|
Interlinking Of Rivers In India
The Indian rivers interlinking project is a proposed large-scale civil engineering project that aims to effectively manage water resources in India by linking rivers using a network of reservoirs and canals to enhance irrigation and groundwater recharge and reduce persistent floods in some parts and water shortages in other parts of the country.Jayanta Bandyopadhyay and Shama Perveen (2003)The Interlinking of Indian Rivers: Some Questions on the Scientific, Economic and Environmental Dimensions of the Proposal IIM Calcutta, IISWBM, Kolkata India accounts for 18% of global population and about 4% of the world's water resources. One of the solutions to solve the country's water woes is to link its rivers and lakes. The interlinking project has been split into three parts: a northern Himalayan rivers interlink component, a southern peninsular component, and starting in 2005, an intrastate river-linking component. The project is being managed by India's National Water Developme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interbasin Transfer
Interbasin transfer or transbasin diversion are (often hyphenated) terms used to describe man-made conveyance schemes which move water from one river basin where it is available, to another basin where water is less available or could be utilized better for human development. The purpose of such water resource engineering schemes can be to alleviate water shortages in the receiving basin, to generate electricity, or both. Rarely, as in the case of the Glory River which diverted water from the Tigris to Euphrates River in modern Iraq, interbasin transfers have been undertaken for political purposes. While ancient water supply examples exist, the first modern developments were undertaken in the 19th century in Australia, India and the United States, feeding large cities such as Denver and Los Angeles. Since the 20th century many more similar projects have followed in other countries, including Israel and China, and contributions to the Green Revolution in India and hydropower deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport In India
Transport in India consists of transport by land, water and air. Road transport is the primary mode of transport for most Indian citizens, and India's road transport systems are among the most heavily used in the world. India's road network is the largest, and the busiest in the world, transporting 8.225 billion passengers and over 980 million tonnes of cargo annually, as of 2015. India's rail network is the fourth largest and second busiest in the world, transporting 8.09 billion passengers and 1.20 billion tonnes of freight annually, Aviation in India is broadly divided into military and civil aviation which is the fastest-growing aviation market in the world (IATA data). India's waterways network, in the form of rivers, canals, backwaters and creeks, is the ninth largest waterway network in the world. Freight transport by waterways is highly under utilised in India with the total cargo moved (in tonne kilometres) by inland waterways being 0.1 percent of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanuri Lakshmana Rao
Kanuru Lakshmana Rao (15 July 1902 – 18 May 1986) was an Indian Civil engineer and a Padma Bhushan awardee who served as the Union Minister of Irrigation & Power and Member of Parliament for Vijayawada from 1962 to 1977. Personal life and education Rao was born in a Telugu Niyogi brahmin family in Kankipadu, Krishna district, Andhra Pradesh. His father was a village attorney. He lost his father when he was nine years old. His High school studies went well in SKPVV HINDU HIGH SCHOOL, VIJAYAWADA. He lost vision in one eye due to injury during childhood days while playing at school. He studied Intermediate (+2) at Presidency College, Madras. He took his B.E. degree in Civil Engineering from College of Engineering, Guindy and he was the first student from College of Engineering, Guindy to obtain a master's degree in engineering. Later he took his PhD in 1939 from the University of Birmingham in the United Kingdom. Honours In 1963, Rao was awarded the Padma Bhush ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odisha
Odisha (), formerly Orissa (List of renamed places in India, the official name until 2011), is a States and union territories of India, state located in East India, Eastern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, eighth-largest state by area, and the List of states and union territories of India by population, eleventh-largest by population, with over 41 million inhabitants. The state also has the third-largest population of Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes, Scheduled Tribes in India. It neighbours the states of Jharkhand and West Bengal to the north, Chhattisgarh to the west, and Andhra Pradesh to the south. Odisha has a coastline of along the Bay of Bengal in the ''Indian Ocean''. The region is also known as Utkaḷa and is mentioned by this name in India's national anthem, Jana Gana Mana. The language of Odisha is Odia language, Odia, which is one of the Classical languages of India. The ancient kingdom of Kalinga (historical region), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (ISO 15919, ISO: , , AP) is a States and union territories of India, state on the East Coast of India, east coast of southern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, seventh-largest state and the List of states and union territories of India by population, tenth-most populous in the country. Telugu language, Telugu is the most widely spoken language in the state, as well as its official language. Amaravati is the state capital, while the largest city is Visakhapatnam. Andhra Pradesh shares borders with Odisha to the northeast, Chhattisgarh to the north, Karnataka to the southwest, Tamil Nadu to the south, Telangana to northwest and the Bay of Bengal to the east. It has the Coastline of Andhra Pradesh, third-longest coastline in India at about . Archaeological evidence indicates that Andhra Pradesh has been continuously inhabited for over 247,000 years, from early archaic Hominini, hominins to Neolithic settlements. The earliest r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drought
A drought is a period of drier-than-normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, and O. Zolina, 2021Water Cycle Changes. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1055–1210, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.010. A drought can last for days, months or years. Drought often has large impacts on the ecosystems and agriculture of affected regions, and causes harm to the local economy. Annua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
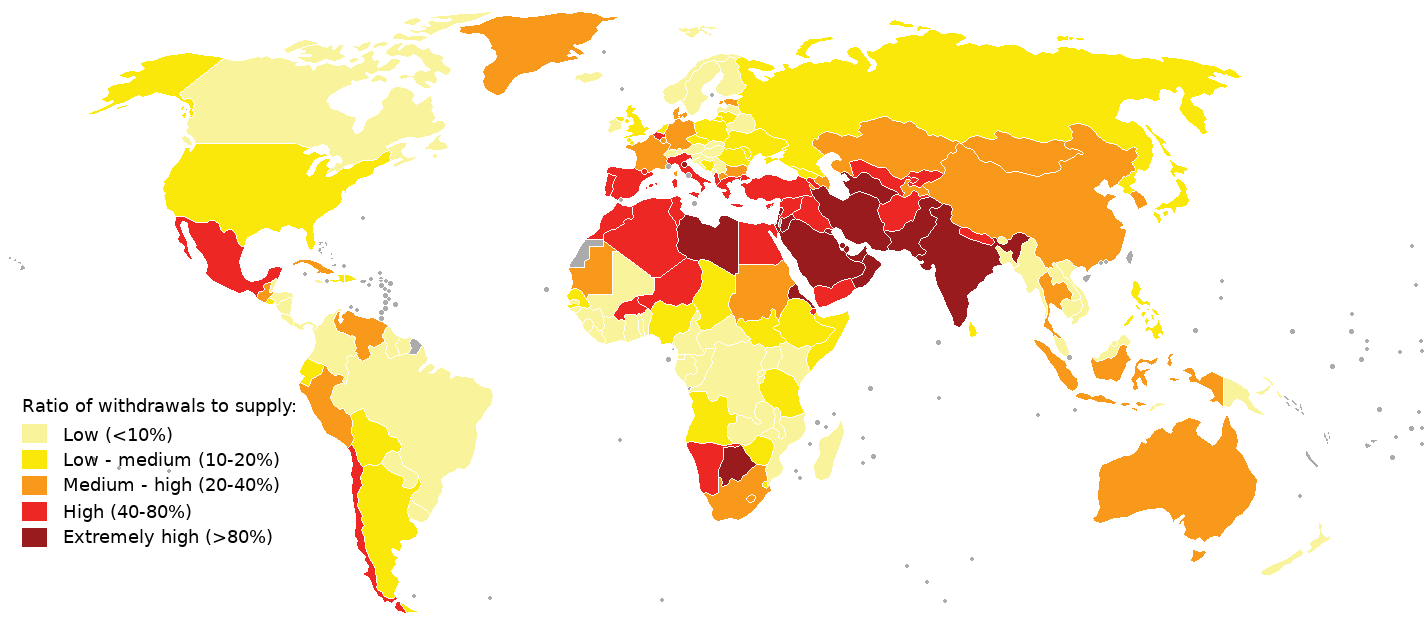
Water Scarcity
Water scarcity (closely related to water stress or water crisis) is the lack of fresh water resources to meet the standard water demand. There are two types of water scarcity. One is ''physical.'' The other is ''economic water scarcity''. Physical water scarcity is where there is not enough water to meet all demands. This includes water needed for ecosystems to function. Regions with a desert climate often face physical water scarcity. Central Asia, West Asia, and North Africa are examples of arid areas. Economic water scarcity results from a lack of investment in infrastructure or technology to draw water from rivers, aquifers, or other water sources. It also results from weak human capacity to meet water demand.Caretta, M.A., A. Mukherji, M. Arfanuzzaman, R.A. Betts, A. Gelfan, Y. Hirabayashi, T.K. Lissner, J. Liu, E. Lopez Gunn, R. Morgan, S. Mwanga, and S. Supratid, 2022Chapter 4: Water InClimate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Asia
South Asia is the southern Subregion#Asia, subregion of Asia that is defined in both geographical and Ethnicity, ethnic-Culture, cultural terms. South Asia, with a population of 2.04 billion, contains a quarter (25%) of the world's population. As commonly conceptualised, the modern State (polity), states of South Asia include Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, the Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka, with Afghanistan also often included, which may otherwise be classified as part of Central Asia. South Asia borders East Asia to the northeast, Central Asia to the northwest, West Asia to the west and Southeast Asia to the east. Apart from Southeast Asia, Littoral South Asia, Maritime South Asia is the only subregion of Asia that lies partly within the Southern Hemisphere. The British Indian Ocean Territory and two out of Atolls of Maldives, 26 atolls of the Maldives in South Asia lie entirely within the Southern Hemisphere. Topographically, it is dominated by the Indian subcontinent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakistan. (subscription required) Although the terms "Indian subcontinent" and "South Asia" are often also used interchangeably to denote a wider region which includes, in addition, Bhutan, the Maldives, Nepal and Sri Lanka, the "Indian subcontinent" is more of a geophysical term, whereas "South Asia" is more geopolitical. "South Asia" frequently also includes Afghanistan, which is not considered part of the subcontinent even in extended usage.Jim Norwine & Alfonso González, ''The Third World: states of mind and being'', pages 209, Taylor & Francis, 1988, Quote: ""The term "South Asia" also signifies the Indian Subcontinent""Raj S. Bhopal, ''Ethnicity, race, and health in multicultural societies'', pages 33, Oxford University Press, 2007, ; Q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Cotton
General Sir Arthur Thomas Cotton (15 May 1803 – 24 July 1899) was a British army officer and irrigation engineer who worked in the Madras Presidency. Cotton devoted his life to the construction of irrigation and navigation canals throughout British India. He helped many people by building the Dowleswaram Barrage (Rajahmundry), the Prakasam Barrage, and the Kurnool Cuddappah Canal (K. C. Canal). His dream was only partially realised, but he is still honoured in Andhra Pradesh and parts of Tamil Nadu for his efforts. The Sir Arthur Cotton Museum has been built in his honour in Rajamahendravaram, Andhra Pradesh. The museum holds approximately one hundred images and 15 machine tools that Cotton used when constructing the barrage in Andhra Pradesh from 1847 to 1852. He was the father of the evangelist Elizabeth Hope. Biography Arthur Cotton was born on 15May 1803 at Combermere, the tenth son of Henry Calvely Cotton, uncle of the noted Field Marshal Lord Combermere, and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Raj
The British Raj ( ; from Hindustani language, Hindustani , 'reign', 'rule' or 'government') was the colonial rule of the British The Crown, Crown on the Indian subcontinent, * * lasting from 1858 to 1947. * * It is also called Crown rule in India, * * * * or direct rule in India. * Quote: "Mill, who was himself employed by the British East India company from the age of seventeen until the British government assumed direct rule over India in 1858." * * The region under British control was commonly called India in contemporaneous usage and included areas directly administered by the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom, which were collectively called ''Presidencies and provinces of British India, British India'', and areas ruled by indigenous rulers, but under British British paramountcy, paramountcy, called the princely states. The region was sometimes called the Indian Empire, though not officially. As ''India'', it was a founding member of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Rivers Of India
With a land area of consisting of diverse ecosystems, India has many river systems and perennial streams. The rivers of India can be classified into four groups – Himalayan, Deccan, Coastal, and Inland drainage. The Himalayan rivers, mainly fed by glaciers and snow melt, arise from the Himalayas. The Deccan rivers system consists of rivers in Peninsular India, that drain into the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea. There are numerous short coastal rivers, predominantly on the West Coast of India, West coast. There are few inland rivers, which do not drain into the sea. Most of the rivers in India originate from the four major water divide, watersheds in India. The Himalayan watershed is the source of majority of the major river systems in India including the three longest rivers–the Ganges, the Brahmaputra and the Indus River, Indus. These three river systems are fed by more than 5000 glaciers. The Aravalli range in the north-west serves the origin of few of the rivers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |