|
Insoles
A removable shoe insert, otherwise known as a foot orthosis, insole or inner sole, accomplishes many purposes, including daily wear comfort, height enhancement, plantar fasciitis treatment, Arches of the foot, arch support, foot and joint pain relief from arthritis, overuse, injuries, leg length discrepancy, and other causes such as orthopedic correction and athletic performance. Medical use of foot orthoses has been criticized as lacking evidence of benefit, and practice is very inconsistent: reputed podiatrists prescribe completely different orthoses for a single patient. Further, effect of a given design of orthosis varies significantly by patient, and standard practice to personalize prescription is not available. However, evidence is mixed: patients often report at least short-term improvements in comfort, and other studies have found effectiveness. Fitting patients There are three standard methods for fitting patients: plaster casts, foam box impressions, or three-dimensio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plantar Fasciitis Insoles
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek language, Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes, axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether a vertebrate is a biped or a quadruped, due to the difference in the neuraxis, or if an invertebrate is a non-bilaterian. A non-bilaterian has no anterior or posterior surface for example but can still have a descriptor used such as proximal or distal in relation to a body part that is nearest to, or furthest from its middle. International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standards for subdisciplines of anatomy. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
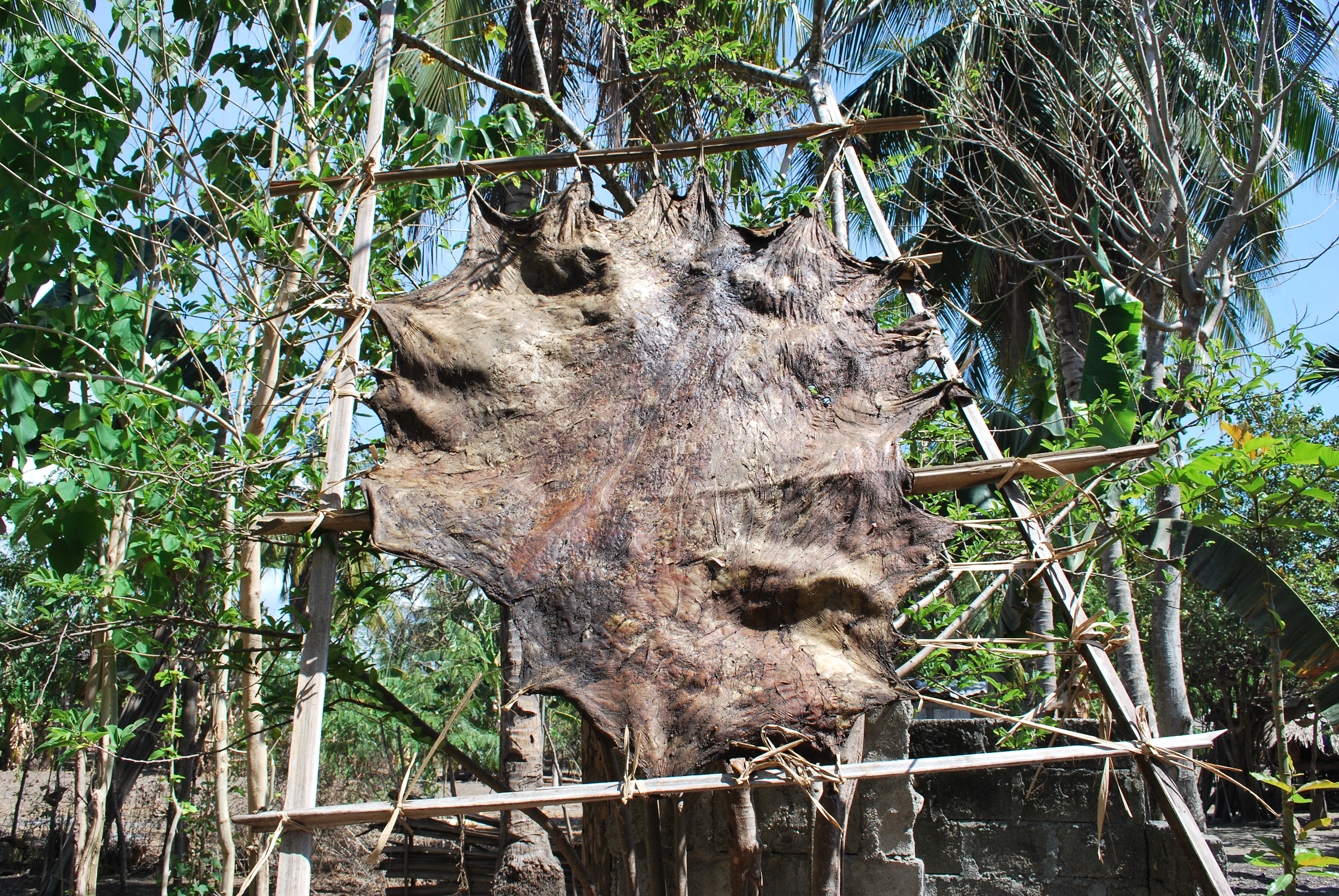
Leather Inner Soles - Upper And Underside
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffalo, pigs and hogs, ostriches, and aquatic animals such as seals and alligators. Leather can be used to make a variety of items, including clothing, footwear, handbags, furniture, tools and sports equipment, and lasts for decades. Leather making has been practiced for more than 7,000 years and the leading producers of leather today are China and India. Critics of tanneries claim that they engage in unsustainable practices that pose health hazards to the people and the environment near them. Production processes The leather manufacturing process is divided into three fundamental subprocesses: preparatory stages, tanning, and crusting. A further subprocess, finishing, can be added into the leather process sequence, but not all leathers receive finishing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis or plantar heel pain is a disorder of the plantar fascia, which is the connective tissue that supports the Arches of the foot, arch of the foot. It results in pain in the heel and Sole (foot), bottom of the foot that is usually most severe with the first steps of the day or following a period of rest. Pain is also frequently brought on by dorsiflexion, bending the foot and toes up towards the shin. The pain typically comes on gradually, and it affects both feet in about one-third of cases. The cause of plantar fasciitis is not entirely clear. Risk factors include overuse, such as from long periods of standing, an increase in exercise, and obesity. It is also associated with pronation of the foot, inward rolling of the foot, a tight Achilles tendon, and a sedentary lifestyle. It is unclear if calcaneal spur, heel spurs have a role in causing plantar fasciitis even though they are commonly present in people who have the condition. Plantar fasciitis is a disorder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arches Of The Foot
The arches of the foot, formed by the tarsal and metatarsal bones, strengthened by ligaments and tendons, allow the foot to support the weight of the body in the erect posture with the least weight. They are categorized as longitudinal and transverse arches. Structure Longitudinal arches The longitudinal arches of the foot can be divided into medial and lateral arches. Medial arch The medial arch is higher than the lateral longitudinal arch. It is made up by the calcaneus, the talus, the navicular, the three cuneiforms (medial, intermediate, and lateral), and the first, second, and third metatarsals. Its summit is at the superior articular surface of the talus, and its two extremities or piers, on which it rests in standing, are the tuberosity on the plantar surface of the calcaneus posteriorly and the heads of the first, second, and third metatarsal bones anteriorly. The chief characteristic of this arch is its elasticity, due to its height and to the number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw-Hill Connect. Webp.274/ref> They are constructed to allow for different degrees and types of movement. Some joints, such as the knee, elbow, and shoulder, are self-lubricating, almost frictionless, and are able to withstand compression and maintain heavy loads while still executing smooth and precise movements. Other joints such as suture (joint), sutures between the bones of the skull permit very little movement (only during birth) in order to protect the brain and the sense organs. The connection between a tooth and the jawbone is also called a joint, and is described as a fibrous joint known as a gomphosis. Joints are classified both structurally and functionally. Joints play a vital role in the human body, contributing to movement, sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthritis
Arthritis is a general medical term used to describe a disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, Joint effusion, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints. In certain types of arthritis, other organs such as the skin are also affected. Onset can be gradual or sudden. There are several types of arthritis. The most common forms are osteoarthritis (most commonly seen in weightbearing joints) and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis usually occurs as an individual ages and often affects the hips, knees, shoulders, and fingers. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that often affects the hands and feet. Other types of arthritis include gout, lupus, and septic arthritis. These are inflammatory based types of rheumatic disease. Early treatment for arthritis commonly includes resting the affected joint and conservative measures such as heating or icing. Weight Weight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthopedic
Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics ( alternative spelling orthopaedics) is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal trauma, spine diseases, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, tumors and congenital disorders. Etymology Nicholas Andry coined the word in French as ', derived from the Ancient Greek words ("correct", "straight") and ("child"), and published ''Orthopedie'' (translated as ''Orthopædia: Or the Art of Correcting and Preventing Deformities in Children'') in 1741. The word was assimilated into English as ''orthopædics''; the ligature ''æ'' was common in that era for ''ae'' in Greek- and Latin-based words. As the name implies, the discipline was initially developed with attention to children, but the correction of spinal and bone deformities in all stages of life eventually became the cornerstone of orthopedic pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Podiatrist
A podiatrist ( ) is a medical professional devoted to the treatment of disorders of the foot, ankle, and related structures of the leg. The term originated in North America but has now become the accepted term in the English-speaking world for all practitioners of podiatric medicine. The word chiropodist was previously used in the United States, but it is now regarded as antiquated. In the United States, podiatrists are educated and licensed as Doctors of Podiatric Medicine (DPM). The preparatory education of most podiatric physicians—similar to the paths of traditional physicians ( MD or DO)—includes four years of undergraduate work, followed by four years in an accredited podiatric medical school, followed by a three- or four-year hospital-based podiatry residency. Optional one- to two-year fellowship in foot and ankle reconstruction, surgical limb salvage, sports medicine, plastic surgery, pediatric foot and ankle surgery, and wound care is also available. Podiatric me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plaster Cast
A plaster cast is a copy made in plaster of another 3-dimensional form. The original from which the cast is taken may be a sculpture, building, a face, a pregnant belly, a fossil or other remains such as fresh or fossilised footprints – particularly in palaeontology (a track of dinosaur footprints made in this way can be seen outside the Oxford University Museum of Natural History). Sometimes a blank block of plaster itself was carved to produce mock-ups or first drafts of sculptures (usually relief sculptures) that would ultimately be sculpted in stone, by measuring exactly from the cast, for example by using a pointing machine. These are still described as plaster casts. Examples of these by John Flaxman may be found in the central rotunda of the library at University College London, and elsewhere in the university's collections. It may also describe a finished original sculpture made out of plaster, though these are rarer. Method Plaster is applied to the original ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
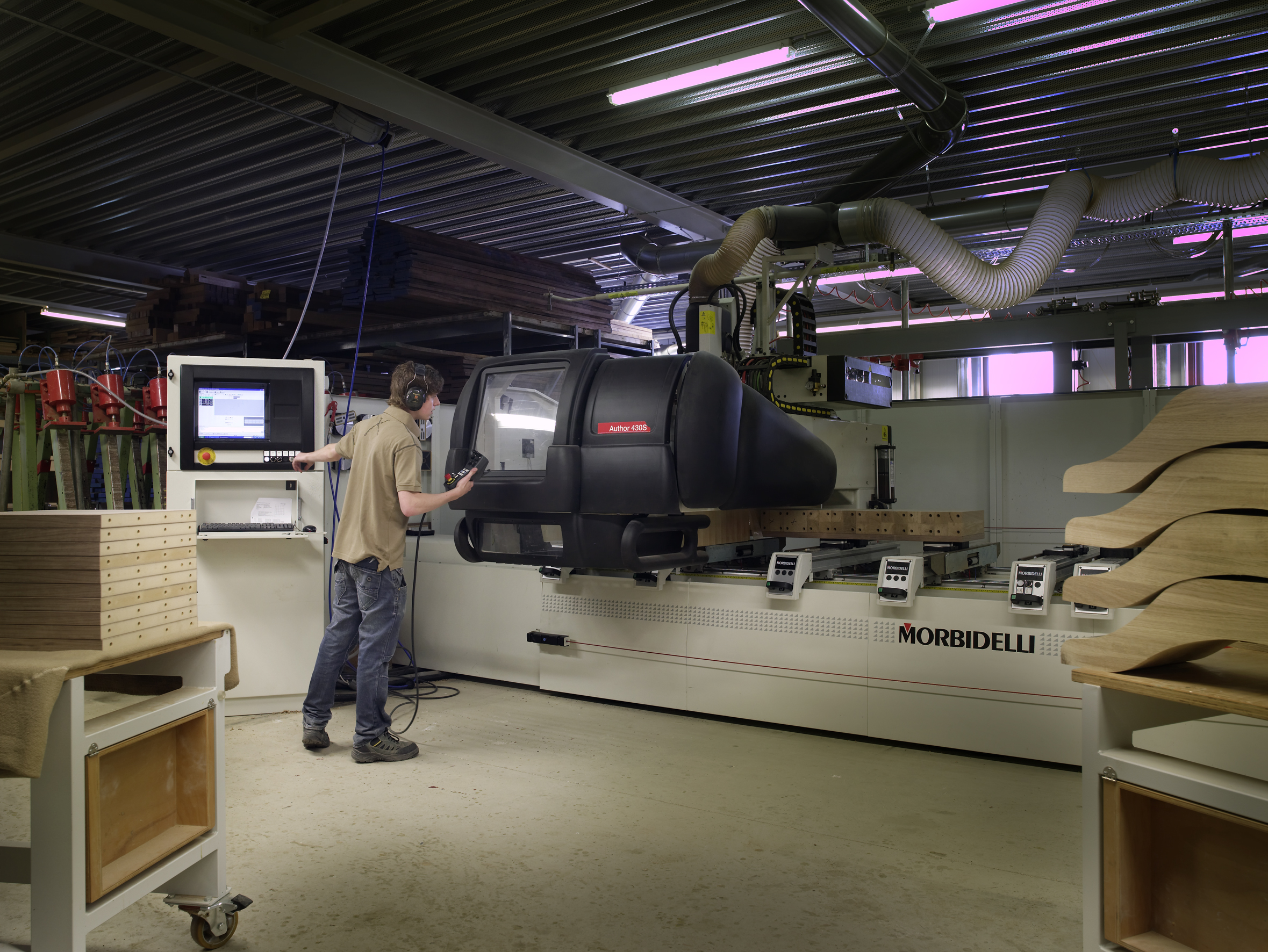
CNC Machine
Computer numerical control (CNC) or CNC machining is the automated control of machine tools by a computer. It is an evolution of numerical control (NC), where machine tools are directly managed by data storage media such as punched cards or punched tape. Because CNC allows for easier programming, modification, and real-time adjustments, it has gradually replaced NC as computing costs declined. A CNC machine is a motorized maneuverable tool and often a motorized maneuverable platform, which are both controlled by a computer, according to specific input instructions. Instructions are delivered to a CNC machine in the form of a sequential program of machine control instructions such as G-code and M-code, and then executed. The program can be written by a person or, far more often, generated by graphical computer-aided design (CAD) or computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software. In the case of 3D printers, the part to be printed is "sliced" before the instructions (or the progra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparison Of Orthotics
Podiatrists mold custom orthotics to address patients' foot malformations. There are multiple means developed to create the basis for the molds, including plaster casts, foam box impressions, and three-dimensional computer imaging. The molds are used to create custom inserts that tend to be firm, flexible, and relatively soft. History Over the years podiatrists have developed numerous means to create the basis for their molds, plaster casts, foam box impressions, or three-dimensional computer imaging. None is very accurate: all produce proper fit under 80% of the time. Traditionally, they were created from plaster casts made from the patient's foot. These casts were made by wrapping dipped plaster or fiberglass strips around the foot to capture the form, then letting it dry and harden. Once the cast was hardened, the doctor would carefully remove it from the patient's foot and ship the cast, along with a prescription, to an orthotics lab which would use the negative of the cast to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthotics
Orthotics () is a medical specialty that focuses on the design and application of orthoses, sometimes known as braces, calipers, or splints. An is "an externally applied device used to influence the structural and functional characteristics of the neuromuscular and skeletal systems." Orthotists are medical professionals who specialize in designing orthotic devices such as braces or foot orthoses. Classification Orthotic devices are classified into four areas of the body according to the international classification system (ICS): orthotics of the lower extremities, orthotics of the upper extremities, orthotics for the trunk, and orthotics for the head. Orthoses are also classified by function: paralysis orthoses and relief orthoses. Under the International Standard terminology, orthoses are classified by an acronym describing the anatomical joints they support. Some examples include KAFO, or knee-ankle-foot orthoses, which span the knee, ankle, and foot; TLSO, or thor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |