|
Isotope Perfusion Imaging
Perfusion is the passage of fluid through the lymphatic system or blood vessels to an organ or a tissue. The practice of perfusion scanning is the process by which this perfusion can be observed, recorded and quantified. The term perfusion scanning encompasses a wide range of medical imaging modalities.http://www.webmd.com/heart-disease/cardiac-perfusion-scan#1 www.webmd.com/ Applications With the ability to ascertain data on the blood flow to vital organs such as the heart and the brain, doctors are able to make quicker and more accurate choices on treatment for patients. Nuclear medicine has been leading perfusion scanning for some time, although the modality has certain pitfalls. It is often dubbed 'unclear medicine' as the scans produced may appear to the untrained eye as just fluffy and irregular patterns. More recent developments in CT and MRI have meant clearer images and solid data, such as graphs depicting blood flow, and blood volume charted over a fixed period of time. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfusion
Perfusion is the passage of fluid through the circulatory system or lymphatic system to an organ (anatomy), organ or a tissue (biology), tissue, usually referring to the delivery of blood to a capillary bed in tissue. Perfusion may also refer to fixation via perfusion, used in histological studies. Perfusion is measured as the rate at which blood is delivered to tissue, or volume of blood per unit time (blood volumetric flow rate, flow) per unit tissue mass. The SI unit is m3/(s·kg), although for human organs perfusion is typically reported in ml/min/g. The word is derived from the French verb ''perfuser'', meaning to "pour over or through". All animal tissues require an adequate blood supply for health and life. Poor perfusion (malperfusion), that is, ischemia, causes health problems, as seen in cardiovascular disease, including coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral artery disease, and many other conditions. Tests verifying that adequate perfusion exists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contrast Agent
A contrast agent (or contrast medium) is a substance used to increase the contrast of structures or fluids within the body in medical imaging. Contrast agents absorb or alter external electromagnetism or ultrasound, which is different from radiopharmaceuticals, which emit radiation themselves. In X-ray imaging, contrast agents enhance the radiodensity in a target tissue or structure. In magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), contrast agents shorten (or in some instances increase) the relaxation times of nuclei within body tissues in order to alter the contrast in the image. Contrast agents are commonly used to improve the visibility of blood vessels and the gastrointestinal tract. The types of contrast agent are classified according to their intended imaging modalities. Radiocontrast media For radiography, which is based on X-rays, iodine and barium are the most common types of contrast agent. Various sorts of iodinated contrast agents exist, with variations occurring between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine
Adenosine (symbol A) is an organic compound that occurs widely in nature in the form of diverse derivatives. The molecule consists of an adenine attached to a ribose via a β-N9- glycosidic bond. Adenosine is one of the four nucleoside building blocks of RNA (and its derivative deoxyadenosine is a building block of DNA), which are essential for all life on Earth. Its derivatives include the energy carriers adenosine mono-, di-, and triphosphate, also known as AMP/ADP/ATP. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) is pervasive in signal transduction. Adenosine is used as an intravenous medication for some cardiac arrhythmias. Adenosyl (abbreviated Ado or 5'-dAdo) is the chemical group formed by removal of the 5′-hydroxy (OH) group. It is found in adenosylcobalamin (an active form of vitamin B12) and as a radical in the radical SAM enzymes. Medical uses Supraventricular tachycardia In individuals with supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), adenosine is a first line trea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lantheus Medical Imaging
Lantheus, headquartered in Billerica, Massachusetts, is a company in the radiopharmaceuticals business. It has strategic partnerships with Bayer, Novartis, Regeneron as well as GE Healthcare and Siemens Healthineers Siemens Healthineers is a German multinational company with specializing in medical technology. It was spun off from its parent company Siemens in 2017, which retains a 75% stake. Siemens Healthineers is the parent company for several medical te .... Lantheus Holding, which became a NASDAQ company in 2015, is the parent company of Lantheus Medical Imaging, Inc. (formerly BMS Medical Imaging), Progenics Pharmaceuticals (acquired 2020), Inc. and EXINI Diagnostics AB (est. 1999, acquired 2020). Lantheus has offices in Massachusetts, New Jersey, Canada and Sweden. Brian Markison has served as the company's CEO since March 1, 2024, following the retirement of Mary Anne Heino, who had led Lantheus for the preceding decade. References External links *{{Official websit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tc-sestamibi
Technetium (99mTc) sestamibi (INN; commonly sestamibi; USP: technetium Tc 99m sestamibi; trade name Cardiolite) is a pharmaceutical agent used in nuclear medicine imaging. The drug is a coordination complex consisting of the radioisotope technetium-99m bound to six (sesta=6) methoxyisobutylisonitrile (MIBI) ligands. The anion is not defined. The generic drug became available late September 2008. A scan of a patient using MIBI is commonly known as a "MIBI scan". Sestamibi is taken up by tissues with large numbers of mitochondria and negative plasma membrane potentials. Sestamibi is mainly used to image the myocardium (heart muscle). It is also used in the work-up of primary hyperparathyroidism to identify parathyroid adenomas, for radioguided surgery of the parathyroid and in the work-up of possible breast cancer. Cardiac imaging (MIBI scan) A ''MIBI scan'' or ''sestamibi scan'' is now a common method of cardiac imaging. Technetium (99mTc) sestamibi is a lipophilic cation w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
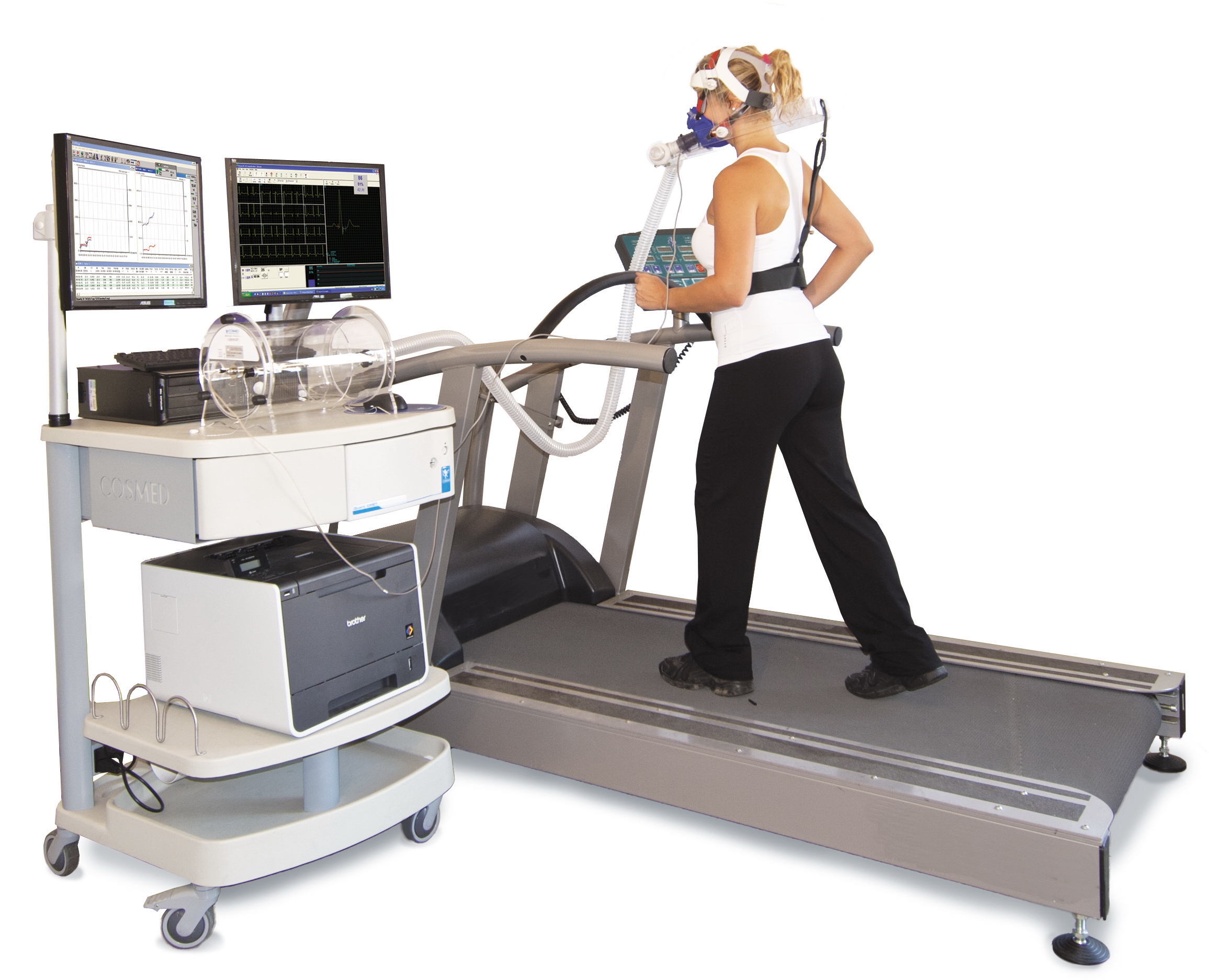
Cardiac Stress Test
A cardiac stress test is a cardiological examination that evaluates the cardiovascular system's response to external stress within a controlled clinical setting. This stress response can be induced through physical exercise (usually a treadmill) or intravenous pharmacological stimulation of heart rate. As the heart works progressively harder (stressed) it is monitored using an electrocardiogram (ECG) monitor. This measures the heart's electrical rhythms and broader electrophysiology. Pulse rate, blood pressure and symptoms such as chest discomfort or fatigue are simultaneously monitored by attending clinical staff. Clinical staff will question the patient throughout the procedure asking questions that relate to pain and perceived discomfort. Abnormalities in blood pressure, heart rate, ECG or worsening physical symptoms could be indicative of coronary artery disease. Stress testing does not accurately diagnose all cases of coronary artery disease, and can often indicate that it e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myocardium
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle or myocardium) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, the others being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall of the heart. The cardiac muscle (myocardium) forms a thick middle layer between the outer layer of the heart wall (the pericardium) and the inner layer (the endocardium), with blood supplied via the coronary circulation. It is composed of individual cardiac muscle cells joined by intercalated discs, and encased by collagen fibers and other substances that form the extracellular matrix. Cardiac muscle contracts in a similar manner to skeletal muscle, although with some important differences. Electrical stimulation in the form of a cardiac action potential triggers the release of calcium from the cell's internal calcium store, the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The rise in calcium causes the cell's myofilaments to slide past each other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
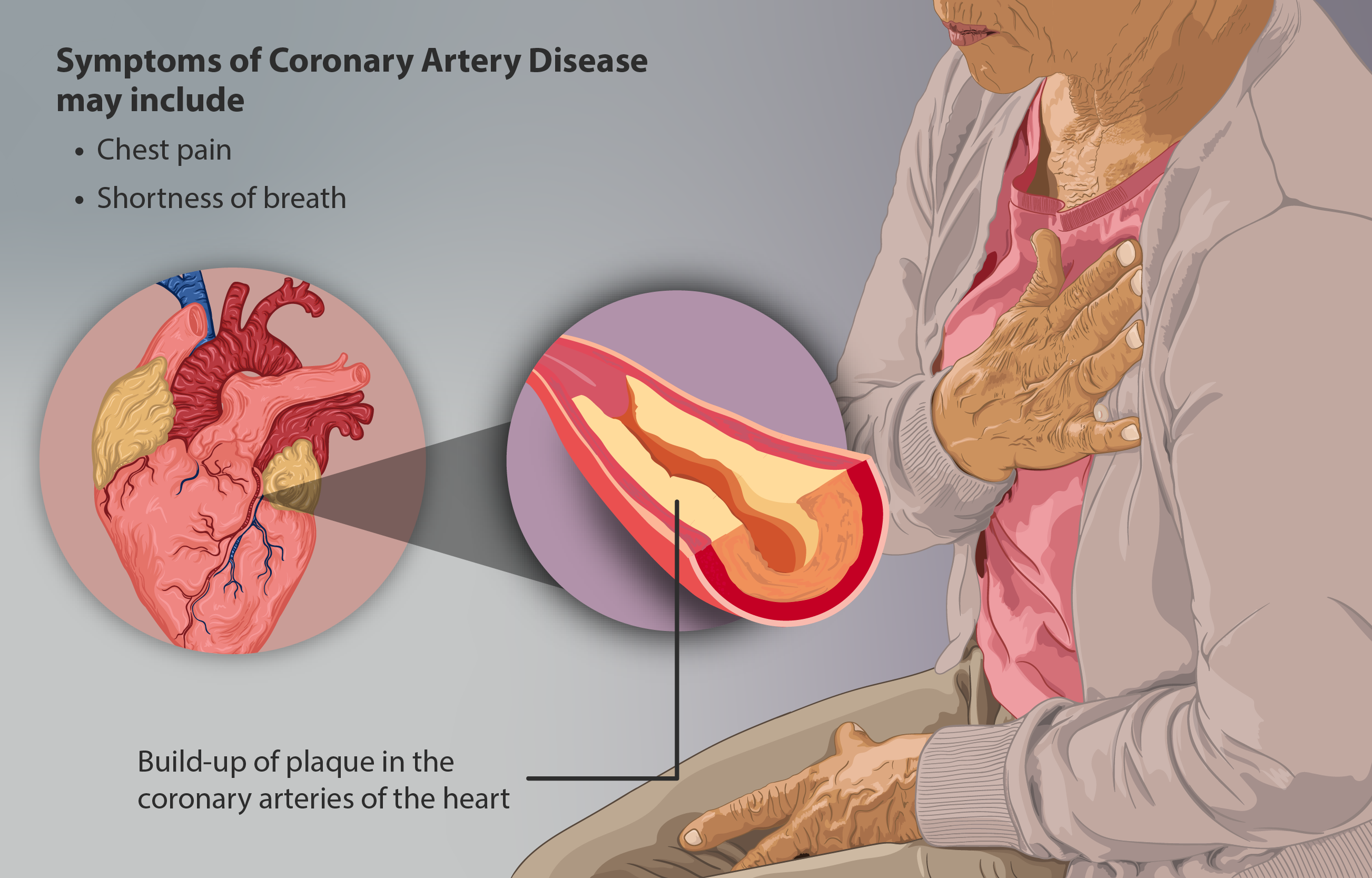
Ischemic Heart Disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), or ischemic heart disease (IHD), is a type of heart disease involving the reduction of blood flow to the cardiac muscle due to a build-up of atheromatous plaque in the arteries of the heart. It is the most common of the cardiovascular diseases. CAD can cause stable angina, unstable angina, myocardial ischemia, and myocardial infarction. A common symptom is angina, which is chest pain or discomfort that may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Occasionally it may feel like heartburn. In stable angina, symptoms occur with exercise or emotional stress, last less than a few minutes, and improve with rest. Shortness of breath may also occur and sometimes no symptoms are present. In many cases, the first sign is a heart attack. Other complications include heart failure or an abnormal heartbeat. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes mellitus, lack of exercise, obesity, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Embolus
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include shortness of breath, chest pain particularly upon breathing in, and coughing up blood. Symptoms of a blood clot in the leg may also be present, such as a red, warm, swollen, and painful leg. Signs of a PE include low blood oxygen levels, rapid breathing, rapid heart rate, and sometimes a mild fever. Severe cases can lead to passing out, abnormally low blood pressure, obstructive shock, and sudden death. PE usually results from a blood clot in the leg that travels to the lung. The risk of blood clots is increased by advanced age, cancer, prolonged bed rest and immobilization, smoking, stroke, long-haul travel over 4 hours, certain genetic conditions, estrogen-based medication, pregnancy, obesity, trauma or bone fracture, and after some types of surgery. A small proportion of cases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Neuroimaging
Functional neuroimaging is the use of neuroimaging technology to measure an aspect of brain function, often with a view to understanding the relationship between activity in certain brain areas and specific mental functions. It is primarily used as a research tool in cognitive neuroscience, cognitive psychology, neuropsychology, and social neuroscience. Overview Common methods of functional neuroimaging include * Positron emission tomography (PET) * Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) * Electroencephalography (EEG) * Magnetoencephalography (MEG) * Functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) * Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) * Functional ultrasound imaging (fUS) PET, fMRI, fNIRS and fUS can measure localized changes in cerebral blood flow related to neural activity. These changes are referred to as ''activations''. Regions of the brain which are activated when a subject performs a particular task may play a role in the computational neuroscience, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myocardial Perfusion Imaging
Myocardial perfusion imaging or scanning (also referred to as MPI or MPS) is a nuclear medicine procedure that illustrates the function of the heart muscle (myocardium). It evaluates many heart conditions, such as coronary artery disease (CAD), hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and heart wall motion abnormalities. It can also detect regions of myocardial infarction by showing areas of decreased resting perfusion. The function of the myocardium is also evaluated by calculating the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of the heart. This scan is done in conjunction with a cardiac stress test. The diagnostic information is generated by provoking controlled regional ischemia in the heart with variable perfusion. Planar techniques, such as conventional scintigraphy, are rarely used. Rather, single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) is more common in the US. With multihead SPECT systems, imaging can often be completed in less than 10 minutes. With SPECT, inferior and posterior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventilation/perfusion Scan
A ventilation/perfusion lung scan, also called a V/Q lung scan, or ventilation/perfusion scintigraphy, is a type of medical imaging using scintigraphy and medical isotopes to evaluate the circulation of air and blood within a patient's lungs, in order to determine the ventilation/perfusion ratio. The ventilation part of the test looks at the ability of air to reach all parts of the lungs, while the perfusion part evaluates how well blood circulates within the lungs. As Q in physiology is the letter used to describe bloodflow the term V/Q scan emerged. Uses This test is most commonly done in order to check for the presence of a blood clot or abnormal blood flow inside the lungs (such as a pulmonary embolism (PE) although computed tomography with radiocontrast is now more commonly used for this purpose. The V/Q scan may be used in some circumstances where radiocontrast would be inappropriate, as in allergy to contrast agent or kidney failure. A V/Q lung scan may be performed in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |