|
Isothermal Amplification
Variants of PCR represent a diverse array of techniques that have evolved from the basic polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method, each tailored to specific applications in molecular biology, such as genetic analysis, DNA sequencing, and disease diagnosis, by modifying factors like primer design, temperature conditions, and enzyme usage. Basic modifications Often only a small modification needs to be made to the standard PCR protocol to achieve a desired goal: '' Multiplex-PCR'' uses several pairs of primers annealing to different target sequences. This permits the simultaneous analysis of multiple targets in a single sample. For example, in testing for genetic mutations, six or more amplifications might be combined. In the standard protocol for DNA fingerprinting, the targets assayed are often amplified in groups of 3 or 4. ''Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification'' (''MLPA'') permits multiple targets to be amplified using only a single pair of primers, avoiding the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymerase Chain Reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to make millions to billions of copies of a specific DNA sample rapidly, allowing scientists to amplify a very small sample of DNA (or a part of it) sufficiently to enable detailed study. PCR was invented in 1983 by American biochemist Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation. Mullis and biochemist Michael Smith (chemist), Michael Smith, who had developed other essential ways of manipulating DNA, were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993. PCR is fundamental to many of the procedures used in genetic testing and research, including analysis of Ancient DNA, ancient samples of DNA and identification of infectious agents. Using PCR, copies of very small amounts of DNA sequences are exponentially amplified in a series of cycles of temperature changes. PCR is now a common and often indispensable technique used in medical laboratory research for a broad variety of applications including biomedical research and forensic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Melting
Nucleic acid thermodynamics is the study of how temperature affects the nucleic acid structure of double-stranded DNA (dsDNA). The melting temperature (''Tm'') is defined as the temperature at which half of the DNA strands are in the random coil or single-stranded (ssDNA) state. ''Tm'' depends on the length of the DNA molecule and its specific nucleotide sequence. DNA, when in a state where its two strands are dissociated (i.e., the dsDNA molecule exists as two independent strands), is referred to as having been denatured by the high temperature. Concepts Hybridization Hybridization is the process of establishing a non-covalent, sequence-specific interaction between two or more complementary strands of nucleic acids into a single complex, which in the case of two strands is referred to as a duplex. Oligonucleotides, DNA, or RNA will bind to their complement under normal conditions, so two perfectly complementary strands will bind to each other readily. In order to reduce t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Polymerase Chain Reaction
Digital polymerase chain reaction (digital PCR, DigitalPCR, dPCR, or dePCR) is a biotechnological refinement of conventional polymerase chain reaction methods that can be used to directly quantify and clonally amplify nucleic acids strands including DNA, cDNA, or RNA. The key difference between dPCR and qPCR lies in the method of measuring nucleic acids amounts, with the former being a more precise method than PCR, though also more prone to error in the hands of inexperienced users. PCR carries out one reaction per single sample. dPCR also carries out a single reaction within a sample, however the sample is separated into a large number of partitions and the reaction is carried out in each partition individually. This separation allows a more reliable collection and sensitive measurement of nucleic acid amounts. The method has been demonstrated as useful for studying variations in gene sequences—such as copy number variants and point mutations. Principles The polymerase cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmid
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria and archaea; however plasmids are sometimes present in and eukaryotic organisms as well. Plasmids often carry useful genes, such as those involved in antibiotic resistance, virulence, secondary metabolism and bioremediation. While chromosomes are large and contain all the essential genetic information for living under normal conditions, plasmids are usually very small and contain additional genes for special circumstances. Artificial plasmids are widely used as vectors in molecular cloning, serving to drive the replication of recombinant DNA sequences within host organisms. In the laboratory, plasmids may be introduced into a cell via transformation. Synthetic plasmids are available for procurement over the internet by various vendors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Ligase
DNA ligase is a type of enzyme that facilitates the joining of DNA strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. It plays a role in repairing single-strand breaks in duplex DNA in living organisms, but some forms (such as DNA ligase IV) may specifically repair double-strand breaks (i.e. a break in both complementary strands of DNA). Single-strand breaks are repaired by DNA ligase using the complementary strand of the double helix as a template, with DNA ligase creating the final phosphodiester bond to fully repair the DNA. DNA ligase is used in both DNA repair and DNA replication (see '' Mammalian ligases''). In addition, DNA ligase has extensive use in molecular biology laboratories for recombinant DNA experiments (see '' Research applications''). Purified DNA ligase is used in gene cloning to join DNA molecules together to form recombinant DNA. Enzymatic mechanism The mechanism of DNA ligase is to form two covalent phosphodiester bonds between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymerase Cycling Assembly
Polymerase cycling assembly (or PCA, also known as Assembly PCR) is a method for the assembly of large DNA oligonucleotides from shorter fragments. The process uses the same technology as PCR, but takes advantage of DNA hybridization and annealing as well as DNA polymerase to amplify a complete sequence of DNA in a precise order based on the single stranded oligonucleotides used in the process. It thus allows for the production of synthetic genes and even entire synthetic genomes. PCA principles Much like how primers are designed such that there is a forward primer and a reverse primer capable of allowing DNA polymerase to fill the entire template sequence, PCA uses the same technology but with multiple oligonucleotides. While in PCR the customary size of oligonucleotides used is 18 base pairs, in PCA lengths of up to 50 are used to ensure uniqueness and correct hybridization. Each oligonucleotide is designed to be either part of the top or bottom strand of the target sequence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Touchdown Polymerase Chain Reaction
The touchdown polymerase chain reaction or touchdown style polymerase chain reaction is a method of polymerase chain reaction by which primers avoid amplifying nonspecific sequences. The annealing temperature during a polymerase chain reaction determines the specificity of primer annealing. The melting point of the primer sets the upper limit on annealing temperature. At temperatures just above this point, only very specific base pairing between the primer and the template will occur. At lower temperatures, the primers bind less specifically. Nonspecific primer binding obscures polymerase chain reaction results, as the nonspecific sequences to which primers anneal in early steps of amplification will "swamp out" any specific sequences because of the exponential nature of polymerase In biochemistry, a polymerase is an enzyme (Enzyme Commission number, EC 2.7.7.6/7/19/48/49) that synthesizes long chains of polymers or nucleic acids. DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase are used to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibody
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as pathogenic bacteria, bacteria and viruses, including those that cause disease. Each individual antibody recognizes one or more specific antigens, and antigens of virtually any size and chemical composition can be recognized. Antigen literally means "antibody generator", as it is the presence of an antigen that drives the formation of an antigen-specific antibody. Each of the branching chains comprising the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope that specifically binds to one particular epitope on an antigen, allowing the two molecules to bind together with precision. Using this mechanism, antibodies can effectively "tag" the antigen (or a microbe or an infected cell bearing such an antigen) for attack by cells of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly (for example, by blocking a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TaqMan
TaqMan probes are hydrolysis probes that are designed to increase the specificity of quantitative PCR. The method was first reported in 1991 by researcher David Gefland at Cetus Corporation, and the technology was subsequently developed by Hoffmann-La Roche for diagnostic assays and by Applied Biosystems (now part of Thermo Fisher Scientific) for research applications. The TaqMan probe principle relies on the 5´–3´ exonuclease activity of ''Taq'' polymerase to cleave a dual-labeled probe during hybridization to the complementary target sequence and fluorophore-based detection. As in other quantitative PCR methods, the resulting fluorescence signal permits quantitative measurements of the accumulation of the product during the exponential stages of the PCR; however, the TaqMan probe significantly increases the specificity of the detection. TaqMan probes were named after the videogame Pac-Man (''Taq'' Polymerase + PacMan = TaqMan) as its mechanism is based on the Pac-Man princi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
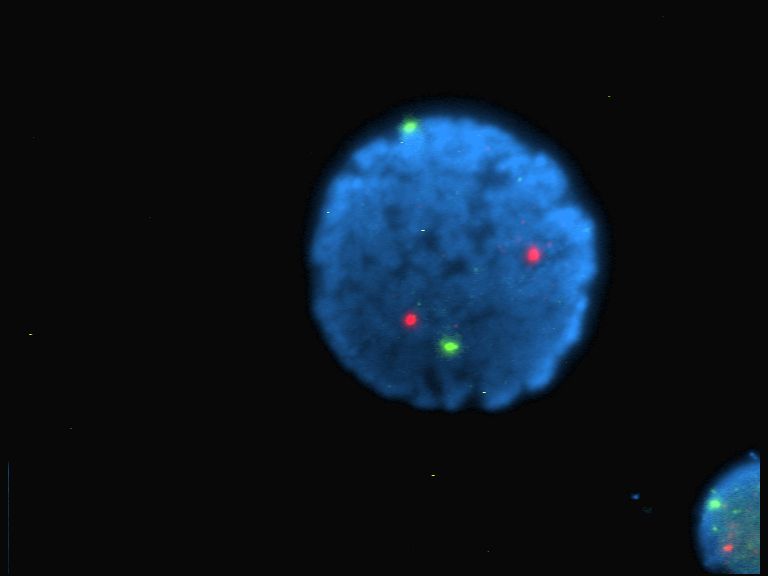
Fluorophore
A fluorophore (or fluorochrome, similarly to a chromophore) is a fluorescent chemical compound that can re-emit light upon light excitation. Fluorophores typically contain several combined aromatic groups, or planar or cyclic molecules with several π bonds. Fluorophores are sometimes used alone, as a tracer in fluids, as a dye for staining of certain structures, as a substrate of enzymes, or as a probe or indicator (when its fluorescence is affected by environmental aspects such as polarity or ions). More generally they are covalently bonded to macromolecules, serving as a markers (or dyes, or tags, or reporters) for affine or bioactive reagents (antibodies, peptides, nucleic acids). Fluorophores are notably used to stain tissues, cells, or materials in a variety of analytical methods, such as fluorescent imaging and spectroscopy. Fluorescein, via its amine-reactive isothiocyanate derivative fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), has been one of the most popular fluorophores ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
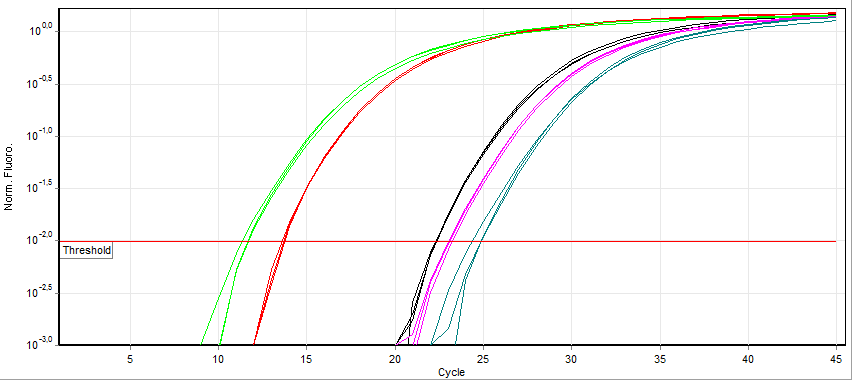
Quantitative PCR
A real-time polymerase chain reaction (real-time PCR, or qPCR when used quantitatively) is a laboratory technique of molecular biology based on the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It monitors the amplification of a targeted DNA molecule during the PCR (i.e., in real time), not at its end, as in conventional PCR. Real-time PCR can be used quantitatively and semi-quantitatively (i.e., above/below a certain amount of DNA molecules). Two common methods for the detection of PCR products in real-time PCR are (1) non-specific fluorescent dyes that intercalate with any double-stranded DNA and (2) sequence-specific DNA probes consisting of oligonucleotides that are labelled with a fluorescent reporter, which permits detection only after hybridization of the probe with its complementary sequence. The Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments (MIQE) guidelines propose that the abbreviation ''qPCR'' be used for quantitative real-time PCR and that ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
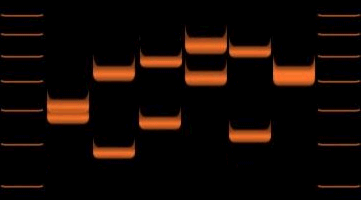
Nested PCR
Nested polymerase chain reaction (nested PCR) is a modification of polymerase chain reaction intended to reduce non-specific binding in products due to the amplification of unexpected primer binding sites. Polymerase chain reaction Polymerase chain reaction itself is the process used to amplify DNA samples, via a temperature-mediated DNA polymerase. The products can be used for sequencing or analysis, and this process is a key part of many genetics research laboratories, along with uses in DNA fingerprinting for forensics Forensic science combines principles of law and science to investigate criminal activity. Through crime scene investigations and laboratory analysis, forensic scientists are able to link suspects to evidence. An example is determining the time and ... and other human genetic cases. Conventional PCR requires primers complementary to the termini of the target DNA. The amount of product from the PCR increases with the number of temperature cycles that the reactio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |