|
Interleukin-13
Interleukin 13 (IL-13) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IL13'' gene. IL-13 was first cloned in 1993 and is located on chromosome 5q31.1 with a length of 1.4kb. It has a mass of 13 kDa and folds into 4 alpha helical bundles. The secondary structural features of IL-13 are similar to that of Interleukin 4 (IL-4); however it only has 25% sequence identity to IL-4 and is capable of IL-4 independent signaling. IL-13 is a cytokine secreted by T helper type 2 (Th2) cells, CD4 cells, natural killer T cell, mast cells, basophils, eosinophils and nuocytes. Interleukin-13 is a central regulator in IgE synthesis, goblet cell hyperplasia, mucus hypersecretion, airway hyperresponsiveness, fibrosis and chitinase up-regulation. It is a mediator of allergic inflammation and different diseases including asthma, and atopic dermatitis. Functions IL-13 has effects on immune cells that are similar to those of the closely related cytokine IL-4. However, IL-13 is suspected to be the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin-13 Receptor
The interleukin-13 receptor is a type I cytokine receptor, binding Interleukin-13. It consists of two subunits, encoded by IL13RA1 and IL4R, respectively. These two genes encode the proteins IL-13Rα1 and IL-4Rα. These form a dimer with IL-13 binding to the IL-13Rα1 chain and IL-4Rα stabilises this interaction. This IL-13 receptor can also instigate Interleukin-4, IL-4 signalling. In both cases this occurs via activation of the Janus kinase (JAK)/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STAT protein, STAT) pathway, resulting in phosphorylation of STAT6. Phosphorylated STAT6 dimerises and acts as a transcription factor activating many genes, such as eotaxin. There is also another receptor that can bind IL-13: IL-13Rα2 encoded by the IL13RA2 gene. This binds IL-13 with very high affinity (and can therefore sequester it) but does not allow IL-4 binding. It acts as a negative regulator of both IL-13 and IL-4, however the mechanism of this is still undetermined. Funct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eosinophil
Eosinophils, sometimes called eosinophiles or, less commonly, acidophils, are a variety of white blood cells and one of the immune system components responsible for combating multicellular parasites and certain infections in vertebrates. Along with mast cells and basophils, they also control mechanisms associated with allergy and asthma. They are granulocytes that develop during hematopoiesis in the bone marrow before migrating into blood, after which they are terminally differentiated and do not multiply. These cells are eosinophilic or "acid-loving" due to their large acidophilic cytoplasmic granules, which show their affinity for acids by their affinity to coal tar dyes: Normally transparent, it is this affinity that causes them to appear brick-red after staining with eosin, a red dye, using the Romanowsky method. The staining is concentrated in small granules within the cellular cytoplasm, which contain many chemical mediators, such as eosinophil peroxidase, ribonucl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematopoiesis
Haematopoiesis (; ; also hematopoiesis in American English, sometimes h(a)emopoiesis) is the formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cells. In a healthy adult human, roughly ten billion () to a hundred billion () new blood cells are produced per day, in order to maintain steady state levels in the peripheral circulation.Semester 4 medical lectures at Uppsala University 2008 by Leif Jansson Process Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) reside in the medulla of the bone ( bone marrow) and have the unique ability to give rise to all of the different mature blood cell types and tissues. HSCs are self-renewing cells: when they differentiate, at least some of their daughter cells remain as HSCs so the pool of stem cells is not depleted. This phenomenon is called asymmetric division. The other daughters of HSCs ( myeloid and lymphoid progenitor cells) can follow any of the other diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
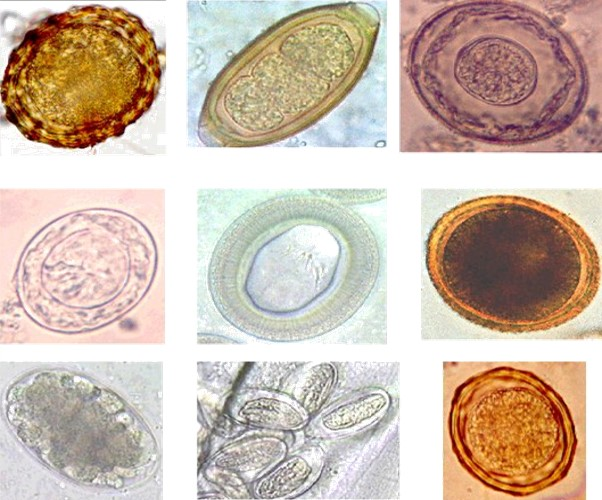
Helminth
Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are a polyphyletic group of large macroparasites; adults can generally be seen with the naked eye. Many are intestinal worms that are soil-transmitted and infect the gastrointestinal tract. Other parasitic worms such as schistosomes reside in blood vessels. Some parasitic worms, including leeches and monogeneans, are ectoparasites thus, they are not classified as helminths, which are endoparasites. Parasitic worms live in and feed in living hosts. They receive nourishment and protection while disrupting their hosts' ability to absorb nutrients. This can cause weakness and disease in the host, and poses a global health and economic problem. Parasitic worms cannot reproduce entirely within their host's body; they have a life cycle that includes some stages that need to take place outside of the host. Helminths are able to survive in their mammalian hosts for many years due to their ability to manipulate the host's immune respon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitism
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson characterised parasites' way of feeding as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the broomrapes. There are six major parasitic strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropredation. One major axis of classification concerns invasiveness: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type 2 Inflammation
Type 2 inflammation is a pattern of immune response. Its physiological function is to defend the body against helminths, but a dysregulation of the type 2 inflammatory response has been implicated in the pathophysiology of several diseases. Molecular biology IL-25, IL-33, and TSLP are alarmins released from damaged epithelial cells. These cytokines mediate the activation of type 2 T helper cells (Th2 cells), type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2 cells), and dendritic cells. Th2 cells and ILC2 cells secrete IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13. IL-4 further drives CD4+ T cell differentiation towards the Th2 subtype and induces isotype switching to IgE in B cells. IL-4 and IL-13 stimulate trafficking of eosinophils to the site of inflammation, while IL-5 promotes both eosinophil trafficking and production. Dysregulation in human disease Type 2 inflammation has been implicated in several chronic diseases: * Asthma * Atopic dermatitis * Chronic sinusitis with nasal polyps * Eosinophilic esop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucin 5AC
Mucin-5AC (MUC-5AC) is a protein that is encoded by the ''MUC5AC'' gene in humans. MUC-5AC is a large gel-forming glycoprotein. In the respiratory tract, it protects against infection by binding to inhaled pathogens, which are subsequently removed by mucociliary clearance. Overproduction of MUC-5AC can contribute to diseases such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and has also been associated with greater protection against influenza infection. Clinical relevance This gene has been linked to mucus hypersecretion in the respiratory tract and is associated to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by chronic respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. GOLD defines COPD as a heterogeneous lung condition characterized by chronic respiratory s ... (COPD). References External links PDBe-KBprovides an overview of all the structure information available in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goblet Cell Metaplasia
Goblet cells are simple columnar epithelial cells that secrete gel-forming mucins, like mucin 2 in the lower gastrointestinal tract, and mucin 5AC in the respiratory tract. The goblet cells mainly use the merocrine method of secretion, secreting vesicles into a duct, but may use apocrine methods, budding off their secretions, when under stress. The term ''goblet'' refers to the cell's goblet-like shape. The apical portion is shaped like a cup, as it is distended by abundant mucus laden granules; its basal portion lacks these granules and is shaped like a stem. The goblet cell is highly polarized with the nucleus and other organelles concentrated at the base of the cell and secretory granules containing mucin, at the apical surface. The apical plasma membrane projects short microvilli to give an increased surface area for secretion. Goblet cells are typically found in the respiratory, reproductive and lower gastrointestinal tract and are surrounded by other columnar cells. Bia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Janus Kinase
Janus kinase (JAK) is a family of intracellular, non-receptor tyrosine kinases that transduce cytokine-mediated signals via the JAK-STAT pathway. They were initially named "just another kinase" 1 and 2 (since they were just two of many discoveries in a PCR-based screen of kinases), but were ultimately published as "Janus kinase". The name is taken from the two-faced Roman god of beginnings, endings and duality, Janus, because the JAKs possess two near-identical phosphate-transferring domains. One domain exhibits the kinase activity, while the other negatively regulates the kinase activity of the first. Family The four JAK family members are: * Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) * Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) * Janus kinase 3 (JAK3) * Tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) Transgenic mice that do not express JAK1 have defective responses to some cytokines, such as interferon-gamma. JAK1 and JAK2 are involved in type II interferon (interferon-gamma) signalling, whereas JAK1 and TYK2 are involved in type I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription Factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The function of TFs is to regulate—turn on and off—genes in order to make sure that they are Gene expression, expressed in the desired Cell (biology), cells at the right time and in the right amount throughout the life of the cell and the organism. Groups of TFs function in a coordinated fashion to direct cell division, cell growth, and cell death throughout life; cell migration and organization (body plan) during embryonic development; and intermittently in response to signals from outside the cell, such as a hormone. There are approximately 1600 TFs in the human genome. Transcription factors are members of the proteome as well as regulome. TFs work alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STAT6
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) is a transcription factor that belongs to the Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STAT) family of proteins. The proteins of STAT family transmit signals from a receptor complex to the nucleus and activate gene expression. Similarly as other STAT family proteins, STAT6 is also activated by growth factors and cytokines. STAT6 is mainly activated by cytokines interleukin-4 and interleukin-13. Molecular biology In the human genome, STAT6 protein is encoded by the STAT6 gene, located on the chromosome 12q13.3-q14.1. The gene encompasses over 19 kb and consists of 23 exons. STAT6 shares structural similarity with the other STAT proteins and is composed of the N-terminal domain, DNA binding domain, SH3- like domain, SH2 domain and transactivation domain (TAD). STAT proteins are activated by the Janus family (JAKs) tyrosine kinases in response to cytokine exposure. STAT6 is activated by cytokines in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |