|
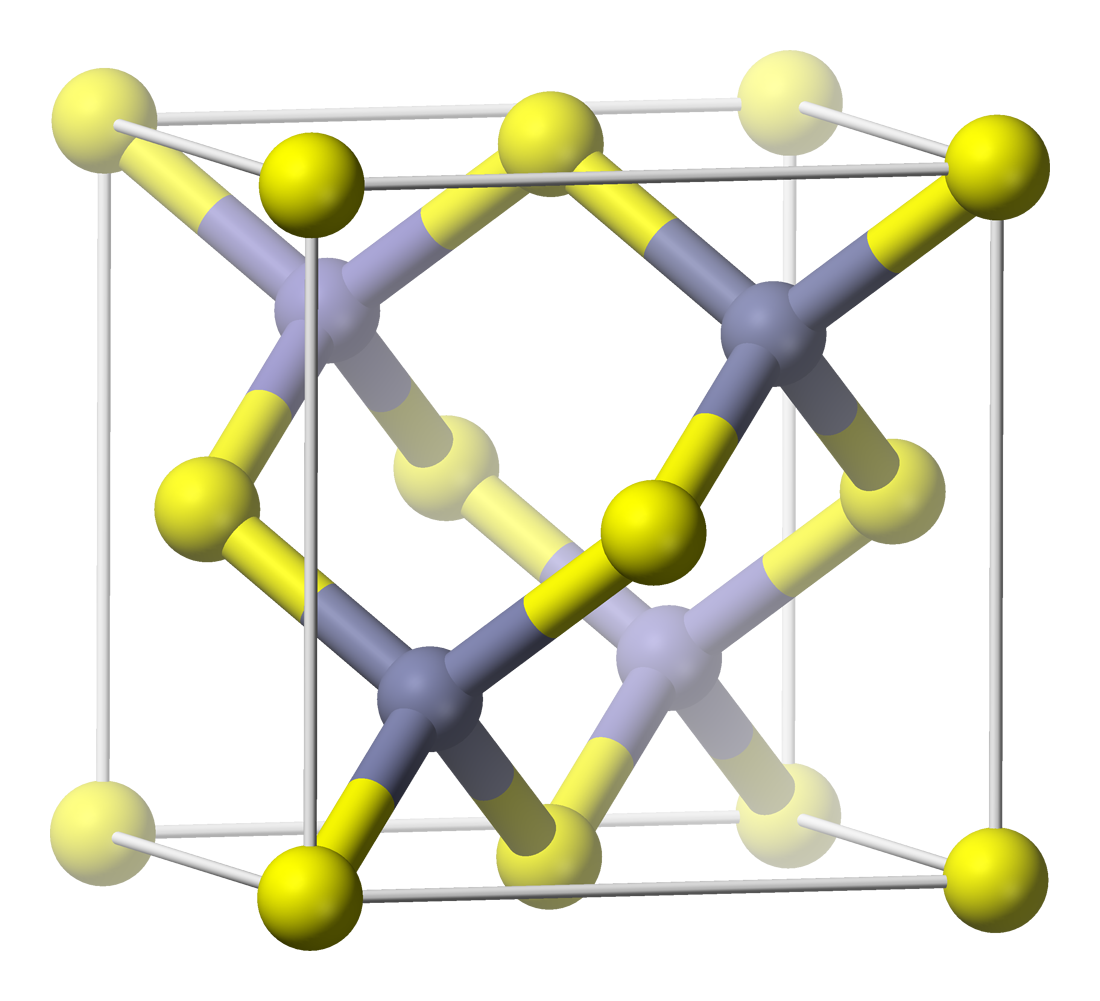
Indium(III) Hydroxide
Indium(III) hydroxide is the chemical compound with the formula . Its prime use is as a precursor to indium(III) oxide, . It is sometimes found as the rare mineral dzhalindite. __TOC__ Structure Indium(III) hydroxide has a cubic structure, space group Im3, a distorted structure. Preparation and reactions Neutralizing a solution containing an salt such as indium nitrate () or a solution of indium trichloride () gives a white precipitate that on aging forms indium(III) hydroxide. A thermal decomposition of freshly prepared shows the first step is the conversion of to cubic indium(III) hydroxide. The precipitation of indium hydroxide was a step in the separation of indium from zincblende ore by Reich and Richter, the discoverers of indium. Indium(III) hydroxide is amphoteric, like gallium(III) hydroxide () and aluminium hydroxide Aluminium hydroxide, , is found as the mineral gibbsite (also known as hydrargillite) and its three much rarer polymorphs: bayerite, doyle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boric Acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen orthoborate, trihydroxidoboron or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white powder, that dissolves in water, and occurs in nature as the mineral sassolite. It is a weak acid that yields various borate anions and salt (chemistry), salts, and can react with Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols to form borate esters. Boric acid is often used as an antiseptic, insecticide, flame retardant, neutron absorber, or precursor to other boron compounds. The term "boric acid" is also used generically for any oxyacid of boron, such as metaboric acid and tetraboric acid . History Orthoboric acid was first prepared by Wilhelm Homberg (1652–1715) from borax, by the action of mineral acids, and was given the name ("sedative salt of Homberg"). However, boric acid and borates have been used since the time of the ancient Greece, anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Decomposition
Thermal decomposition, or thermolysis, is a chemical decomposition of a substance caused by heat. The decomposition temperature of a substance is the temperature at which the substance chemically decomposes. The reaction is usually endothermic as heat is required to break chemical bonds in the compound undergoing decomposition. If decomposition is sufficiently exothermic, a positive feedback loop is created producing thermal runaway and possibly an explosion or other chemical reaction. Decomposition temperature definition A simple substance (like water) may exist in equilibrium with its thermal decomposition products, effectively halting the decomposition. The equilibrium fraction of decomposed molecules increases with the temperature. Since thermal decomposition is a kinetic process, the observed temperature of its beginning in most instances will be a function of the experimental conditions and sensitivity of the experimental setup. For a rigorous depiction of the process, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indium Compounds
Indium is a chemical element; it has symbol In and atomic number 49. It is a silvery-white post-transition metal and one of the softest elements. Chemically, indium is similar to gallium and thallium, and its properties are largely intermediate between the two. It was discovered in 1863 by Ferdinand Reich and Hieronymous Theodor Richter by spectroscopic methods and named for the indigo blue line in its spectrum. Indium is used primarily in the production of flat-panel displays as indium tin oxide (ITO), a transparent and conductive coating applied to glass. It is also used in the semiconductor industry, in low-melting-point metal alloys such as solders and soft-metal high-vacuum seals. It is produced exclusively as a by-product during the processing of the ores of other metals, chiefly from sphalerite and other zinc sulfide ores. Indium has no biological role and its compounds are toxic when inhaled or injected into the bloodstream, although they are poorly absorbed foll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium Hydroxide
Aluminium hydroxide, , is found as the mineral gibbsite (also known as hydrargillite) and its three much rarer polymorphs: bayerite, doyleite, and nordstrandite. Aluminium hydroxide is amphoteric, i.e., it has both basic and acidic properties. Closely related are aluminium oxide hydroxide, AlO(OH), and aluminium oxide or alumina (), the latter of which is also amphoteric. These compounds together are the major components of the aluminium ore bauxite. Aluminium hydroxide also forms a gelatinous precipitate in water. Structure is built up of double layers of hydroxyl groups with aluminium ions occupying two-thirds of the octahedral holes between the two layers. Four polymorphs are recognized. All feature layers of octahedral aluminium hydroxide units, with hydrogen bonds between the layers. The polymorphs differ in terms of the stacking of the layers. All forms of crystals are hexagonal : * gibbsite is also known as γ- or α- * bayerite is also known as α- or ''β ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallium(III) Hydroxide
Gallium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is formed as a gel following the addition of ammonia to salts.Anthony John Downs, (1993), ''Chemistry of Aluminium, Gallium, Indium, and Thallium'', Springer, It is also found in nature as the rare mineral söhngeite which is reported to contain octahedrally coordinated gallium atoms. Crystal Structure of a new mineral söhngeite, J.D. Scott, The American Mineralogist, (1971), 56, 355 Gallium hydroxide is amphoteric. In strongly acidic conditions, the gallium ion An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ..., is formed. In strongly basic conditions, (tetrahydroxogallate(III)) is formed. Salts of are sometimes called gallates. References Hydroxides Gallium compounds {{inorganic-compou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphoteric
In chemistry, an amphoteric compound () is a molecule or ion that can react both as an acid and as a base. What exactly this can mean depends on which definitions of acids and bases are being used. Etymology and terminology Amphoteric is derived from the Greek word () meaning "both". Related words in acid-base chemistry are amphichromatic and amphichroic, both describing substances such as acid-base indicators which give one colour on reaction with an acid and another colour on reaction with a base. Amphiprotism Amphiprotism is exhibited by compounds with both Brønsted acidic and basic properties. A prime example is H2O. Amphiprotic molecules can either donate or accept a proton (). Amino acids (and proteins) are amphiprotic molecules because of their amine () and carboxylic acid () groups. Ampholytes Ampholytes are zwitterions ‒ molecules or ions that contain both acidic and basic functional groups. Amino acids have both a basic group and an acidic group . Of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hieronymous Theodor Richter
Hieronymus Theodor Richter (21 November 1824 – 25 September 1898) was a German chemist. In 1863, while working at the Freiberg University of Mining and Technology, he co-discovered indium with Ferdinand Reich. Life From 1843 to 1847, he studied at the Bergakademie Freiberg (with Carl Friedrich Plattner, among others) and became a member of the Corps Saxo-Borussia Freiberg. He then worked for the Freiberg Hüttenwerken, since 1853 as a metallurgist chemist. From 1875 to 1896, Theodor Richter worked as director of the Mining Academy and was the last of the Freiberg directors elected for lifetime. In 1890 he was elected a member of the Leopoldina. He died September 25, 1898, in Freiberg, Saxony Freiberg () is a college town, university and former mining town in Saxony, Germany, with around 41,000 inhabitants. The city lies in the foreland of the Ore Mountains, in the Saxon urbanization axis, which runs along the northern edge of the ..., at the age of 73. Honours In 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand Reich
Ferdinand Reich (19 February 1799 – 27 April 1882) was a German chemist who co-discovered indium in 1863 with Hieronymous Theodor Richter. Reich was born in Bernburg, Anhalt-Bernburg, Holy Roman Empire and died in Freiberg, Saxony, Freiberg. He was color blindness, color blind, or could only see in whites and blacks, and that is why Theodor Richter became his science partner. Richter would examine the colors produced in reactions that they studied. Reich and Richter ended up isolating the indium, creating a small supply, although it was later found in more regions. They isolated the indium at the Technische Universität Bergakademie Freiberg, Freiberg University of Mining and Technology in Germany. In 1803, Laplace and Gauss both derived that, if a heavy object is dropped from a height h at latitude \Phi, and the earth rotates from west to east with angular velocity \Omega, then the object would be deflected to the east by a distance of d=2 / 3 \Omega \cos (\Phi) \sqrt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zincblende
Sphalerite is a sulfide mineral with the chemical formula . It is the most important ore of zinc. Sphalerite is found in a variety of deposit types, but it is primarily in sedimentary exhalative, Mississippi-Valley type, and volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits. It is found in association with galena, chalcopyrite, pyrite (and other sulfides), calcite, dolomite, quartz, rhodochrosite, and fluorite. German geologist Ernst Friedrich Glocker discovered sphalerite in 1847, naming it based on the Greek word ''sphaleros'', meaning "deceiving", due to the difficulty of identifying the mineral. In addition to zinc, sphalerite is an ore of cadmium, gallium, germanium, and indium. Miners have been known to refer to sphalerite as ''zinc blende'', ''black-jack'', and ''ruby blende''. Marmatite is an opaque black variety with a high iron content. Crystal habit and structure Sphalerite crystallizes in the face-centered cubic zincblende crystal structure, which was named after the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indium Trichloride
Indium(III) chloride is the chemical compound with the formula which forms a tetrahydrate. This salt is a white, flaky solid with applications in organic synthesis as a Lewis acid. It is also the most available soluble derivative of indium. This is one of three known indium chlorides. Synthesis and structure Being a relatively electropositive metal, indium reacts quickly with chlorine to give the trichloride. Indium trichloride is very soluble and deliquescent. A synthesis has been reported using an electrochemical cell in a mixed methanol-benzene solution. Like and , crystallizes as a layered structure consisting of a close-packed chloride arrangement containing layers of octahedrally coordinated In(III) centers,Egon Wiberg, Arnold Frederick Holleman (2001) ''Inorganic Chemistry'', Elsevier a structure akin to that seen in .Wells, A.F. Structural Inorganic Chemistry, Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1984. . In contrast, crystallizes as dimers containing . Molten conducts elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium Hydroxide
Aluminium hydroxide, , is found as the mineral gibbsite (also known as hydrargillite) and its three much rarer polymorphs: bayerite, doyleite, and nordstrandite. Aluminium hydroxide is amphoteric, i.e., it has both basic and acidic properties. Closely related are aluminium oxide hydroxide, AlO(OH), and aluminium oxide or alumina (), the latter of which is also amphoteric. These compounds together are the major components of the aluminium ore bauxite. Aluminium hydroxide also forms a gelatinous precipitate in water. Structure is built up of double layers of hydroxyl groups with aluminium ions occupying two-thirds of the octahedral holes between the two layers. Four polymorphs are recognized. All feature layers of octahedral aluminium hydroxide units, with hydrogen bonds between the layers. The polymorphs differ in terms of the stacking of the layers. All forms of crystals are hexagonal : * gibbsite is also known as γ- or α- * bayerite is also known as α- or ''β ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indium Nitrate
Indium(III) nitrate is a nitrate salt of indium which forms various hydrates. Only the pentahydrate has been crystallographically verified. Other hydrates are also reported in literature, such as the trihydrate. Production and reactions Indium(III) nitrate hydrate is produced by the dissolution of indium metal in concentrated nitric acid followed by evaporation of the solution: : The hydrate first decomposes to a basic salt and then to indium(III) oxide at 240 °C. Anhydrous indium(III) nitrate is claimed to be produced by the reaction of anhydrous indium(III) chloride and dinitrogen pentoxide. In the presence of excess nitrate ions, indium(III) nitrate converts to the n(NO3)4sup>− ion. The hydrolysis of indium(III) nitrate yields indium(III) hydroxide. It also reacts with sodium tungstate Sodium tungstate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2WO4. This white, water-soluble solid is the sodium salt of tungstic acid. It is useful as a source of tungsten for chemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |