|
Intermuscular Coordination
Intermuscular coordination describes the coordination within different muscles and groups of muscles. These are used for sceletoral movement, stabilisation of joints, as well as stabilisation of body positioning. central nervous system is controlling positioning of joints via anticipatory and correcting adaptions of posture, that work against occurring intersegmental forces. The specific role and hierarchy of certain muscles and their meaning for certain movements is further differentiated within literature. Usage Joints are stabilised by interacting muscles, so called synergist muscle. Different synergists feature partial similar functions. Therefore, a certain movement can be formed out of different combinations and participations of muscles acting on a certain joint. Even muscles not being in a direct connection towards a certain joint can fulfill a stabilising function for that very joint. For a clear specification of any muscles function it is necessary to measure precis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contraction, contract. Muscle tissue contains special Muscle contraction, contractile proteins called actin and myosin which interact to cause movement. Among many other muscle proteins, present are two regulatory proteins, troponin and tropomyosin. Muscle is formed during embryonic development, in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle tissue is striated consisting of elongated, multinucleate muscle cells called muscle fibers, and is responsible for movements of the body. Other tissues in skeletal muscle include tendons and perimysium. Smooth and cardiac muscle contract involuntarily, without conscious intervention. These muscle types may be activated both through the interaction of the central nervous system as well as by innervation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilateria, bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and Coelenterata, diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the Anatomical_terms_of_location#Rostral,_cranial,_and_caudal, rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain, though precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets. The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
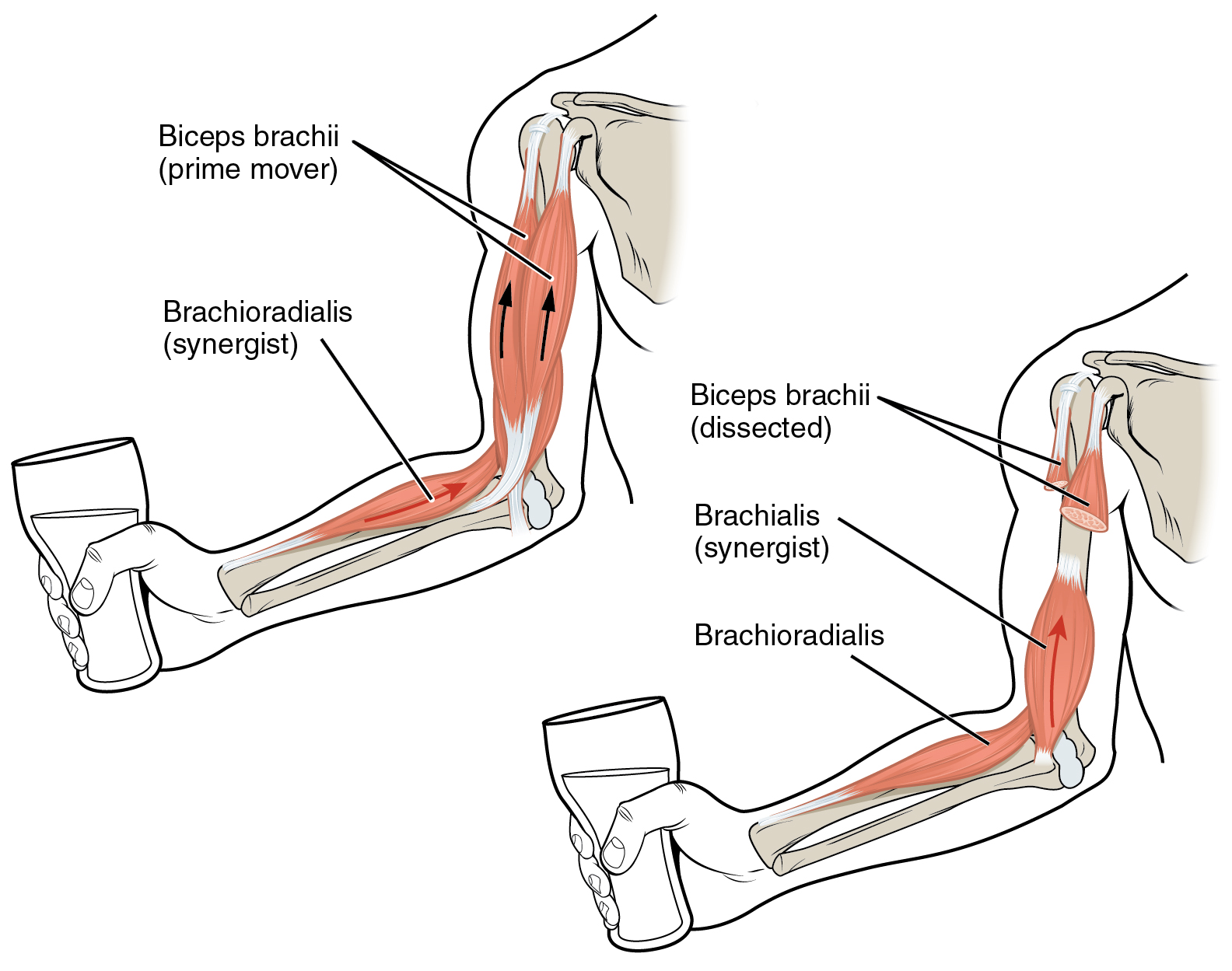
Synergist Muscle
Anatomical terminology is used to uniquely describe aspects of skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle such as their actions, structure, size, and location. Types There are three types of muscle tissue in the body: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Skeletal muscle Skeletal muscle, or "voluntary muscle", is a striated muscle tissue that primarily joins to bone with tendons. Skeletal muscle enables movement of bones, and maintains posture. The widest part of a muscle that pulls on the tendons is known as the belly. Muscle slip A muscle slip is a slip of muscle that can either be an anatomical variant, or a branching of a muscle as in rib connections of the serratus anterior muscle. Smooth muscle Smooth muscle is involuntary and found in parts of the body where it conveys action without conscious intent. The majority of this type of muscle tissue is found in the digestive and urinary systems where it acts by propelling forward food, chyme, and feces in the former and ur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Gollhofer
Albert Gollhofer (born 24 March 1954) is a German sport scientist and academic scholar. Life Born in Fellbach, Gollhofer studied sports science, physics and performance physiology at the Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg. In 1986, his doctoral thesis on "Components of fast strength performance in the stretch-shortening cycle" was accepted in Freiburg, between 1988 and 1994 he led a project funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. From 1993 to 2000, Gollhofer worked at the University of Stuttgart as a professor of biomechanics. In September 2000, he took up a position at the Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg as a professor in the department of exercise and movement sciences, becoming director and full professor at the Institute of Sport and Sport Science. From 2014 to 2016, Gollhofer was dean of the faculty of economics and behavioural sciences. From 2007 to 2009, Gollhofer held the position of chairman of the European College of Sport Science. From 2000 to 2002, Gol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebellum
The cerebellum (: cerebella or cerebellums; Latin for 'little brain') is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or even larger. In humans, the cerebellum plays an important role in motor control and cognition, cognitive functions such as attention and language as well as emotion, emotional control such as regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established. The human cerebellum does not initiate movement, but contributes to motor coordination, coordination, precision, and accurate timing: it receives input from sensory systems of the spinal cord and from other parts of the brain, and integrates these inputs to fine-tune motor activity. Cerebellar damage produces disorders in fine motor skill, fine movement, sense of balance, equilibrium, list of human positions, posture, and motor learning in humans. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |