|
Item Bank
An item bank or question bank is a repository of test items that belong to a testing program, as well as all information pertaining to those items. In most applications of testing and assessment, the items are of multiple choice format, but any format can be used. Items are pulled from the bank and assigned to test forms for publication either as a paper-and-pencil test or some form of e-assessment. Types of information An item bank will not only include the text of each item, but also extensive information regarding test development and psychometric characteristics of the items. Examples of such information include: * Item author * Date written * Item status (e.g., new, pilot, active, retired) * Angoff ratings * Correct answer * Item format * Classical test theory statistics * Item response theory statistics * Linkage to test blueprint * Item history (e.g., usage date(s) and reviews) * User-defined fields Item banking software Because an item bank is essentially a simple databa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Test Item
Questionnaire construction refers to the design of a questionnaire to gather statistically useful information about a given topic. When properly constructed and responsibly administered, questionnaires can provide valuable data about any given subject. Questionnaires Questionnaires are frequently used in quantitative marketing research and social research. They are a valuable method of collecting a wide range of information from a large number of individuals, often referred to as respondents. What is often referred to as "adequate questionnaire construction" is critical to the success of a survey. Inappropriate questions, incorrect ordering of questions, incorrect scaling, or a bad questionnaire format can make the survey results valueless, as they may not accurately reflect the views and opinions of the participants. Different methods can be useful for checking a questionnaire and making sure it is accurately capturing the intended information. Initial advice may include: * con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
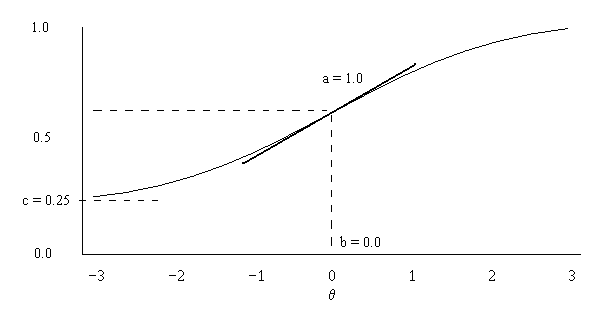
Item Information Function
In psychometrics, item response theory (IRT, also known as latent trait theory, strong true score theory, or modern mental test theory) is a paradigm for the design, analysis, and scoring of tests, questionnaires, and similar instruments measuring abilities, attitudes, or other variables. It is a theory of testing based on the relationship between individuals' performances on a test item and the test takers' levels of performance on an overall measure of the ability that item was designed to measure. Several different statistical models are used to represent both item and test taker characteristics. Unlike simpler alternatives for creating scales and evaluating questionnaire responses, it does not assume that each item is equally difficult. This distinguishes IRT from, for instance, Likert scaling, in which ''"''All items are assumed to be replications of each other or in other words items are considered to be parallel instruments". By contrast, item response theory treats the diffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
School Examinations
A school is the educational institution (and, in the case of in-person learning, the building) designed to provide learning environments for the teaching of students, usually under the direction of teachers. Most countries have systems of formal education, which is sometimes compulsory. In these systems, students progress through a series of schools that can be built and operated by both government and private organization. The names for these schools vary by country (discussed in the '' Regional terms'' section below) but generally include primary school for young children and secondary school for teenagers who have completed primary education. An institution where higher education is taught is commonly called a university college or university. In addition to these core schools, students in a given country may also attend schools before and after primary (elementary in the U.S.) and secondary (middle school in the U.S.) education. Kindergarten or preschool provide some s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Common University Entrance Test
The Common University Entrance Test (CUET), formerly Central Universities Common Entrance Test (CUCET) is a standardised test in India conducted by the National Testing Agency at various levels for admission to undergraduate and postgraduate programmes in Central Universities and other participating institutes. It is also accepted by number of other State Universities and Deemed universities in India. History CUCET was first conducted to admission for seven central universities for 1,500 seats in 41 undergraduate, postgraduate and integrated courses from 2010. The application form was filled up through ''CUCET-2010'' which held on 19 and 20 June 2010 in about 30 examination centers spread across the country. From its inception in 2010 till 2020, the CUCET was conducted by the Central University of Rajasthan for 12 Central Universities. The National Testing Agency took over the conduct of these exams in 2021. In 2024, as a part of National Education Policy 2020, CUET is introdu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Common Law Admission Test
The Common Law Admission Test (CLAT) is a centralized national-level entrance test for admissions to the 25 out of 27 National Law Universities (NLU) except NLU Delhi and NLU Meghalaya. CLAT was first introduced in 2008 as a centralized entrance examination for admission to the National Law Schools/Universities in India. NLU Delhi and NLU Meghalaya administer their own entrance exams, the All India Law Entrance Test (AILET) and the NLU Meg Undergraduate Admission Test (MEG UAT), respectively. Both AILET & MEG UAT are anticipated to be merged into CLAT in the coming years. A few private and self-financed law schools in India also use these scores for law admissions. Public sector undertakings in India like ONGC, Coal India, BHEL, the Steel Authority of India, Oil India, the Indian Army (for the recruitment of Judge Advocate General officers) use CLAT Post Graduation (CLAT PG) scores. The test is taken after the Higher Secondary Examination or the 12th grade for admissio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
National Eligibility Cum Entrance Test (Undergraduate)
The National Eligibility cum Entrance Test (Undergraduate) or NEET (UG), formerly known as the All India Pre-Medical Test (AIPMT), is an Indian nationwide entrance examination conducted by the National Testing Agency (NTA) for admission in undergraduate medical programs. Being a mandatory exam for admission in medical programs, it is the biggest exam in India in terms of number of applicants. Until 2012, the All India Pre-Medical Test (AIPMT) was conducted by the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE). In 2013, NEET-UG was introduced, conducted by CBSE, replacing AIPMT. However, due to legal challenges, NEET was temporarily replaced by AIPMT in both 2014 and 2015. In 2016, NEET was reintroduced and conducted by CBSE. From 2019 onwards, the National Testing Agency (NTA) has been responsible for conducting the NEET exam. After the enactment of NMC Act 2019 in September 2019, NEET-UG became the sole entrance test for admissions to medical colleges in India including the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Joint Entrance Examination
The Joint Entrance Examination (JEE) is an engineering entrance assessment conducted for admission to various engineering colleges in India. It comprises two different examinations: the JEE-Main and the JEE-Advanced. The Joint Seat Allocation Authority (JoSAA) conducts the joint admission process for a total of 23 Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs), 31 National Institutes of Technology (NITs), 25 Indian Institutes of Information Technology (IIITs) campuses and other Government Funded Technical Institutes (GFTIs) based on the rank obtained by a student in JEE-Main or JEE-Advanced, depending on the engineering college. There are some institutes, such as the Indian Institutes of Science Education and Research (IISERs), the Indian Institute of Petroleum and Energy (IIPE), the Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Petroleum Technology (RGIPT), the Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology (IIST), and the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), which use the score obtained in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pre-university Course
According to the International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED), basic education comprises the two stages primary education and lower secondary education. Universal basic education Basic education featured heavily in the 1997 ISCED document, but the term was not included in the glossary. Each country interpreted the term in different ways, and leading up to the 2011 revision, a discussion paper was issued to seek clarification. In most countries, ISCED 1 corresponds to the nationally designated primary education, and basic education includes that and also ISCED 2 lower secondary education (the lower level of secondary school). In other countries, where there is no break between primary and lower secondary education, “basic education” covers the entire compulsory school period. For statistical reasons, ISCED 1 is then considered to be the first six years of schooling. Universal basic education is regarded as a priority for developing countries and is the focus o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Council For The Indian School Certificate Examinations
The Council for the Indian School Certificate Examinations (CISCE) is a non-governmental privately held national-level board of school education in India that conducts the Indian Certificate of Secondary Education (ICSE) Examination for Class X and the Indian School Certificate (ISC) for Class XII. History It was established in 1958. Over 2750 schools in India and abroad are affiliated to the CISCE. It is also recognized as a 'Non-Governmental National Board of Secondary Education'. CISCE conducts ICSE exam for Class 10 and ISC exam for Class 12. Derozio Award The Derozio Award is an annual prize awarded to the top Indian educationists by the Council for the Indian School Certificate Examinations. It was instituted in 1999 in memory of Henry Louis Vivian Derozio, a poet and educator from West Bengal. It is the highest award conferred by the council for contributions in the field of education. Curriculum The ISCE and ISC syllabi intend to incorporate comprehensive a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Central Board Of Secondary Education
The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) is a national-level board of education in India for public and private schools, controlled and managed by the Government of India. Established in 1929 by a resolution of the government, the Board was an experiment towards inter-state integration and cooperation in the sphere of secondary education. There are more than 27,000 schools in India and 240 schools in 28 foreign countries affiliated with the CBSE. All schools affiliated with CBSE follow the NCERT curriculum, especially those in classes 9 to 12. The current Chairperson of CBSE is Rahul Singh, IAS. The constitution of the Board was amended in 1952 to give its present name, the Central Board of Secondary Education. The Board was reconstituted on 1 July 1962 so as to make its services available to students and various educational institutions in the entire country. History The first education board to be set up in India was the Uttar Pradesh Board of High School and Interme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
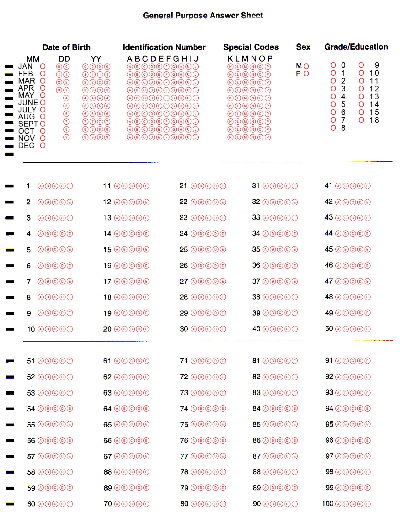
Bubble Sheet
Optical mark recognition (OMR) collects data from people by identifying markings on a paper. OMR enables the hourly processing of hundreds or even thousands of documents. A common application of this technology is used in exams, where students mark cells as their answers. This allows for very fast automated grading of exam sheets. Background Many OMR devices have a scanner that shines a light onto a form. The device then looks at the contrasting reflectivity of the light at certain positions on the form. It will detect the black marks because they reflect less light than the blank areas on the form. Some OMR devices use forms that are printed on transoptic paper. The device can then measure the amount of light that passes through the paper. It will pick up any black marks on either side of the paper because they reduce the amount of light passing through. In contrast to the dedicated OMR device, desktop OMR software allows a user to create their own forms in a word process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |