistics at the University of Melbourne and graduated in 1972. She worked at Monash University as a research assistant from 1973 to 1975, where she taught herself to program. She worked with Watterson on the Watterson estimator, a means to determine the genetic diversity of a population. Research and career Wu joined CSIRO as a technical officer in 1977. She earned a graduate diploma in computer studies from the Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology in 1985. Wu became a high school teacher at Ivanhoe Girls' Grammar School, teaching Chinese and mathematics. She was appointed as a senior research fellow in the Australian Council of Educational Research Development (ACER) in 1992, where she was deputy director of Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA). Working with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Computer
A personal computer, commonly referred to as PC or computer, is a computer designed for individual use. It is typically used for tasks such as Word processor, word processing, web browser, internet browsing, email, multimedia playback, and PC game, gaming. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or technician. Unlike large, costly minicomputers and mainframes, time-sharing by many people at the same time is not used with personal computers. The term home computer has also been used, primarily in the late 1970s and 1980s. The advent of personal computers and the concurrent Digital Revolution have significantly affected the lives of people. Institutional or corporate computer owners in the 1960s had to write their own programs to do any useful work with computers. While personal computer users may develop their applications, usually these systems run commercial software, free-of-charge software ("freeware"), which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Andrich
David Andrich is an Australian academic and assessment specialist. He has made substantial contributions to quantitative social science including seminal work on the Polytomous Rasch model for measurement, which is used in the social sciences, in health and other areas. Andrich is currently a Winthrop Professor at the University of Western Australia, where he holds the Chapple Chair in Education. He was elected a Fellow of the Academy of Social Sciences of Australia in 1990 for contributions to measurement in the social sciences. Andrich also worked with Georg Rasch in Denmark and Australia. He is one of the most prominent advocates of Rasch's probabilistic measurement models. Biography Education David Andrich completed his BSc in mathematics and applied mathematics at the University of Western Australia. He briefly taught high school mathematics and worked in the curriculum branch of the Education Department of Western Australia, before being appointed to the Department of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benjamin Drake Wright
Benjamin Drake Wright (March 30, 1926 – October 25, 2015) was an American psychometrician. He is largely responsible for the widespread adoption of Georg Rasch's measurement principles and models.Rasch, G. (1988/1972, Summer). Review of the cooperation of Professor B. D. Wright, University of Chicago, and Professor G. Rasch, University of Copenhagen; letter of June 18, 1972. Rasch Measurement Transactions, 2(2), 1 In the wake of what Rasch referred to as Wright's “almost unbelievable activity in this field” in the period from 1960 to 1972, Rasch's ideas entered the mainstream in high-stakes testing, professional certification and licensure examinations, and in research employing tests, and surveys and assessments across a range of fields. Wright's seminal contributions to measurement continued until 2001, and included articulation of philosophical principles, production of practical results and applications, software development, development of estimation methods and model ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Lazarsfeld
Paul Felix Lazarsfeld (February 13, 1901August 30, 1976) was an Austrian-American sociologist and mathematician. The founder of Columbia University's Bureau of Applied Social Research, he exerted influence over the techniques and the organization of social research. "It is not so much that he was an American sociologist," one colleague said of him after his death, "as it was that he determined what American sociology would be." Lazarsfeld said that his goal was "to produce Paul Lazarsfelds". He was a founding figure in 20th-century empirical sociology. Early life Lazarsfeld was born to Jewish parents in Vienna: his mother was the Adlerian therapist Sophie Lazarsfeld, and his father Robert was a lawyer. He attended the University of Vienna, eventually receiving a doctorate in mathematics (his doctoral dissertation dealt with mathematical aspects of Einstein's gravitational theory) in 1925. In the 1920s, he moved in the same circles as the Vienna Circle of philosophers, inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Rasch
Georg William Rasch () (21 September 1901 – 19 October 1980) was a Danish mathematician, statistician, and psychometrician, most famous for the development of a class of measurement models known as Rasch models. He studied with R.A. Fisher and also briefly with Ragnar Frisch, and was elected a member of the International Statistical Institute in 1948. In 1919, Rasch began studying mathematics at the University of Copenhagen. He completed a master's degree in 1925 and received a doctorate in science with thesis director Niels Erik Nørlund in 1930. Rasch married in 1928. Unable to find work as a mathematician in the 1930s, he turned to work as a statistical consultant. In this capacity, he worked on a range of problems, including problems of biological growth. Contributions to psychometrics Georg Rasch is best known for his contributions to psychometrics. His work in this field began when he used the Poisson distribution to model the number of errors made by students when re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederic M
Frederic may refer to: Places United States * Frederic, Wisconsin, a village in Polk County * Frederic Township, Michigan, a township in Crawford County ** Frederic, Michigan, an unincorporated community Other uses * Frederic (band), a Japanese rock band * Frederic (given name), a given name (including a list of people and characters with the name) * Hurricane Frederic, a hurricane that hit the U.S. Gulf Coast in 1979 * Trent Frederic, American ice hockey player See also * Frédéric * Frederick (other) * Fredrik Fredrik or Frederik is a masculine Germanic given name derived from the German name '' Friedrich'' or Friederich, from the Old High German ''fridu'' meaning "peace" and ''rîhhi'' meaning "ruler" or "power". It is the common form of Frederick in N ... * Fryderyk (other) {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Educational Testing Service
Educational Testing Service (ETS), founded in 1947, is the world's largest private educational testing and assessment organization. It is headquartered in Lawrence Township, Mercer County, New Jersey, Lawrence Township, New Jersey, but has a Princeton, New Jersey, Princeton address. ETS develops various standardized tests primarily in the United States for K–12 education, K–12 and higher education, and it also administers international tests including the TOEFL (Test of English as a Foreign Language), TOEIC (Test of English for International Communication), Graduate Record Examination (GRE) General and Subject Tests, and The Praxis test Series—in more than 180 countries, and at over 9,000 locations worldwide. Many of the assessments it develops are associated with entry to US tertiary education, tertiary (undergraduate) and quaternary education (graduate) institutions, but it also develops K–12 statewide assessments used for accountability testing in many states, inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymptote
In analytic geometry, an asymptote () of a curve is a line such that the distance between the curve and the line approaches zero as one or both of the ''x'' or ''y'' coordinates tends to infinity. In projective geometry and related contexts, an asymptote of a curve is a line which is tangent to the curve at a point at infinity. The word asymptote is derived from the Greek ἀσύμπτωτος (''asumptōtos'') which means "not falling together", from ἀ priv. + σύν "together" + πτωτ-ός "fallen". The term was introduced by Apollonius of Perga in his work on conic sections, but in contrast to its modern meaning, he used it to mean any line that does not intersect the given curve. There are three kinds of asymptotes: ''horizontal'', ''vertical'' and ''oblique''. For curves given by the graph of a function , horizontal asymptotes are horizontal lines that the graph of the function approaches as ''x'' tends to Vertical asymptotes are vertical lines near which the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |