|
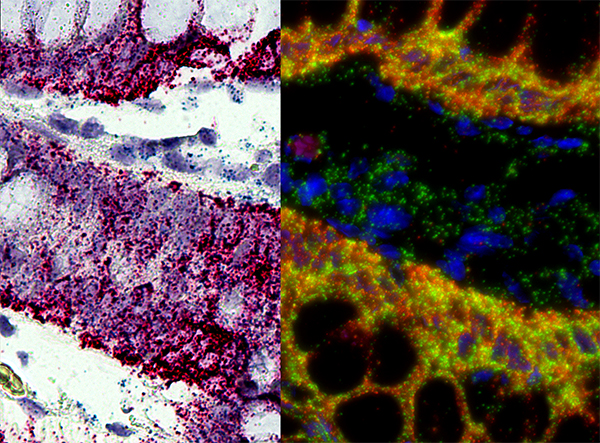
In Situ Hybridisation
''In situ'' hybridization (ISH) is a type of Hybridisation (molecular biology), hybridization that uses a labeled complementary DNA, RNA or modified nucleic acid strand (i.e., a Hybridization probe, probe) to localize a specific DNA or RNA sequence in a portion or section of tissue (biology), tissue (''in situ'') or if the tissue is small enough (e.g., plant seeds, ''Drosophila'' embryos), in the entire tissue (whole mount ISH), in cells, and in circulating tumor cells (CTCs). This is distinct from immunohistochemistry, which usually localizes proteins in tissue sections. In situ hybridization is used to reveal the location of specific nucleic acid sequences on chromosomes or in tissues, a crucial step for understanding the organization, regulation, and function of genes. The key techniques currently in use include ''in situ'' hybridization to mRNA with oligonucleotide and RNA probes (both radio-labeled and hapten-labeled), analysis with light and electron microscopes, whole mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA In Situ Hybridization In FFPE Samples
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) are nucleic acids. The nucleic acids constitute one of the four major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the nucleobase, nitrogenous bases of guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine, denoted by the letters G, U, A, and C) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome. Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is Protein biosynthesis, protein synthesis, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formaldehyde
Formaldehyde ( , ) (systematic name methanal) is an organic compound with the chemical formula and structure , more precisely . The compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde. It is stored as aqueous solutions (formalin), which consists mainly of the hydrate CH2(OH)2. It is the simplest of the aldehydes (). As a precursor to many other materials and chemical compounds, in 2006 the global production of formaldehyde was estimated at 12 million tons per year. It is mainly used in the production of industrial resins, e.g., for particle board and coatings. Formaldehyde also occurs naturally. It is derived from the degradation of serine, dimethylglycine, and lipids. Demethylases act by converting N-methyl groups to formaldehyde. Formaldehyde is classified as a group 1 carcinogen and can cause respiratory and skin irritation upon exposure. Forms Formaldehyde is more complicated than many simple carbon compounds in that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromogenic In Situ Hybridization
Chromogenic ''in situ'' hybridization (CISH) is a cytogenetic technique that combines the chromogenic signal detection method of immunohistochemistry (IHC) techniques with ''in situ'' hybridization. It was developed around the year 2000 as an alternative to fluorescence ''in situ'' hybridization (FISH) for detection of HER-2/neu oncogene amplification. CISH is similar to FISH in that they are both ''in situ'' hybridization techniques used to detect the presence or absence of specific regions of DNA. However, CISH is much more practical in diagnostic laboratories because it uses bright-field microscopes rather than the more expensive and complicated fluorescence microscopes used in FISH. Procedure Probe design Probe design for CISH is very similar to that for FISH with differences only in labelling and detection. FISH probes are generally labelled with a variety of different fluorescent tags and can only be detected under a fluorescence microscope, whereas CISH probes are labell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CEM (German Company)
Cem Sultan (1459–1495) was a prince of the Ottoman Empire. Cem or CEM may also refer to: Colleges * College of Eastern Medicine, a branch of Southern California University of Health Sciences, in Los Angeles, California, US * College of Emergency Medicine, now part of the Royal College of Emergency Medicine * College of Engineering Munnar, an engineering college in Munnar, India * College of Estate Management, former name of the University College of Estate Management Organizations * Commission of Ecosystem Management, a commission of the International Union for Conservation of Nature * Compagnie Électro-Mécanique, a former French electrical engineering manufacturer * Companhia de Electricidade de Macau, a private public utility company of Macau * Curtis Electromusic Specialties, an integrated circuit manufacturer Science and technology * Card Electromechanical, a computer hardware specification related to PCI Express * CEM cell, a cell line derived from human T cells * Ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaline Phosphatase
The enzyme alkaline phosphatase (ALP, alkaline phenyl phosphatase, also abbreviated PhoA) is a phosphatase with the physiological role of dephosphorylating compounds. The enzyme is found across a multitude of organisms, prokaryotes and eukaryotes alike, with the same general function, but in different structural forms suitable to the environment they function in. Alkaline phosphatase is found in the periplasmic space of '' E. coli'' bacteria. This enzyme is heat stable and has its maximum activity at high pH. In humans, it is found in many forms depending on its origin within the body – it plays an integral role in metabolism within the liver and development within the skeleton. Due to its widespread prevalence in these areas, its concentration in the bloodstream is used by diagnosticians as a biomarker in helping determine diagnoses such as hepatitis or osteomalacia. The level of alkaline phosphatase in the blood is checked through the ALP test, which is often par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteinase K
In molecular biology, Proteinase K (, ''protease K'', ''endopeptidase K'', ''Tritirachium alkaline proteinase'', ''Tritirachium album serine proteinase'', ''Tritirachium album proteinase K'') is a broad-spectrum serine protease. The enzyme was discovered in 1974 in extracts of the fungus '' Parengyodontium album'' (formerly '' Engyodontium album or Tritirachium album''). Proteinase K is able to digest hair (keratin), hence, the name "Proteinase K". The predominant site of cleavage is the peptide bond adjacent to the carboxyl group of aliphatic and aromatic amino acids with blocked alpha amino groups. It is commonly used for its broad specificity. This enzyme belongs to Peptidase family S8 (subtilisin). The molecular weight of Proteinase K is 28,900 daltons (28.9 kDa). Enzyme activity Activated by calcium, the enzyme digests proteins preferentially after hydrophobic amino acids (aliphatic, aromatic and other hydrophobic amino acids). Although calcium ions do not affect the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branched DNA Assay
In biology, a branched DNA assay is a signal amplification assay (as opposed to a target amplification assay) that is used to detect nucleic acid molecules. Method A branched DNA assay begins with a dish or some other solid support (e.g., a plastic dipstick). The dish is peppered with small, single stranded DNA molecules (or chains) that stick out into the solution. These are known as capture probe DNA molecules. Next, an extender DNA molecule is added. Each extender has two domains; one that hybridizes to the capture DNA molecule and one that sticks out above the surface. The purpose of the extender is two-fold. First, it creates more available surface area for target DNA molecules to bind, and second, it allows the assay to be easily adapted to detect a variety of target DNA molecules. Once the capture and extender molecules are in place and they have hybridized, the sample can be added. Target molecules in the sample will bind to the extender molecule. This results in a base p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescence Microscopy
A fluorescence microscope is an optical microscope that uses fluorescence instead of, or in addition to, scattering, reflection, and attenuation or absorption, to study the properties of organic or inorganic substances. A fluorescence microscope is any microscope that uses fluorescence to generate an image, whether it is a simple setup like an epifluorescence microscope or a more complicated design such as a confocal microscope, which uses optical sectioning to get better resolution of the fluorescence image. Principle The specimen is illuminated with light of a specific wavelength (or wavelengths) which is absorbed by the fluorophores, causing them to emit light of longer wavelengths (i.e., of a different color than the absorbed light). The illumination light is separated from the much weaker emitted fluorescence through the use of a spectral emission filter. Typical components of a fluorescence microscope are a light source (xenon arc lamp or mercury-vapor lamp are com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoradiography
An autoradiograph is an image on an X-ray film or nuclear emulsion produced by the pattern of decay emissions (e.g., beta particles or gamma rays) from a distribution of a radioactive substance. Alternatively, the autoradiograph is also available as a digital image (digital autoradiography), due to the recent development of scintillation gas detectors or rare-earth phosphorimaging systems. The film or emulsion is apposed to the labeled tissue section to obtain the autoradiograph (also called an autoradiogram). The '' auto-'' prefix indicates that the radioactive substance is within the sample, as distinguished from the case of historadiography or microradiography, in which the sample is marked using an external source. Some autoradiographs can be examined microscopically for localization of silver grains (such as on the interiors or exteriors of cells or organelles) in which the process is termed micro-autoradiography. For example, micro-autoradiography was used to examine whet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digoxigenin
Digoxigenin (DIG) is a steroid found exclusively in the flowers and leaves of the plants ''Digitalis purpurea'', ''Digitalis orientalis'' and ''Digitalis lanata'' (foxgloves), where it is attached to sugars, to form the glycosides (e.g. digoxin, lanatoside C). Uses in biotechnology Digoxigenin is a hapten, a small molecule with high antigenicity, that is used in many molecular biology applications similarly to other popular haptens such as 2,4-Dinitrophenol, biotin, and fluorescein. Typically, digoxigenin is introduced chemically (conjugation) into biomolecules (proteins, nucleic acids) to be detected in further assays. Kd of the digoxigenin-antibody interaction has been estimated at ~12 nM (compare to Kd~0.1pM for the biotin-streptavidin interaction). ;DIG-binding proteins Tinberg et al. designed artificial proteins that bind DIG. Their best binder, DIG10.3, was a 141 amino acid protein that bound DIG with a dissociation constant (Kd) of 541 (+/- 193) pM. Anti-digoxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riboprobe
A Riboprobe, abbreviation of RNA probe, is a segment of labelled RNA that can be used to detect a target mRNA or DNA during in situ hybridization. RNA Hybridization probe, probes can be produced by ''in vitro'' transcription of cloned DNA inserted in a suitable plasmid downstream of a viral promoter. Some bacterial viruses code for their own RNA polymerases, which are highly specific for the viral promoters. Using these enzymes, labeled Nucleoside triphosphate, NTPs, and inserts inserted in both forward and reverse orientations, both sense and antisense riboprobes can be generated from a cloned gene. Since James Watson and Francis Crick revealed the Double-helix, double helix nature of DNA molecule (Watson & Crick, 1953), the hydrogen bonds between the four bases are well known: adenine always binds to thymine and cytosine always binds to guanine. This binding pattern is the basic principle of modern genetic technologies. Joseph Gall and Mary Lou Pardue published a paper in 1969 demo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
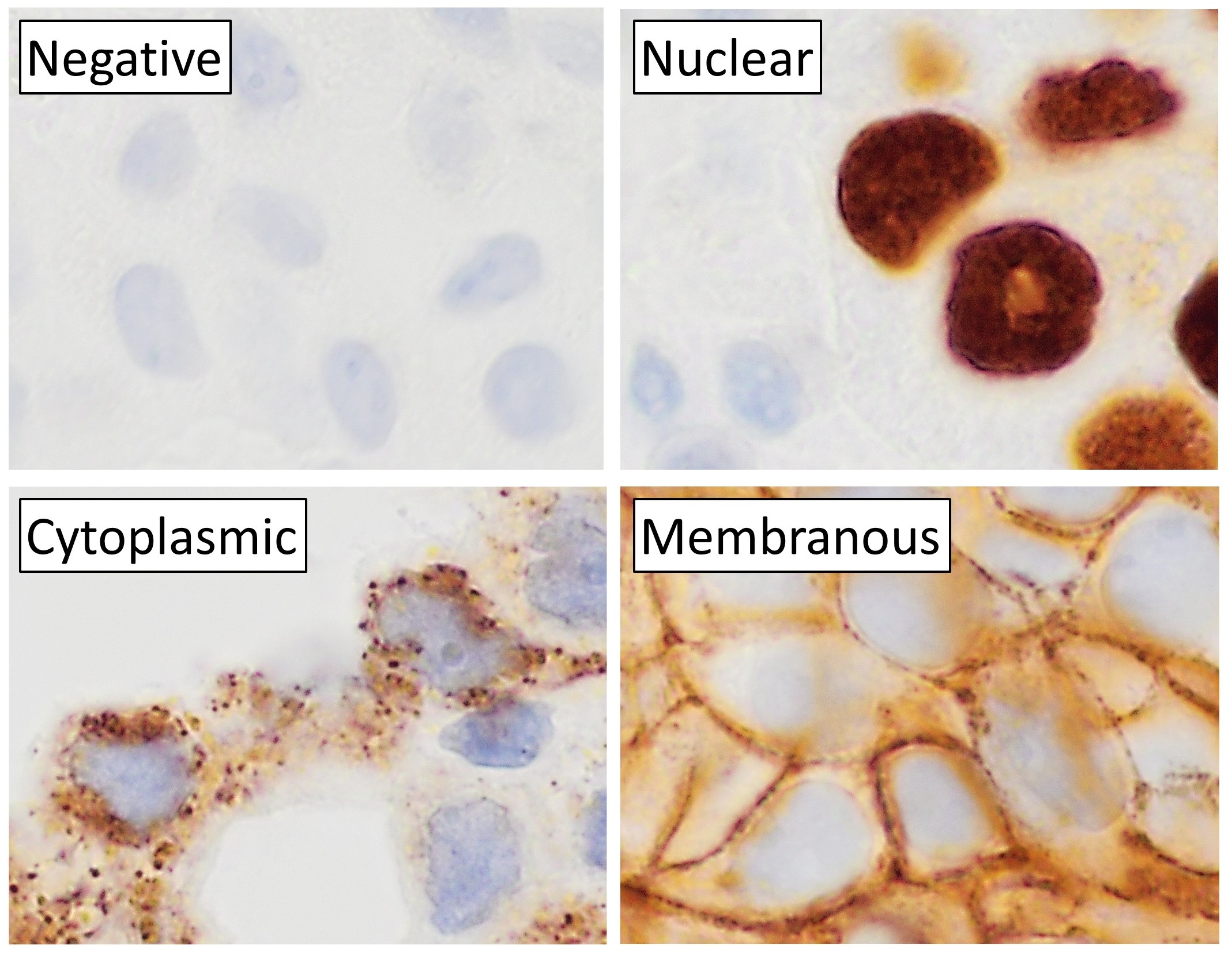
Histochemistry
Immunohistochemistry is a form of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens in cells and tissue, by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. Albert Hewett Coons, Ernest Berliner, Norman Jones and Hugh J Creech was the first to develop immunofluorescence in 1941. This led to the later development of immunohistochemistry. Immunohistochemical staining is widely used in the diagnosis of abnormal cells such as those found in cancerous tumors. In some cancer cells certain tumor antigens are expressed which make it possible to detect. Immunohistochemistry is also widely used in basic research, to understand the distribution and localization of biomarkers and differentially expressed proteins in different parts of a biological tissue. Sample preparation Immunohistochemistry can be performed on tissue that has been fixed and embedded in paraffin, but also cryopreservated (frozen) tissue. Based on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |