|
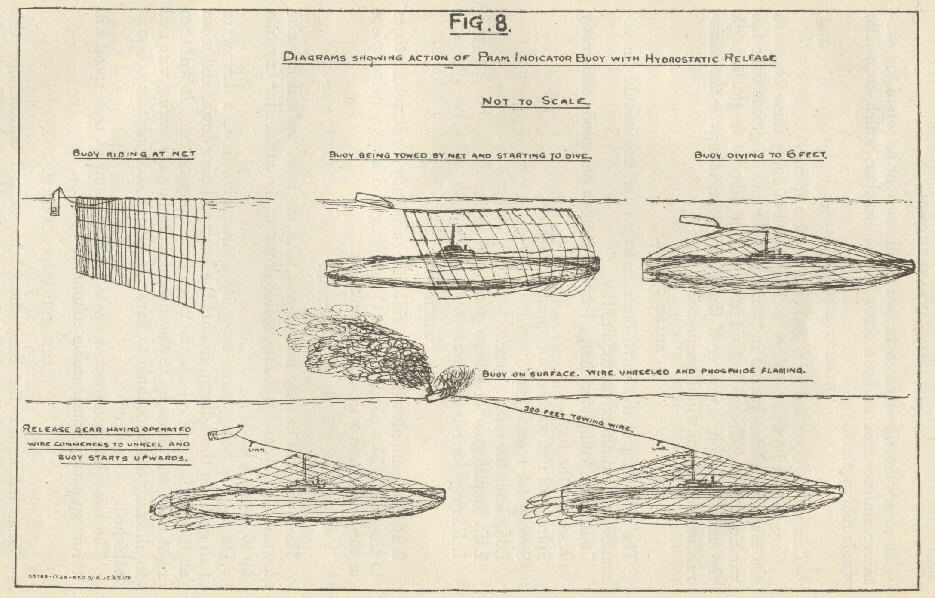
Indicator Net
Constructed using light steel nets, indicator nets were often anchored at various depths to the sea bed around Allied naval bases during both world wars. They were intended to entangle U-boat traffic of the enemy, even though the submarines often managed to disentangle themselves and escape before being blown up by depth charges. Predominantly deployed by the Royal Navy as a means of discouraging enemy submarines from entering Allied waters, indicator nets were used extensively during World War I. Individual nets were sometimes as much as in length. Instead of being used as the sole anti-submarine measure, indicator nets were often mixed with extensive minefields and patrolling warships. Sometimes mines were attached directly to the nets, thus reducing submarine survival chances. After a submarine became entangled in the net, a marker buoy attached to the net drifted along the water's surface indicating an enemy below. The first example of indicator nets causing the destruct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uboot Netz 1
U-boat (German: ''U-Boot'') is a German military submarine of World War I and II. U-boat or U-Boot may also refer to: Games Board games * ''U-Boat'' (game), a board game published by Avalon Hill in 1959 * ''U-Boat'' (wargame), a board game published in 1977 by Tabletop Games Video games * ''U-boat'' (video game), a 1994 submarine simulation video game * ''Uboat'' (video game), a 2024 submarine simulation video game Software *Das U-Boot, computer software, a GNU GPL boot loader Transport *U-boat, a nickname for the GE Universal Series of diesel locomotives built by General Electric *Southern Railway's U and U1 class locomotives, nicknamed "U-boats" *U-boat, an Australian class of interurban railcars, otherwise known as U sets *U-boat, a nickname for the WAGR U Class steam locomotives built by the North British Locomotive Company in 1942 Other *U-Boot (beer cocktail) A U-boot is a beer cocktail that is made by placing a shot of vodka into a glass of beer, typica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
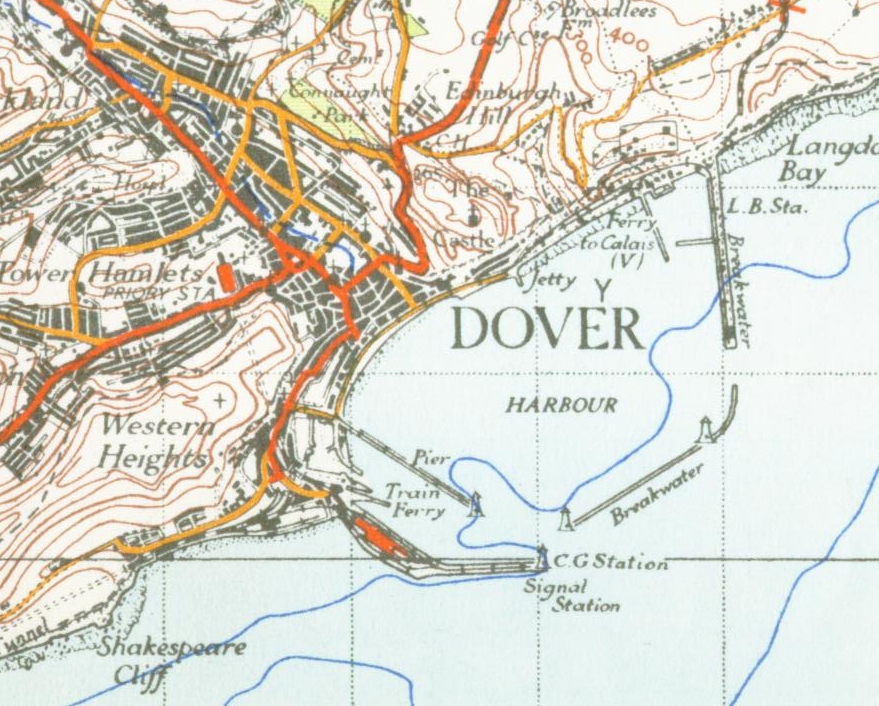
Dover
Dover ( ) is a town and major ferry port in Kent, southeast England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies southeast of Canterbury and east of Maidstone. The town is the administrative centre of the Dover District and home of the Port of Dover. Archaeological finds have revealed that the area has always been a focus for peoples entering and leaving Great Britain, Britain. The name derives from the River Dour that flows through it. In recent times the town has undergone transformations with a high-speed rail link to London, new retail in town with St James' area opened in 2018, and a revamped promenade and beachfront. This followed in 2019, with a new 500m Pier to the west of the Harbour, and new Marina unveiled as part of a £330m investment in the area. It has also been a point of destination for many English Channel migrant crossings (2018-present), illegal migrant crossings. The Port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-submarine Indicator Loop
An anti-submarine indicator loop was a submerged cable laid on the sea bed and used to detect the passage of enemy submarines. History In the early years of World War I submarines were fearful, one-sided weapons because they were invisible. In July 1915 Arthur Balfour replaced Winston Churchill as First Lord of the Admiralty. Balfour appreciated the importance of science, so he established a Board of Invention and Research (BIR), composed of a three-man central committee supported by an eminent consulting panel. The remits of Section II of the panel, the members of which included physicists Ernest Rutherford and William Henry Bragg, included anti-submarine measures. The panel concluded that the most promising approach was to listen for submarines, so they sought to improve hydrophones. Bragg soon moved to the hydrophone research centre HMS Tarlair at Aberdour on the Firth of Forth (which later relocated to Harwich in Essex). Independently from the BIR, in August 1915, a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unmanned Underwater Vehicle
Unmanned underwater vehicles (UUV), also known as underwater drones, are submersible vehicles that can operate underwater without a human occupant. These vehicles may be divided into two categories: remotely operated underwater vehicles (ROUVs) and autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs). ROUVs are remotely controlled by a human operator. AUVs are automated and operate independently of direct human input. Classifications Remotely operated underwater vehicle Remotely operated underwater vehicle, Remotely Operated Underwater Vehicles (ROUVs) is a subclass of UUVs with the primary purpose of replacing humans for underwater tasks due to the difficult underwater conditions. ROUVs are designed to perform educational or industrial missions. They are manually controlled by an operator to perform tasks that include surveillance and patrolling. The structure of ROUVs disqualify it from being able to operate autonomously. In addition to a camera, actuators, and sensors, ROUVs often incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unmanned Surface Vehicle
An unmanned surface vehicle, unmanned surface vessel or uncrewed surface vessel (USV), colloquially called a drone boat, drone ship or sea drone, is a boat or ship that operates on the surface of the water without a crew. USVs operate with various levels of autonomy, from remote control to fully autonomous surface vehicles (ASV). Regulatory environment The regulatory environment for USV operations is changing rapidly as the technology develops and is more frequently deployed on commercial projects. The Maritime Autonomous Surface Ship UK Industry Conduct Principles and Code of Practice 2020 (V4) has been prepared by the UK Maritime Autonomous Systems Regulatory Working Group (MASRWG) and published by Maritime UK through the Society of Maritime Industries. Organisations that contributed to the development of the MASS Code of Practice include The Maritime & Coastguard Agency (MCA), Atlas Elektronik UK Ltd, AutoNaut, Fugro, the UK Chamber of Shipping, UKHO, Trinity House ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attack On Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Empire of Japan on the United States Pacific Fleet at Naval Station Pearl Harbor, its naval base at Pearl Harbor on Oahu, Territory of Hawaii, Hawaii, on December 7, 1941. At the time, the U.S. was a Neutral powers during World War II, neutral country in World War II. The air raid on Pearl Harbor, which was launched from Aircraft carrier, aircraft carriers, resulted in the U.S. entering the war on the side of the Allies of World War II, Allies on the day following the attack. The Imperial General Headquarters, Japanese military leadership referred to the attack as the Hawaii Operation and Operation AI, and as Operation Z during its planning. The attack on Pearl Harbor was preceded by months of negotiations between the U.S. and Japan over the future of the Pacific Ocean, Pacific. Japanese demands included that the U.S. ABCD line, end its sanctions against Japan, cease aidi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bureau Of Ordnance
The Bureau of Ordnance (BuOrd) was a United States Navy organization, which was responsible for the procurement, storage, and deployment of all naval weapons, between the years 1862 and 1959. History The Bureau of Ordnance was established as part of the Department of the Navy by an act of Congress, on July 5, 1862 (12 Stat. 510). The act split the Navy's existing Bureau of Ordnance and Hydrography (1842–1862) into two entities by transferring hydrographic functions into the newly established Bureau of Navigation. During the early 20th century, BuOrd became involved in the development of aerial weapons. This often led to friction with the Bureau of Aeronautics (BuAer), which had responsibility for the development of Naval aircraft. BuAer's work on "pilotless aircraft," or drones, conflicted with BuOrd's development of guided missiles. After World War II, the Navy examined ways to improve coordination between the two bureaus; ultimately, the decision was made to merge the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
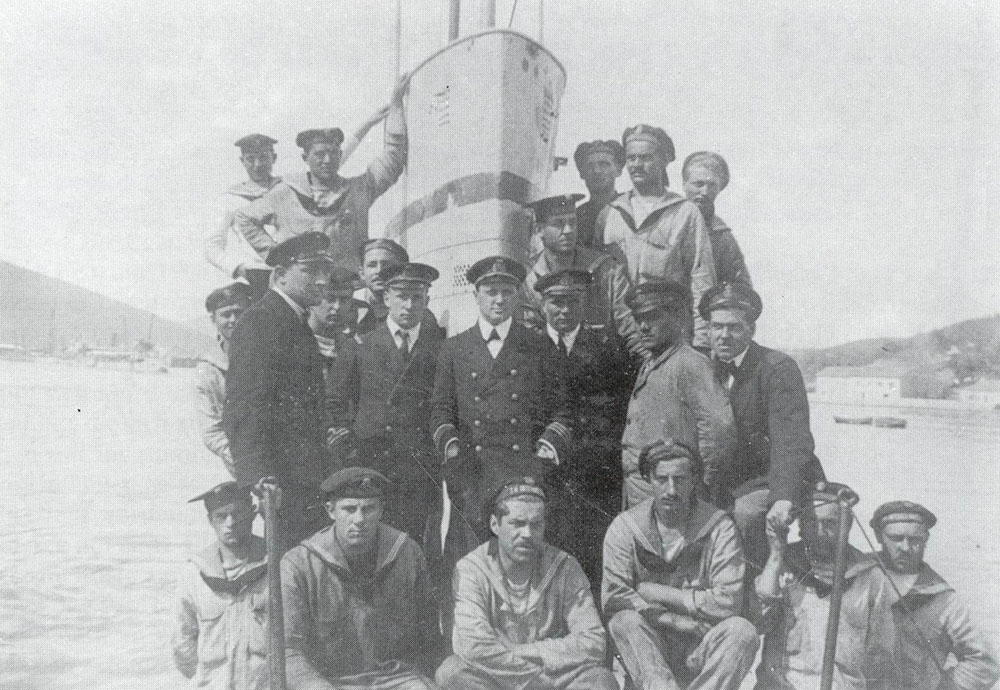
SM U-6 (Austria-Hungary)
SM ''U-6'' or ''U-VI'' was a ''U-5''-class submarine or U-boat built for and operated by the Austro-Hungarian Navy ( or ) before and during the First World War. The submarine was built as part of a plan to evaluate foreign submarine designs, and was the second of three boats of the class built by Whitehead & Co. of Fiume after a design by Irishman John Philip Holland. ''U-6'' was laid down in February 1908 and launched in June 1909. The double-hulled submarine was just over long and displaced between , depending on whether surfaced or submerged. ''U-6''s design had inadequate ventilation and exhaust from her twin gasoline engines often intoxicated the crew. The boat was commissioned into the Austro-Hungarian Navy in July 1910, and served as a training boat—sometimes making as many as ten cruises a month—through the beginning of the First World War in 1914. The submarine had only one wartime success, which was sinking a French destroyer in March 1916. Later that year, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strait Of Otranto
The Strait of Otranto (; ) connects the Adriatic Sea with the Ionian Sea and separates Italy from Albania. Its width between Punta Palascìa, eastern Salento, and Karaburun Peninsula, western Albania, is less than . The strait is named after the Italian city of Otranto. History Since ancient times, the Strait of Otranto was of vital strategic importance. The Romans used it to transport their troops eastwards. The legions marched to Brundisium (now Brindisi), had only a one-day sea voyage to modern Albania territory and then could move eastwards following the Via Egnatia. World War I During World War I, the strait was of strategic significance. The Allied navies of Italy, France, and Great Britain, by blockading the strait, mostly with light naval forces and lightly armed fishing vessels known as drifters, hindered the cautious Austro-Hungarian Navy from freely entering the Mediterranean Sea, and effectively kept them out of the naval theatre of war. The blockade was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otranto Barrage
The Otranto Barrage was an Allied naval blockade of the Strait of Otranto between Brindisi in Italy and Corfu on the Greek side of the Adriatic Sea in the First World War. The operation consisted of over 200 vessels at the height of the blockade. The blockade was intended to prevent the Austro-Hungarian Navy from escaping into the Mediterranean and threatening Allied operations there. The blockade was effective in preventing surface ships from escaping the Adriatic, but it had little or no effect on the submarines based at Cattaro. Blockade attempt The Adriatic is wide at the Otranto Straits. The blockade consisted of over 200 vessels at its height, mainly British and French. A main force of up to 60 drifters were dedicated to anti-submarine operations. The drifters were mostly British and typically armed with a 6-pounder gun and depth charges.''First World War'' – Willmott, H. P., Dorling Kindersley, 2003, Page 186–187 In 1915 when the blockade was begun, two divisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SM U-8
SM ''U-8'' was one of the 329 submarines serving in the Imperial German Navy in World War I. Service history ''U-8'' was engaged in the Naval warfare of World War I, naval warfare and took part in the First Battle of the Atlantic. Fate Trapped in nets, forced to surface and scuttled under gunfire from and , in the English Channel, at position . In June 2015 the submarine's propeller, which had been illegally removed from the wreck, was recovered and presented to the German Navy. It will be exhibited at the Laboe Naval Memorial near Kiel. In July 2016 the wreck of ''U-8'' was officially designated as a protected site. The wreck is a Protected Wreck managed by Historic England. Summary of raiding history References Bibliography * * External links 'U-8 Off South Varne Buoy, English Channel: Undesignated Site Assessment'Historic England project to research First World War Submarines * {{DEFAULTSORT:U0008 World War I submarines of Germany 1911 ships Ships built ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buoy
A buoy (; ) is a buoyancy, floating device that can have many purposes. It can be anchored (stationary) or allowed to drift with ocean currents. History The ultimate origin of buoys is unknown, but by 1295 a seaman's manual referred to navigation buoys in the Guadalquivir River in Spain. To the north there are early medieval mentions of the French / Belgian River Meuse, Maas being buoyed. Such early buoys were probably just timber beams or rafts, but in 1358 there is a record of a barrel buoy in the Dutch Maasmond (also known as the Maas Sluis or Maasgat). The simple barrel was difficult to secure to the seabed, and so a conical ''tonne'' was developed. They had a solid plug at the narrow end through which a mooring ring could be attached. By 1790 the older conical tonne was being replaced by a ''nun'' buoy. This had the same conical section below the waterline as the tonne buoy, but at the waterline a barrel shape was used to allow a truncated cone to be above the water. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |