|
Imposter Syndrome
Impostor syndrome, also known as impostor phenomenon or impostorism, is a psychological experience in which a person suffers from feelings of intellectual and/or professional fraudulence. One source defines it as "the subjective experience of perceived self-doubt in one's abilities and accomplishments compared with others, despite evidence to suggest the contrary". Those who suffer from impostor syndrome often doubt their skills, talents, or accomplishments. They may have a persistent internalized fear of being exposed as frauds. Despite external evidence of their competence, those experiencing this phenomenon do not believe they deserve their success or luck. They may think that they are deceiving others because they feel as if they are not as intelligent as they outwardly portray themselves to be. Impostor syndrome is not a recognized psychiatric disorder and is not featured in the American Psychiatric Association's Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM-5) nor is it listed as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychiatry
Psychiatry is the medical specialty devoted to the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of deleterious mental disorder, mental conditions. These include matters related to cognition, perceptions, Mood (psychology), mood, emotion, and behavior. Initial psychiatric assessment of a person begins with creating a Medical history, case history and conducting a mental status examination. Laboratory tests, physical examinations, and psychological tests may be conducted. On occasion, neuroimaging or neurophysiological studies are performed. Mental disorders are diagnosed in accordance with diagnostic manuals such as the ''International Classification of Diseases'' (ICD), edited by the World Health Organization (WHO), and the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM), published by the American Psychiatric Association (APA). The fifth edition of the DSM (DSM-5) was published in May 2013. Treatment may include psychotropics (psychiatric medicines), psychotherapy, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunning–Kruger Effect
The Dunning–Kruger effect is a cognitive bias in which people with limited competence in a particular domain overestimate their abilities. It was first described by the psychologists David Dunning and Justin Kruger in 1999. Some researchers also include the opposite effect for high performers: their tendency to underestimate their skills. In popular culture, the Dunning–Kruger effect is often misunderstood as a claim about general overconfidence of people with low intelligence instead of specific overconfidence of people unskilled at a particular task. Numerous similar studies have been done. The Dunning–Kruger effect is usually measured by comparing self-assessment with objective performance. For example, participants may take a quiz and estimate their performance afterward, which is then compared to their actual results. The original study focused on logical reasoning, grammar, and social skills. Other studies have been conducted across a wide range of tasks. They in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Popular Psychology
Popular psychology (sometimes shortened as pop psychology or pop psych) refers to the concepts and theories about human mental life and behavior that are supposedly based on psychology and are considered credible and accepted by the wider populace. The concept is cognate with the human potential movement of the 1950s and 1960s. The term ''pop psychologist'' can be used to describe authors, consultants, lecturers, and entertainers who are widely perceived as being psychologists, not because of their academic credentials, but because they have projected that image or have been perceived in that way in response to their work. The term ''popular psychology'' can also be used when referring to the ''popular psychology industry'', a sprawling network of everyday sources of information about human behavior. The term is often used in a pejorative fashion to describe psychological concepts that appear oversimplified, out of date, unproven, misunderstood or misinterpreted; however, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1978 Introductions
Events January * January 1 – Air India Flight 855, a Boeing 747 passenger jet, crashes off the coast of Bombay, killing 213. * January 5 – Bülent Ecevit, of CHP, forms the new government of Turkey (42nd government). * January 6 – The Holy Crown of Hungary (also known as Stephen of Hungary Crown) is returned to Hungary from the United States, where it was held since World War II. * January 10 – Pedro Joaquín Chamorro Cardenal, a critic of the Nicaraguan government, is assassinated; riots erupt against Somoza's government. * January 13 – Former American Vice President Hubert Humphrey, a Democrat, dies of cancer in Waverly, Minnesota, at the age of 66. * January 18 – The European Court of Human Rights finds the British government guilty of mistreating prisoners in Northern Ireland, but not guilty of torture. * January 22 – Ethiopia declares the ambassador of West Germany ''persona non grata''. * January 24 ** Soviet satellite Kosmos 954 burns up in Ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tall Poppy Syndrome
Tall poppy syndrome is a term that originated in Australia and New Zealand in the 1980s that refers to people with notable public success, who excessively promote their own achievements and opinions. Intense scrutiny and criticism of such a person is termed as "cutting down the tall poppy". Etymology The phrase "tall poppies" originates from Livy's account of the tyrannical Roman king Lucius Tarquinius Superbus. He is said to have received a messenger from his son Sextus Tarquinius asking what he should do next in Gabii, since he had become all-powerful there. Rather than answering the messenger verbally, Tarquin went into his garden, took a stick and swept it across his garden, thus cutting off the heads of the tallest poppies that were growing there. The messenger returned to Gabii and told Sextus what he had seen. Sextus realised that his father wished him to put to death all of the most eminent people of Gabii, which he then did. Earlier stories with the same theme are fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Setting Oneself Up To Fail
"Setting up to fail" is a phrase denoting a no-win situation designed in such a way that the person in the situation cannot succeed at the task which they have been assigned. It is considered a form of workplace bullying. There are also situations in which an organization or project is set up to fail, and where individuals set themselves up to fail. The first known documented use of "set up to fail" was in 1969 in the United States. In the workplace Setting up to fail is a well-established workplace bullying tactic. One technique is to overload with work, while denying the victim the authority to handle it and over-interfering; another is the withholding of the information necessary to succeed. If a person puts another individual (usually a subordinate) in a stressful situation in which failure is almost certain, this may be an aspect of bullying wherein the outcome can then be used to discredit and blame the victim. Sometimes, this may involve the bully covertly sabotaging ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
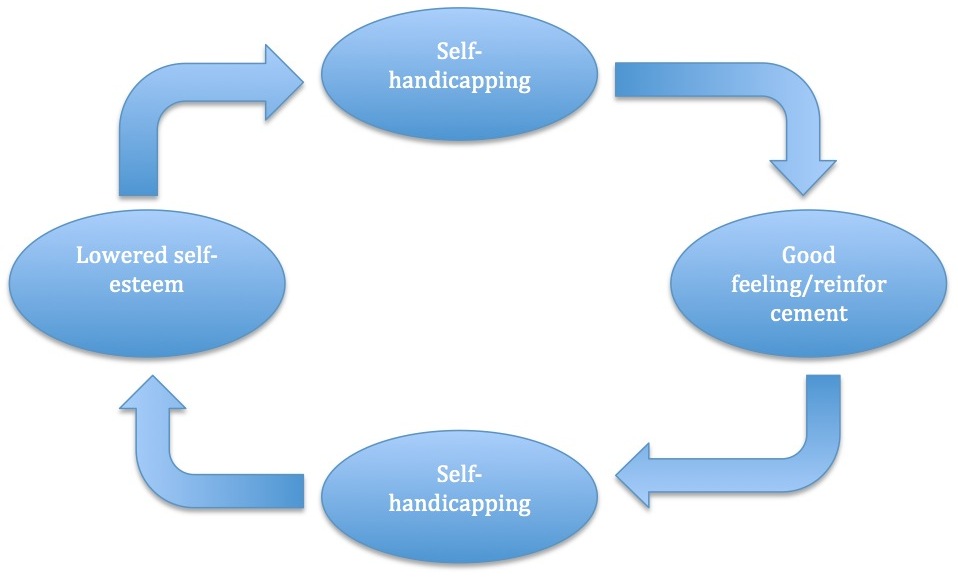
Self-handicapping
Self-handicapping is a cognitive strategy by which people avoid effort in the hopes of keeping potential failure from hurting self-esteem. It was first theorized by Edward E. Jones and Steven Berglas, according to whom self-handicaps are obstacles created, or claimed, by the individual in anticipation of failing performance.Feick, D.L., & Rhodewalt, F. (1997). The Double-Edged Sword of Self-Handicapping: Discounting, Augmentation, and the Protection and Enhancement of Self-Esteem. ''Motivation and Emotion, Vol. 21, No. 2. '' Self-handicapping can be seen as a method of preserving self-esteem but it can also be used for self-enhancement and to impression management, manage the impressions of others.Rhodewalt, F., & Vohs, K. D. (2005). Defensive strategies, motivation, and the self. In A. Elliot & C. Dweck (Eds.). ''Handbook of competence and motivation''(pp. 548-565). New York: Guilford Press. This conservation or augmentation of self-esteem is due to changes in attribution (psychol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poseur
A poseur is someone who poses for effect, or behaves affectedly, who affects a particular attitude, character or manner to impress others, or who pretends to belong to a particular group.Definition of poseur at Dictionary.com A poseur may be a person who pretends to be what they are not or an insincere person; they may have a flair for drama or behave as if they are onstage in daily life.Hardy, Thomas. ''The Literary Notebooks of Thomas Hardy, Volume 2''. Lennart A Björk, ed. Springer, 2016. . page 256. "Poseur" or "poseuse" is also used to mean a person who poses for a visual artist—a . Examples [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jonah Complex
The Jonah complex is the fear of success or the fear of being one's best. This fear prevents self-actualization, or the realization of one's own potential. It is the fear of one's own greatness, the evasion of one's destiny, or the avoidance of exercising one's talents. As the fear of achieving a personal worst may serve to motivate personal growth, likewise the fear of achieving a personal best may hinder achievement. The Jonah complex is evident in neurotic people. Etymology Although Abraham Maslow is credited for the term, the name "Jonah complex" was originally suggested by Maslow's friend, Professor Frank E. Manuel. The name comes from the story of the Biblical prophet Jonah's evasion of the destiny to prophesy the destruction of Nineveh. Maslow states, "So often we run away from the responsibilities dictated (or rather suggested) by nature, by fate, even sometimes by accident, just as Jonah tried—in vain—to run away from ''his'' fate". Causes Any dilemma, paradox or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferiority Complex
In psychology, an inferiority complex is a consistent feeling of inadequacy, often resulting in the belief that one is in some way deficient, or inferior, to others. According to Alfred Adler, a feeling of inferiority may be brought about by upbringing as a child (for example, being consistently compared unfavorably to a sibling), physical and mental limitations, or experiences of lower social status (for example, being treated unfavorably by one's peers). An inferiority complex may cause an individual to overcompensate in a number of ways. For example, a person who feels inferior because they are shorter than average (also known as a Napoleon complex) due to common modern day heightism may become overly concerned with how they appear to others. They may wear special shoes to make themself appear taller or surround themselves with individuals who are even shorter than they are. If this is taken to the extreme, it becomes a neurosis. It may also cause an individual to be p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fakin' It (Simon & Garfunkel Song)
"Fakin' It" is a song recorded by American music duo Simon & Garfunkel for their fourth studio album, ''Bookends'' (1968). The song was initially released only as a single on July 7, 1967 through Columbia Records. It was later compiled into the second half of ''Bookends''. The song's lyrics stem from Simon wondering about his occupation and life had he been born a century earlier as well as reflection on his insecurities, facing a situation akin to impostor syndrome. All the same, the dramatic interplay between the burden of said insecurities and a simultaneous air of outwardly cool confidence generate significant interest for the listener. Even after numerous listenings, due to the concealment of specifics the fertile ambiguity that permeates "Fakin' It" allows for both of the two competing interpretations (faking contentment with a mediocre situation, or faking competence in order to hold down a more favorable one?) to be plausible, probably even as disparate aspects of the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inner Voice
Interior may refer to: Arts and media * ''Interior'' (Degas) (also known as ''The Rape''), painting by Edgar Degas * ''Interior'' (play), 1895 play by Belgian playwright Maurice Maeterlinck * ''The Interior'' (novel), by Lisa See * Interior design, the trade of designing an architectural interior * ''The Interior'' (Presbyterian periodical), an American Presbyterian periodical * Interior architecture, process of designing building interiors or renovating existing home interiors Places * Interior, South Dakota * Interior, Washington * Interior Township, Michigan * British Columbia Interior, commonly known as "The Interior" Government agencies * Interior ministry, sometimes called the ministry of home affairs * United States Department of the Interior Other uses * Interior (topology), mathematical concept that includes, for example, the inside of a shape * Interior FC, a football team in Gambia See also * * * List of geographic interiors * Interiors (other) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |