|
Industrial Web Theory
Industrial web theory is the military concept that an enemy's industrial power can be attacked at nodes of vulnerability, and thus the enemy's ability to wage a lengthy war can be severely limited, as well as his morale—his will to resist. The theory was formulated by American airmen at the Air Corps Tactical School (ACTS) in the 1930s. The term "industrial web theory" cannot be found in any official United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) doctrine.McMullen, John K. ''The United States Strategic Bombing Survey and Air Force Doctrine''. Graduate thesis, School of Advanced Airpower Studies, Air University, Maxwell Air Force Base, Alabama. 2001. Instead, the term was coined in the 1930s by Donald Wilson (general), Donald Wilson, an instructor at ACTS, to cover the concept then under development. Theory Prior theories of bombing were developed by Italian General Giulio Douhet, British Sir Hugh Trenchard, 1st Viscount Trenchard, Hugh Trenchard and American Colonel Billy Mitchell (genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morale
Morale ( , ) is the capacity of a group's members to maintain belief in an institution or goal, particularly in the face of opposition or hardship. Morale is often referenced by authority figures as a generic value judgment of the willpower, obedience, and self-discipline of a group tasked with performing duties assigned by a superior. According to Alexander H. Leighton, "morale is the capacity of a group of people to pull together persistently and consistently in pursuit of a common purpose". With good morale, a force will be less likely to give up or surrender. Morale is usually assessed at a collective, rather than an individual level. In wartime, civilian morale is also important. Definition Military history experts have not agreed on a precise definition of "morale". Clausewitz's comments on the subject have been described as "deliberately vague" by modern scholars. George Francis Robert Henderson, a widely read military author of the pre-World War I era, viewed mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Headquarters Air Force
The United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) was the aerial warfare service component of the United States Army between 1926 and 1941. After World War I, as early aviation became an increasingly important part of modern warfare, a philosophical rift developed between more traditional ground-based army personnel and those who felt that aircraft were being underutilized and that air operations were being stifled for political reasons unrelated to their effectiveness. The USAAC was renamed from the earlier United States Army Air Service on 2 July 1926, and was part of the larger United States Army. The Air Corps became the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) on 20 June 1941, giving it greater autonomy from the Army's middle-level command structure. During World War II, although not an administrative echelon, the Air Corps (AC) remained as one of the combat arms of the Army until 1947, when it was legally abolished by legislation establishing the Department of the Air Force. The Air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
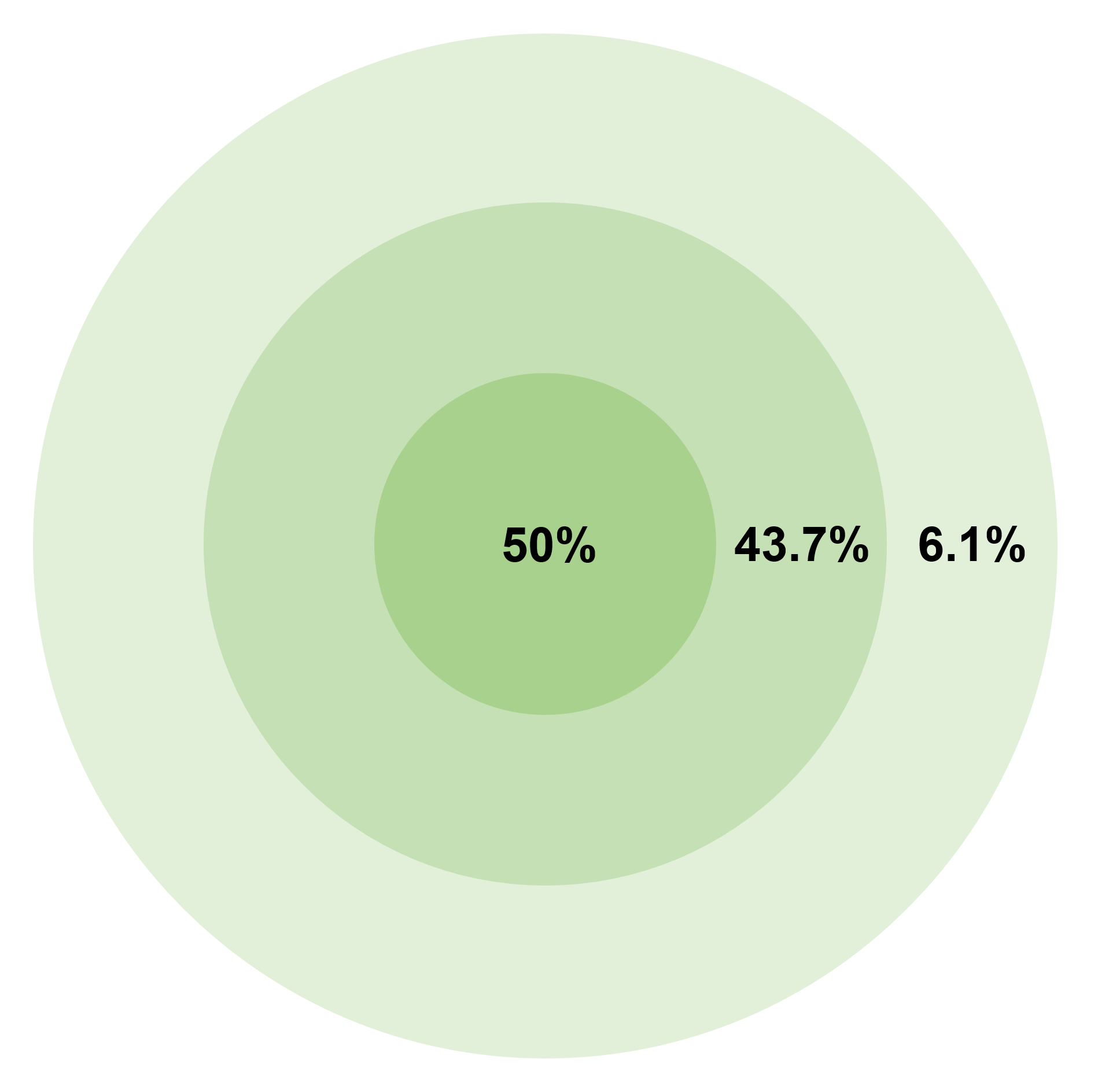
Circular Error Probable
Circular error probable (CEP),Circular Error Probable (CEP), Air Force Operational Test and Evaluation Center Technical Paper 6, Ver 2, July 1987, p. 1 also circular error probability or circle of equal probability, is a measure of a weapon system's Accuracy and precision, precision in the military science of ballistics. It is defined as the radius of a circle, centered on the aimpoint, that is expected to enclose the landing points of 50% of the Round (firearms), rounds; said otherwise, it is the median error radius, which is a 50% confidence interval. That is, if a given munitions design has a CEP of 100 m, when 100 munitions are targeted at the same point, an average of 50 will fall within a circle with a radius of 100 m about that point. There are associated concepts, such as the DRMS (distance root mean square), which is the square root of the average squared distance error, a form of the standard deviation. Another is the R95, which is the radius of the circle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanley Baldwin
Stanley Baldwin, 1st Earl Baldwin of Bewdley (3 August 186714 December 1947), was a British statesman and Conservative politician who was prominent in the political leadership of the United Kingdom between the world wars. He was prime minister on three occasions, from May 1923 to January 1924, from November 1924 to June 1929 and from June 1935 to May 1937. Born to a prosperous family in Bewdley, Worcestershire, Baldwin was educated at Hawtreys, Harrow School and Trinity College, Cambridge. He joined the family iron- and steel-making business and entered the House of Commons in 1908 as the member for Bewdley, succeeding his father Alfred. He was Financial Secretary to the Treasury (1917–1921) and President of the Board of Trade (1921–1922) in the coalition ministry of David Lloyd George and then rose rapidly. In 1922, Baldwin was one of the prime movers in the withdrawal of Conservative support from Lloyd George; he subsequently became Chancellor of the Exchequer in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Bomber Will Always Get Through
"The bomber will always get through" was a phrase used by Stanley Baldwin in a 1932 speech "A Fear for the Future" given to the British Parliament. His speech stated that contemporary bomber aircraft had the performance necessary to conduct a strategic bombing campaign that would destroy a country's cities and there was little that could be done in response. It concluded that the conduct of future wars would require one to "kill more women and children more quickly than the enemy if you want to save yourselves." At the time of the speech aircraft performance was rapidly improving and new techniques and construction methods were producing ever-larger aircraft. For a time, this resulted in a performance gap where multi-engine aircraft outperformed the single-engine fighter aircraft that would have to intercept them. This gap could be further widened through the use of night bombing, which made interception practically impossible. This state of affairs was relatively short-lived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
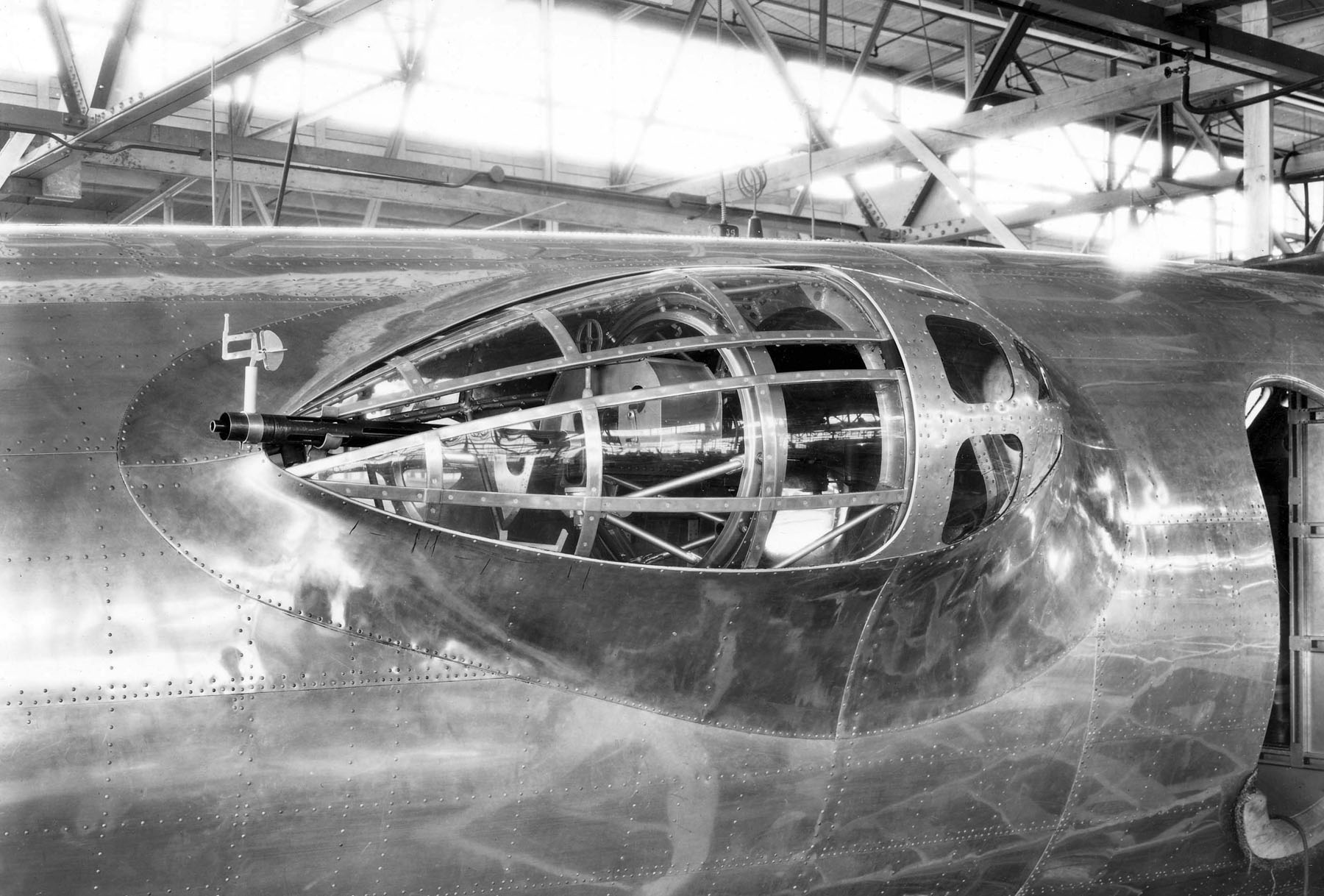
B-17 Flying Fortress
The Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress is an American four-engined heavy bomber aircraft developed in the 1930s for the United States Army Air Corps (USAAC). A fast and high-flying bomber, the B-17 dropped more bombs than any other aircraft during World War II, used primarily in the European Theater of Operations, United States Army, European Theater of Operations. It is the List of most-produced aircraft, third-most produced bomber in history, behind the American four-engined Consolidated B-24 Liberator and the German multirole, twin-engined Junkers Ju 88. The B-17 was also employed in transport, anti-submarine warfare, and search and rescue roles. In a USAAC competition, Boeing, Boeing's prototype Model 299/XB-17 outperformed two other entries but crashed, losing the initial 200-bomber contract to the Douglas B-18 Bolo. Still, the Air Corps ordered 13 more B-17s for further evaluation, which were introduced into service in 1938. The B-17 evolved through numerous Boeing B-17 Flyin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeing Y1B-17 In Flight
The Boeing Company, or simply Boeing (), is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and product support services. Boeing is among the largest global aerospace manufacturers; it is the fourth-largest defense contractor in the world based on 2022 revenue and is the largest exporter in the United States by dollar value. Boeing was founded by William E. Boeing in Seattle, Washington, on July 15, 1916. The present corporation is the result of the merger of Boeing with McDonnell Douglas on August 1, 1997. As of 2023, the Boeing Company's corporate headquarters is located in the Crystal City neighborhood of Arlington County, Virginia. The company is organized into three primary divisions: Boeing Commercial Airplanes (BCA), Boeing Defense, Space & Security (BDS), and Boeing Global Services (BGS). In 2021, Boeing recorded $62.3billion in sales. Boei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fighter Aircraft
Fighter aircraft (early on also ''pursuit aircraft'') are military aircraft designed primarily for air-to-air combat. In military conflict, the role of fighter aircraft is to establish air supremacy, air superiority of the battlespace. Domination of the airspace above a battlefield permits bombers and attack aircraft to engage in tactical bombing, tactical and strategic bombing of enemy targets, and helps prevent the enemy from doing the same. The key performance features of a fighter include not only its firepower but also its high speed and maneuverability relative to the target aircraft. The success or failure of a combatant's efforts to gain air superiority hinges on several factors including the skill of its pilots, the tactical soundness of its doctrine for deploying its fighters, and the numbers and performance of those fighters. Many modern fighter aircraft also have secondary capabilities such as ground-attack aircraft, ground attack and some types, such as fighter-b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bomber
A bomber is a military combat aircraft that utilizes air-to-ground weaponry to drop bombs, launch aerial torpedo, torpedoes, or deploy air-launched cruise missiles. There are two major classifications of bomber: strategic and tactical. Strategic bombing is done by heavy bombers primarily designed for long-range bombing missions against strategic targets to diminish the enemy's ability to wage war by limiting access to resources through crippling infrastructure, reducing industrial output, or inflicting massive civilian casualties to an extent deemed to force surrender. Tactical bombing is aimed at countering enemy military activity and in supporting offensive operations, and is typically assigned to smaller aircraft operating at shorter ranges, typically near the troops on the ground or against enemy shipping. Bombs were first dropped from an aircraft during the Italo-Turkish War, with the first major deployments coming in the World War I, First World War and World War II, Seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeppelin
A Zeppelin is a type of rigid airship named after the German inventor Ferdinand von Zeppelin () who pioneered rigid airship development at the beginning of the 20th century. Zeppelin's notions were first formulated in 1874Eckener 1938, pp. 155–157. and developed in detail in 1893.Dooley 2004, p. A.187. They were patented in German Empire, Germany in 1895 and in the United States in 1899. After the outstanding success of the Zeppelin design, the word ''zeppelin'' came to be commonly used to refer to all forms of rigid airships. Zeppelins were first flown commercially in 1910 by Deutsche Luftschiffahrts-AG (DELAG), the world's first airline in revenue service. By mid-1914, DELAG had carried over 10,000 fare-paying passengers on over 1,500 flights. During World War I, the German military made extensive use of Zeppelins German strategic bombing during World War I, as bombers and aerial reconnaissance in World War I, as scouts. Numerous bombing raids on United Kingdom of Great Brita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |