|
Isas
, or ISAS, is a Japanese national research organization of astrophysics using rockets, astronomical satellites and interplanetary probes which played a major role in Japan's space development. Established as part of the University of Tokyo in 1964, the institute spun off from the university to come under direct purview of the Ministry of Education. Since 2003, it is a division of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). History The ISAS originated as part of the Institute of Industrial Science of the University of Tokyo, where Hideo Itokawa experimented with miniature solid-fuel rockets (Pencil Rocket and ) in the 1950s. This experimentation eventually led to the development of the Κ (''Kappa'') sounding rocket, which was used for observations during the International Geophysical Year (IGY). By 1960, the Κ-8 rocket had reached an altitude of 200 km. In 1964, the rocket group and the ''Institute of Aeronautics'', along with scientific ballooning team, were mer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea in the south. The Japanese archipelago consists of four major islands—Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu—and List of islands of Japan, thousands of smaller islands, covering . Japan has a population of over 123 million as of 2025, making it the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh-most populous country. The capital of Japan and List of cities in Japan, its largest city is Tokyo; the Greater Tokyo Area is the List of largest cities, largest metropolitan area in the world, with more than 37 million inhabitants as of 2024. Japan is divided into 47 Prefectures of Japan, administrative prefectures and List of regions of Japan, eight traditional regions. About three-quarters of Geography of Japan, the countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pencil Rocket
The was developed by the Avionics and Supersonic Aerodynamics (AVSA) research group in the early days of the Japanese space program. A prominent engineer on the project was Hideo Itokawa was a pioneer of Japanese rocketry, popularly known as "Dr. Rocket," and described in the media as the father of Japan's space development. The near-Earth asteroid 25143 Itokawa was named in honor of Itokawa, and is notable as the target of th .... The rocket was first launched on 12 April 1955. The dimensions were 23 cm in length by 1.8 cm in diameter, weighing 200 grams. Development of the Pencil rocket system started in 1954 when Hideo Itokawa formed a center for rocket development at the University of Tokyo. In 1955, Itokawa's team, began conducting experimental launches of pencil-type rockets. The team launched 29 rockets over their course of these first experiments in space launch. Afterwards, the team expanded its focus to atmospheric observation with the larger Kappa 6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASTRO-E
''Suzaku'' (formerly ASTRO-EII) was an X-ray astronomy satellite developed jointly by the Institute of Space and Aeronautical Science at JAXA and NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center to probe high-energy X-ray sources, such as supernova explosions, black holes and galactic clusters. It was launched on 10 July 2005 aboard the M-V launch vehicle on the M-V-6 mission. After its successful launch, the satellite was renamed ''Suzaku'' after the mythical Vermilion bird of the South. Just weeks after launch, on 29 July 2005, the first of a series of cooling system malfunctions occurred. These ultimately caused the entire reservoir of liquid helium to boil off into space by 8 August 2005. This effectively shut down the X-ray Spectrometer-2 (XRS-2), which was the spacecraft's primary instrument. The two other instruments, the X-ray Imaging Spectrometer (XIS) and the Hard X-ray Detector (HXD), were unaffected by the malfunction. As a result, another XRS was integrated into the Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
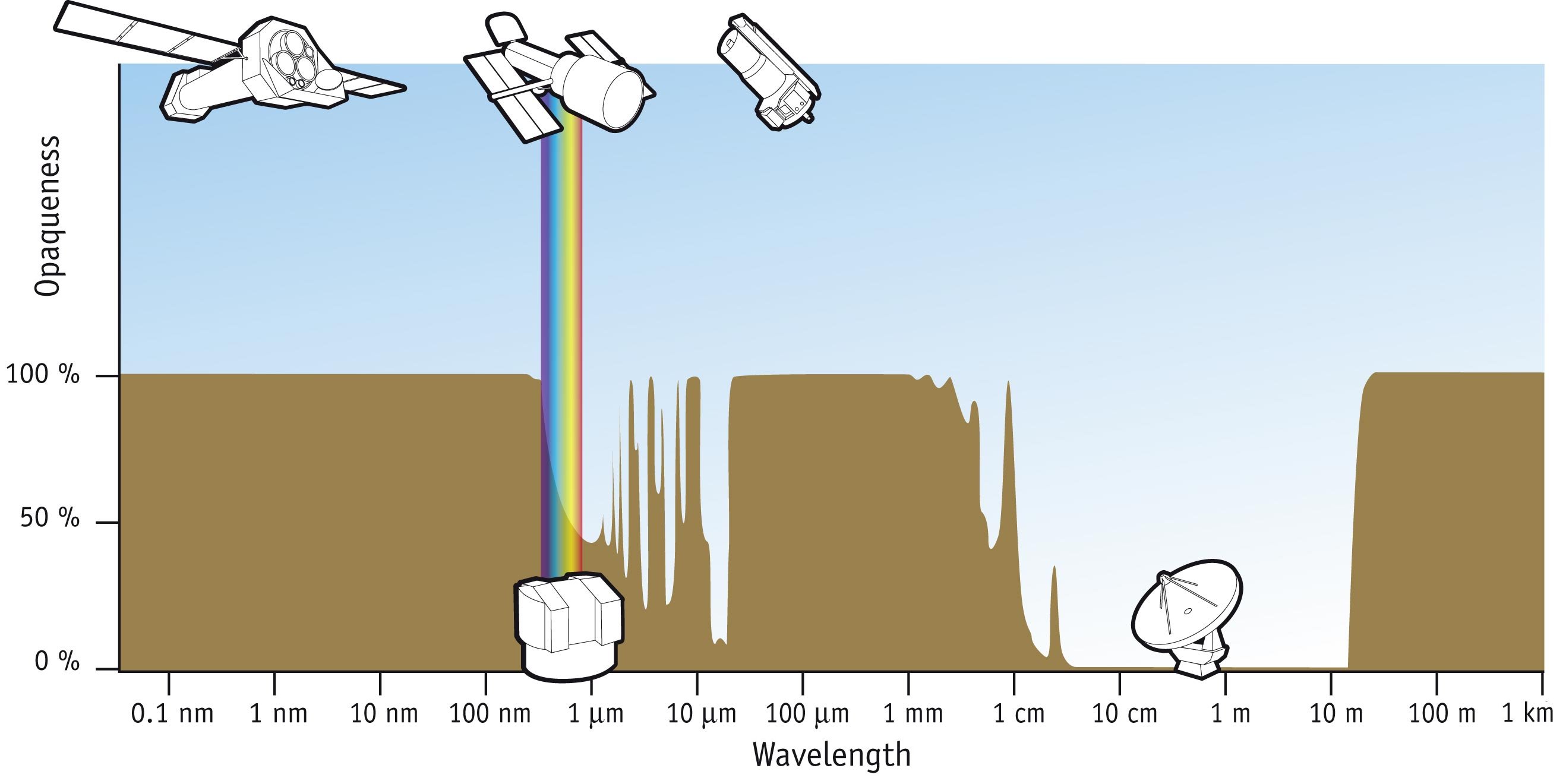
X-ray Astronomy
X-ray astronomy is an observational branch of astronomy which deals with the study of X-ray observation and detection from astronomical objects. X-radiation is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to high altitude by Balloon-borne telescope, balloons, sounding rockets, and X-ray astronomy satellite, satellites. X-ray astronomy uses a type of space telescope that can see x-ray radiation which standard optical telescopes, such as the Mauna Kea Observatories, cannot. X-ray generation, X-ray emission is expected from astronomical objects that contain extremely hot gases at temperatures from about a million kelvin (K) to hundreds of millions of kelvin (MK). Moreover, the maintenance of the E-layer of ionized gas high in the Earth's thermosphere also suggested a strong extraterrestrial source of X-rays. Although theory predicted that the Sun and the stars would be prominent X-ray sources, there was no way to verify this because Earth's atmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hakucho
Hakucho (also known as CORSA-b before launch; CORSA stands for Cosmic Radiation Satellite) was Japan's first X-ray astronomy satellite, developed by the Institute of Space and Aeronautical Science (then a division of the University of Tokyo The University of Tokyo (, abbreviated as in Japanese and UTokyo in English) is a public research university in Bunkyō, Tokyo, Japan. Founded in 1877 as the nation's first modern university by the merger of several pre-westernisation era ins ...). It was launched from the Kagoshima Space Center by the ISAS M-3C rocket on the M-3C-4 mission on February 21, 1979 and reentered the atmosphere on April 15, 1985. Hakucho was a replacement for the Cosmic Radiation Satellite (CORSA) satellite which failed to launch due to rocket failure on February 4, 1976. Highlights *Discovery of soft X-ray transient Cen X-4 and Aql X-1 *Discovery of many burst sources *Long-term monitoring of X-ray pulsar (e.g. Vela X-1) *Discovery of 2 Hz varia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior Dynamo theory, dynamo. In the space environment close to a planetary body with a dipole magnetic field such as Earth, the field lines resemble a simple magnetic dipole. Farther out, field lines can be significantly distorted by the flow of electrically conducting plasma (physics), plasma, as emitted from the Sun (i.e., the solar wind) or a nearby star. Planets having active magnetospheres, like the Earth, are capable of mitigating or blocking the effects of solar radiation or cosmic radiation. Interactions of particles and atmospheres with magnetospheres are studied under the specialized scientific subjects of plasma physics, space physics, and aeronomy. History Study of Earth's magnetosphere began in 1600, when William Gilbert (astronomer), W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionosphere
The ionosphere () is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about to above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an important role in atmospheric electricity and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere. It has practical importance because, among other functions, it influences radio propagation to distant places on Earth. Travel through this layer also impacts GPS signals, resulting in effects such as deflection in their path and delay in the arrival of the signal. History of discovery As early as 1839, the German mathematician and physicist Carl Friedrich Gauss postulated that an electrically conducting region of the atmosphere could account for observed variations of Earth's magnetic field. Sixty years later, Guglielmo Marconi received the first trans-Atlantic radio signal on December 12, 1901, in St. John's, Newfoundland (now in Canada) usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Satellites
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation (GPS), broadcasting, scientific research, and Earth observation. Additional military uses are reconnaissance, early warning, signals intelligence and, potentially, weapon delivery. Other satellites include the final rocket stages that place satellites in orbit and formerly useful satellites that later become defunct. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs). Most satellites also have a method of communication to ground stations, called transponders. Many satellites use a standardized bus to save cost and work, the most popular of which are small CubeSats. Similar satellites can work together as groups, forming constellations. Becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mu (rocket Family)
The Mu, also known as M, was a series of Japanese Solid-fuel rocket, solid-fueled carrier rockets, which were launched from Uchinoura Space Center, Uchinoura between 1966 and 2006. Originally developed by Japan's Institute of Space and Astronautical Science, Mu rockets were later operated by Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency following ISAS becoming part of it. Early Japanese carrier rockets The first Mu rocket, the Mu-1 made a single, sub-orbital, test flight, on 31 October 1966. Subsequently, a series of rockets were produced, designated Mu-3 and Mu-4. In 1969 a suborbital test launch of the Mu-3D was conducted. The first orbital launch attempt for the Mu family, using a Mu-4, Mu-4S, was conducted on 25 September 1970, however the fourth stage did not ignite, and the rocket failed to reach orbit. On 16 February 1971, Tansei 1 was launched by another Mu-4S rocket. Two further Mu-4S launches took place during 1971 and 1972. The Mu-4S was replaced by the Mu-3C, was launched four ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohsumi (satellite)
The Ohsumi ( or Ōsumi, おおすみ) satellite, Japan’s first artificial satellite, was launched on February 11, 1970, at 04:25 UTC (Coordinated Universal Time) by the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science, Institute of Space and Aeronautical Science (''ISAS'') from the Kagoshima Space Center, which is located on the Ōsumi Peninsula, Ohsumi peninsula in Japan. This location was chosen for its strategic position in coordinating eastward launches, optimizing the rocket's trajectory. The launch vehicle was the Lambda 4S-5, a rocket developed by the ISAS of the University of Tokyo. Such an achievement marks Japan as the fourth nation to independently place a satellite into orbit. The satellite achieved an Elliptic orbit, elliptical orbit with an apogee of approximately 5,150 km and a perigee of 335 km, conducting experiments to gather data on the ionosphere and testing satellite launch technologies. Although its operational life ended within hours due to power loss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambda (rocket)
Lambda is the name of a series of Japanese carrier rockets. It consisted of the types Lambda 2, LSC-3, Lambda 3, Lambda 3H, Lambda 4S, Lambda 4SC, and Lambda 4T developed jointly by Institute of Industrial Science of the University of Tokyo, Institute of Space and Astronautical Science of the University of Tokyo, and Prince Motor Company, which merged with Nissan in 1966. Lambda series rockets did not have guidance systems, as they had the potential to be converted for offensive military use, thus interpreted as a violation of Article 9 of the Japanese Constitution. However, future Japanese launch vehicles, such as the H-II, were allowed to have guidance systems. Configurations Lambda types differ regarding the upper stages used. The following table shows the actual configurations: Launches Lambda rockets were launched by ISAS, from Kagoshima pad L. On February 11, 1970, the first Japanese satellite Ohsumi was launched using a Lambda 4S rocket. The Lambda 4S was laun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
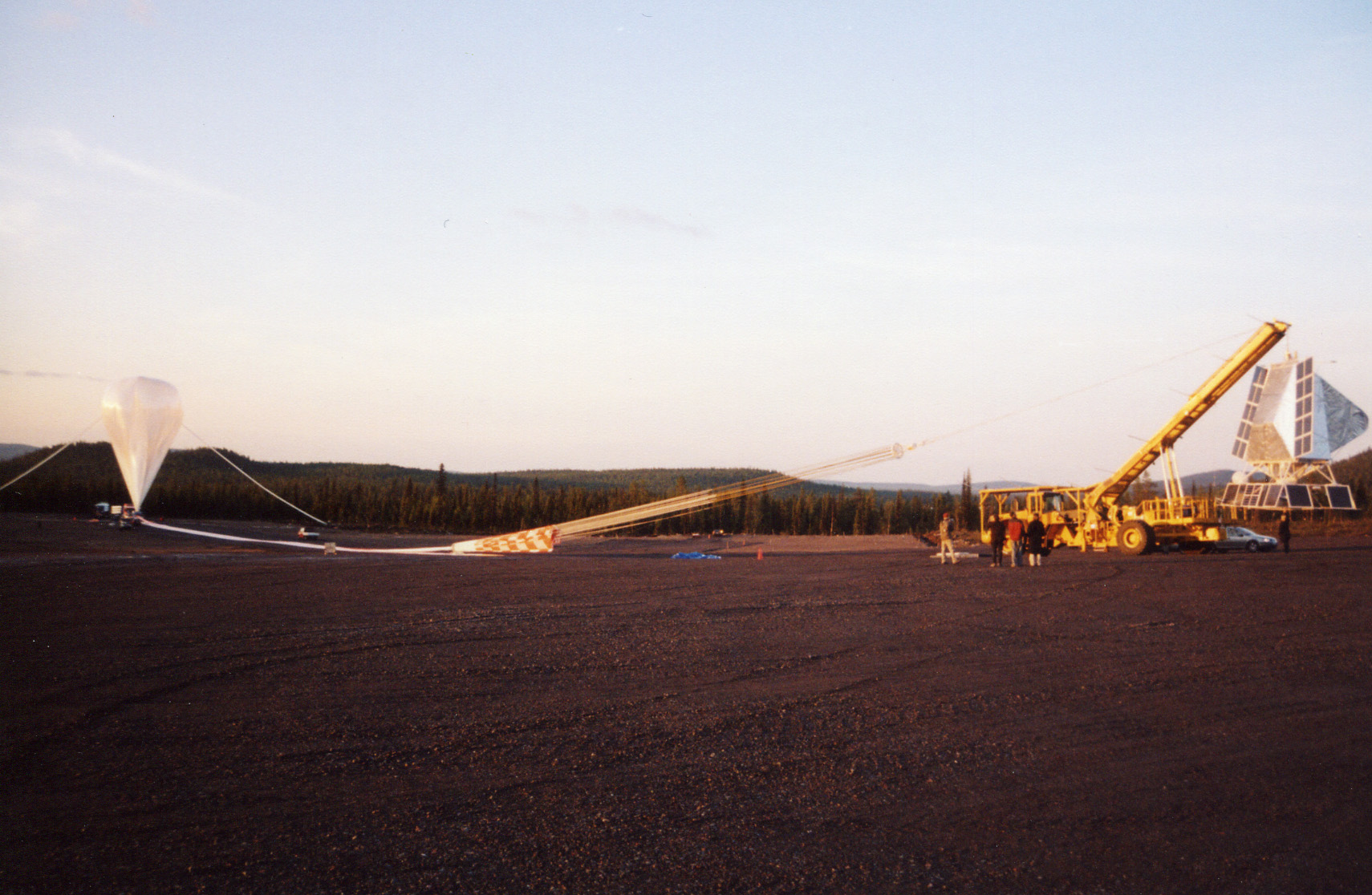
High Altitude Balloon
High-altitude balloons or stratostats are usually uncrewed balloons typically filled with helium or hydrogen and released into the stratosphere, generally attaining between above sea level. In 2013, a balloon named BS 13-08 reached a record altitude of . The most common type of high-altitude balloons are weather balloons. Other purposes include use as a platform for experiments in the upper atmosphere. Modern balloons generally contain electronic equipment such as radio transmitters, cameras, or satellite navigation systems, such as Global Positioning System, GPS receivers. Hobbyists frequently purchase weather balloons because of their ease of use, low price point, and widespread commoditisation. These balloons are launched into what is defined as "near space", defined as the area of atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere between the Armstrong limit ( above sea level), where pressure falls to the point that a human being cannot survive without a pressurised suit, and the Kárm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |