|
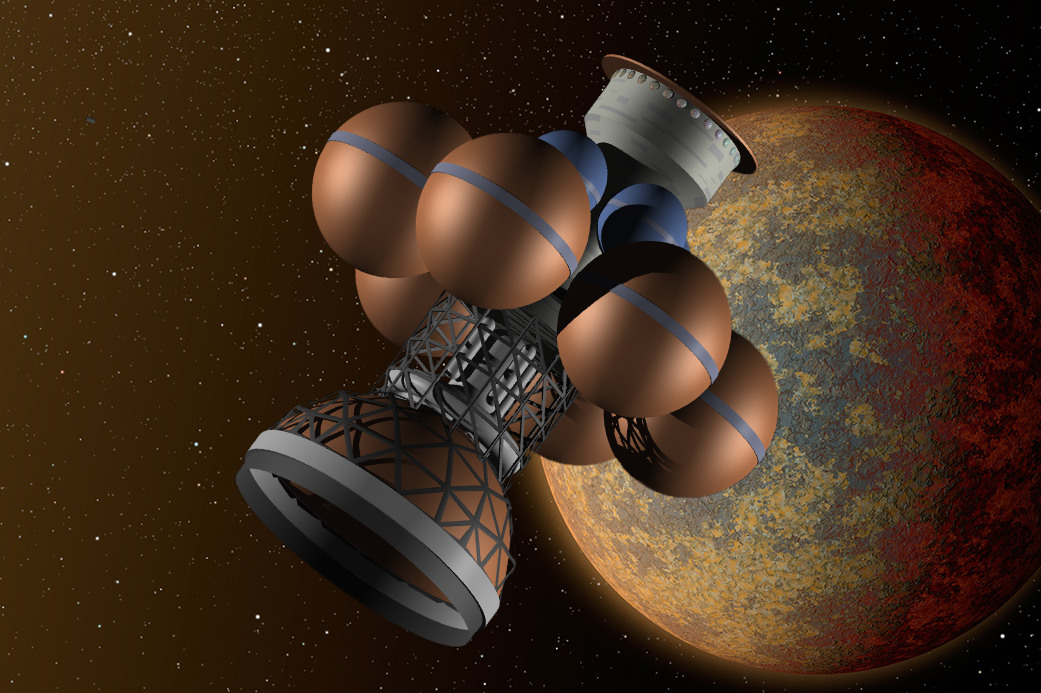
Interstellar Ark
An interstellar ark is a conceptual starship designed for interstellar travel. Interstellar arks may be the most economically feasible method of traveling such distances. The ark has also been proposed as a potential habitat to preserve civilization and knowledge in the event of a global catastrophe. Such a ship would have to be large, requiring a large power plant. The Project Orion concept of propulsion by nuclear pulses has been proposed. The largest spacecraft design analyzed in Project Orion had a diameter and weighed approximately 8 million tons. It could be large enough to host a city of 100,000 or more people. Thrust concepts Another concern is selection of power sources and mechanisms which would remain viable for the long time spans involved in interstellar travel through the desert of space. The longest-lived space probes are the Voyager program probes, which use radioisotope thermoelectric generators having a useful lifespan of a mere 50 years. One propuls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starship
A starship, starcraft, or interstellar spacecraft is a theoretical spacecraft designed for interstellar travel, traveling between planetary systems. The term is mostly found in science fiction. Reference to a "star-ship" appears as early as 1882 in ''Oahspe: A New Bible''. While NASA's ''Voyager program, Voyager'' and ''Pioneer program, Pioneer'' probes have traveled into local interstellar space, the purpose of these uncrewed craft was specifically interplanetary, and they are not predicted to reach another star system; ''Voyager 1'' probe and Gliese 445 will pass one another within 1.6 light years in about 40,000 years. Several preliminary designs for starships have been undertaken through exploratory engineering, using feasibility study, feasibility studies with modern technology or technology thought likely to be available in the near future. In April 2016, scientists announced Breakthrough Starshot, a Breakthrough Initiatives program, to develop a proof-of-concept fleet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speed Of Light
The speed of light in vacuum, commonly denoted , is a universal physical constant exactly equal to ). It is exact because, by international agreement, a metre is defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of second. The speed of light is invariant (physics), the same for all observers, no matter their relative velocity. It is the upper limit for the speed at which Information#Physics_and_determinacy, information, matter, or energy can travel through Space#Relativity, space. All forms of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, travel at the speed of light. For many practical purposes, light and other electromagnetic waves will appear to propagate instantaneously, but for long distances and sensitive measurements, their finite speed has noticeable effects. Much starlight viewed on Earth is from the distant past, allowing humans to study the history of the universe by viewing distant objects. When Data communication, comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothetical Spacecraft
A hypothesis (: hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. A scientific hypothesis must be based on observations and make a testable and reproducible prediction about reality, in a process beginning with an educated guess or thought. If a hypothesis is repeatedly independently demonstrated by experiment to be true, it becomes a scientific theory. In colloquial usage, the words "hypothesis" and "theory" are often used interchangeably, but this is incorrect in the context of science. A working hypothesis is a provisionally-accepted hypothesis used for the purpose of pursuing further progress in research. Working hypotheses are frequently discarded, and often proposed with knowledge (and warning) that they are incomplete and thus false, with the intent of moving research in at least somewhat the right direction, especially when scientists are stuck on an issue and brainstorming ideas. A different meaning of the term ''hypothesis'' is used in formal logic, to deno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Colonization
Space colonization (or extraterrestrial colonization) is the human settlement, settlement or colonization of outer space and astronomical bodies. The concept in its broad sense has been applied to any permanent human presence in space, such as a space habitat or other extraterrestrial settlements. It may involve a process of occupation or control for exploitation, such as Space mining, extraterrestrial mining. Making territorial claims in space is prohibited by international space law, defining space as a Common heritage of humanity, common heritage. International space law has had the goal to prevent colonial claims and militarization of space, and has advocated the installation of international regimes to regulate access to and sharing of space, particularly for specific locations such as the limited space of Geostationary orbit#Orbital allocation, geostationary orbit or the Moon. To date, no permanent space settlement other than temporary Space habitat (facility), space ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science Fiction Themes
The following is a list of articles about recurring theme (narrative), themes in science fiction. Overarching themes *First contact (science fiction), First contact with aliens *Artificial intelligence in fiction, Artificial intelligence **Machine rule/Cybernetic revolt/AI takeover *Extraterrestrials in fiction *End of humanity: Apocalyptic and post-apocalyptic fiction *The future **Apocalyptic and post-apocalyptic fiction: Apocalypses or worldwide disasters and Post-apocalypse, new societies that develop after the event *History **Alternate history (fiction), Alternate history **Scientific prediction of the future (e.g. Psychohistory (fictional), psychohistory) *Human fears: List of science fiction horror films *Language **Alien languages (e.g. Klingon language, Klingon, Hutt (Star Wars), Huttese) **The Sapir–Whorf Hypothesis (e.g. ''Babel 17'', ''The Languages of Pao'') **Universal translators (e.g. Babel fish) *Military science fiction, Military/conflicts **Interstellar wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generation Ship
A generation ship, generation starship or world ship, is a hypothetical type of interstellar ark starship that travels at sub- light speed. Since such a ship might require hundreds to thousands of years to reach nearby stars, the original occupants of a generation ship would grow old and die, leaving their descendants to continue traveling. Origins Rocket pioneer Robert H. Goddard was the first to write about long-duration interstellar journeys in his "The Ultimate Migration" (1918). In this he described the death of the Sun and the necessity of an "interstellar ark". The crew would travel for centuries in suspended animation and be awakened when they reached another star system. He proposed to use small moons or asteroids as ships, and speculated that the crew would endure psychological and genetic changes over the generations. Konstantin Tsiolkovsky, considered a father of astronautic theory, first described the need for multiple generations of passengers in his essay, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Interplanetary Society
The British Interplanetary Society (BIS), founded in Liverpool in 1933 by Philip E. Cleator, is the oldest existing space advocacy organisation in the world. Its aim is exclusively to support and promote astronautics and space exploration. Structure It is a non-profit organisation with headquarters in London and is financed by members' contributions. It is situated on South Lambeth Road ( A203) near Vauxhall station. History The BIS was only preceded in astronautics by the American Interplanetary Society (founded 1930), the German VfR (founded 1927), and Soviet Society for Studies of Interplanetary Travel (founded 1924), but unlike those it never became absorbed into a national industry. Thus it is now the world's oldest existing space advocacy body. When originally formed in October 1933, the BIS aimed not only to promote and raise the public profile of astronautics, but also to undertake practical experimentation into rocketry along similar lines to the organisations ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzmann Starship
The Enzmann starship is a concept for a crewed interstellar spacecraft proposed in 1964 by Dr. Robert Enzmann. A three million ton ball of frozen deuterium would fuel nuclear fusion rocket engines contained in a cylindrical section behind that ball with the crew quarters. The craft would be about long overall. Design The ball of frozen deuterium would fuel thermonuclear-powered pulse propulsion units, similar to Project Orion engines. The spacecraft would be assembled in Earth orbit as part of a larger project preceded by interstellar probes and telescopic observation of target star systems. The rest of the spacecraft would be attached behind the ball as a seamless metallic fuel tank. The proposed method of tank construction would be to expand a plastic balloon in space and coat it with metal. The spacecraft would be modular, and the main living area would be three identical wide and long cylindrical modules. The Enzmann could function as an interstellar ark, supporting a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
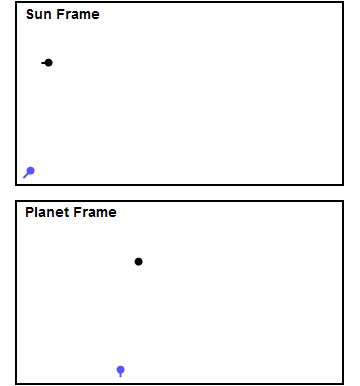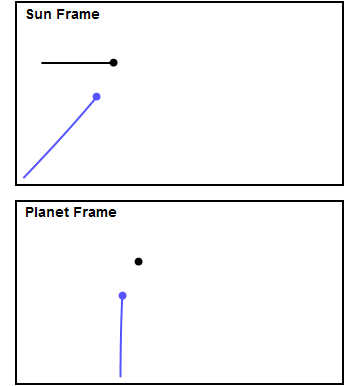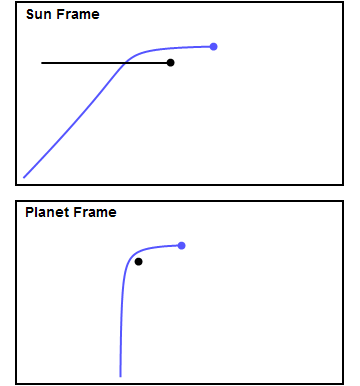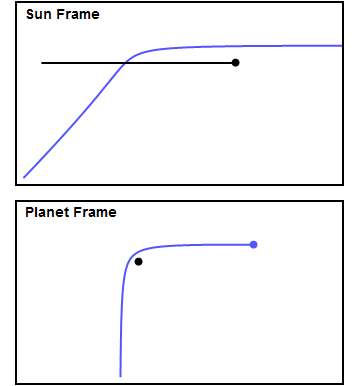
Gravity Assist
A gravity assist, gravity assist maneuver, swing-by, or generally a gravitational slingshot in orbital mechanics, is a type of spaceflight flyby (spaceflight), flyby which makes use of the relative movement (e.g. orbit around the Sun) and gravity of a planet or other astronomical object to alter the Course (navigation), path and speed of a spacecraft, typically to save propellant and reduce expense. Gravity assistance can be used to accelerate a spacecraft, that is, to increase or decrease its speed or redirect its path. The "assist" is provided by the motion of the gravitating body as it pulls on the spacecraft. Any gain or loss of kinetic energy and linear momentum by a passing spacecraft is correspondingly lost or gained by the gravitational body, in accordance with Newton's laws of motion#Newton's third law, Newton's Third Law. The gravity assist maneuver was first used in 1959 when the Soviet probe Luna 3 photographed the far side of Earth's Moon, and it was used by inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Daedalus
Project Daedalus (named after Daedalus, the Greek mythological designer who crafted wings for human flight) was a study conducted between 1973 and 1978 by the British Interplanetary Society to design a plausible uncrewed interstellar probe.Project Daedalus Study Group: A. Bond et al., ''Project Daedalus – The Final Report on the BIS Starship Study'', JBIS Interstellar Studies, Supplement 1978 Intended mainly as a scientific probe, the design criteria specified that the spacecraft had to use existing or near-future technology and had to be able to reach its destination within a human lifetime. Alan Bond led a team of scientists and engineers who proposed using a fusion rocket to reach Barnard's Star 5.9 light years away. The trip was estimated to take 50 years, but the design was required to be flexible enough that it could be sent to any other target star. All the papers produced by the study are available in a BIS book, ''Project Daedalus: Demonstrating the Engineering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interstellar Travel
Interstellar travel is the hypothetical travel of spacecraft between star systems. Due to the vast distances between the Solar System and nearby stars, interstellar travel is not practicable with current propulsion technologies. To travel between stars within a reasonable amount of time (decades or centuries), an interstellar spacecraft must reach a significant fraction of the speed of light, requiring enormous energy. Communication with such interstellar craft will experience years of delay due to the speed of light. Collisions with cosmic dust and gas at such speeds can be catastrophic for such spacecrafts. Crewed interstellar travel could possibly be conducted more slowly (far beyond the scale of a human lifetime) by making a generation ship. Hypothetical interstellar propulsion systems include nuclear pulse propulsion, fission-fragment rocket, fusion rocket, beamed solar sail, and antimatter rocket. The benefits of interstellar travel include detailed surveys of habitable exop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator
A radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG, RITEG), or radioisotope power system (RPS), is a type of nuclear battery that uses an array of thermocouples to convert the Decay heat, heat released by the decay of a suitable radioactive material into electricity by the Seebeck effect. This type of Electricity generation, generator has no moving parts and is ideal for deployment in remote and harsh environments for extended periods with no risk of parts wearing out or malfunctioning. RTGs are usually the most desirable power source for unmaintained situations that need a few hundred watts (or less) of power for durations too long for fuel cells, batteries, or generators to provide economically, and in places where solar cells are not practical. RTGs have been used as power sources in satellites, space probes, and uncrewed remote facilities such as a series of lighthouses built by the Soviet Union inside the Arctic Circle. However, the Western Bloc did not use RTGs in this way due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |