|
Implicit Racism
Aversive racism is a social scientific theory proposed by Samuel L. Gaertner & John F. Dovidio (1986), according to which negative evaluations of racial/ethnic minorities are realized by a persistent avoidance of interaction with other racial and ethnic groups. As opposed to traditional, overt racism, which is characterized by overt hatred for and discrimination against racial/ethnic minorities, aversive racism is characterized by more complex, ambivalent expressions and attitudes nonetheless with prejudicial views towards other races. Aversive racism arises from unconscious personal beliefs taught during childhood. Subtle racist behaviors are usually targeted towards African Americans. Workplace discrimination is one of the best examples of aversive racism. Biased beliefs on how minorities act and think affect how individuals interact with minority members. ''Aversive racism'' was coined by Joel Kovel to describe the subtle racial behaviors of any ethnic or racial group who rat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Social Science
Social science (often rendered in the plural as the social sciences) is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among members within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the field of sociology, the original "science of society", established in the 18th century. It now encompasses a wide array of additional academic disciplines, including anthropology, archaeology, economics, geography, history, linguistics, management, communication studies, psychology, culturology, and political science. The majority of positivist social scientists use methods resembling those used in the natural sciences as tools for understanding societies, and so define science in its stricter modern sense. Speculative social scientists, otherwise known as interpretivist scientists, by contrast, may use social critique or symbolic interpretation rather than constructing empirically falsifiable theories, and thus treat science in its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Brooklyn, New York
Brooklyn is a Boroughs of New York City, borough of New York City located at the westernmost end of Long Island in the New York (state), State of New York. Formerly an independent city, the borough is coextensive with Kings County, one of twelve original counties established under English rule in 1683 in what was then the Province of New York. As of the 2020 United States census, the population stood at 2,736,074, making it the most populous of the five boroughs of New York City, and the most populous Administrative divisions of New York (state)#County, county in the state.Table 2: Population, Land Area, and Population Density by County, New York State - 2020 New York State Department of Health. Accessed January 2, 2024. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Tokenism
In sociology, tokenism is the social practice of making a perfunctory and symbolic effort towards the equitable inclusion of members of a minority group, especially by recruiting people from under-represented social-minority groups in order for the organization to give the public appearance of racial and gender equality, usually within a workplace, government, or a school. The sociological purpose of tokenism is to give the appearance of inclusivity to a workplace or a school that is not as culturally diverse (racial, religious, sexual, etc.) as the rest of society. History The social concept and the employment practice of ''tokenism'' became understood in the popular culture of the United States in the late 1950s. In the face of racial segregation, tokenism emerged as a solution that though earnest in effort, only acknowledged an issue without actually solving it. In the book '' Why We Can't Wait'' (1964), civil rights activist Martin Luther King Jr. discussed the subject of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Allosemitism
Allosemitism is a neologism that encompasses both philosemitic and antisemitic attitudes towards Jews as the Other. Origin of term The term was coined by Polish Jewish literary critic Artur Sandauer and popularized by the Polish Jewish sociologist Zygmunt Bauman. Sandauer used the term "allosemitism" in his essay ''On Situation of Polish Writer of Jewish Descent In the 20th Century'' published as a book in 1982. Zygmunt Bauman proposed the term in his 1997 essay "Allosemitism: Premodern, Modern, Postmodern" in which he argued that "allosemitism" should be used in place of "antisemitism". Bauman's argument was that allosemitism can represent a "radically ambivalent attitude" encompassing both philo-Semitism and anti-Semitism; allosemitism is a form of proteophobia, fear and horror of things that defy clean-cut categories, not, like anti-Semitism, of a simple fear of the " other"; and that Judeophobia is diverse, and, therefore, not adequately encompassed by the term "anti-Sem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Ambivalent Prejudice
Ambivalent prejudice is a Social psychology, social psychological theory that states that, when people become aware that they have conflicting beliefs about an In-group and out-group, outgroup (a group of people that do not belong to an individual's own group), they experience an unpleasant mental feeling generally referred to as cognitive dissonance. These feelings are brought about because the individual on one hand believes in Humanitarianism, humanitarian virtues such as helping those in need, but on the other hand also believes in Individualism, individualistic virtues such as working hard to improve one's life. Bernard Whitley and Mary Kite contend that this dissonance motivates people to alter their thoughts in an attempt to reduce their discomfort. Depending on the situation or context that has primed them, people will give priority to either the positive beliefs or the negative beliefs, leading to a corresponding behavioral shift known as ''response amplification''. Theore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Ambivalent Sexism
Ambivalent sexism is a theoretical framework which posits that sexism has two sub-components: hostile sexism (HS) and benevolent sexism (BS). Hostile sexism reflects overtly negative evaluations and stereotypes about a gender (e.g., the ideas that women are incompetent and inferior to men). Benevolent sexism represents evaluations of gender that may appear subjectively positive (subjective to the person who is evaluating), but are actually damaging to people and gender equality more broadly (e.g., the ideas that women need to be protected by men). For the most part, psychologists have studied hostile forms of sexism. However, theorists using the theoretical framework of ambivalent sexism have found extensive empirical evidence for both varieties. The theory has largely been developed by social psychologists Peter Glick and Susan Fiske. Overview Definition Sexism, like other forms of prejudice, is a type of bias about a group of people. Sexism is founded in conceptualizations of o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Join The Fight Against Racism
Join may refer to: * Join (law), to include additional counts or additional defendants on an indictment *In mathematics: ** Join (mathematics), a least upper bound of sets orders in lattice theory ** Join (topology), an operation combining two topological spaces ** Join (category theory), an operation combining two categories ** Join (simplicial sets), an operation combining two simplicial sets ** Join (sigma algebra), a refinement of sigma algebras ** Join (algebraic geometry), a union of lines between two varieties *In computing: ** Join (relational algebra), a binary operation on tuples corresponding to the relation join of SQL *** Join (SQL), relational join, a binary operation on SQL and relational database tables *** join (Unix), a Unix command similar to relational join ** Join-calculus, a process calculus developed at INRIA for the design of distributed programming languages *** Join-pattern, generalization of Join-calculus *** Joins (concurrency library), a concurrent comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Common Ingroup Identity
The common ingroup identity model is a theoretical model proposed by Samuel L. Gaertner and John F. Dovidio that outlines the processes through which intergroup bias may be reduced.Gaertner, S. L., Dovidio, J. F., Anastasio, P. A., Bachman, B. A., & Rust, M. C. (1993). The Common Ingroup Identity Model: Recategorization and the reduction of intergroup Bias. European Review of Social Psychology, 4, 1-26. Intergroup bias is a preference for one's in-group over the out-group. Derived from the social identity approach to intergroup behaviour, the common ingroup identity model is rooted in the process of social categorization, or how people conceive of group boundaries. The model describes how intergroup bias can be reduced if members of different groups can be induced to conceive of themselves to be part of the same group, then they would develop more positive attitudes of the former outgroup members. An individual will change the way they view the out-group through a social categ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
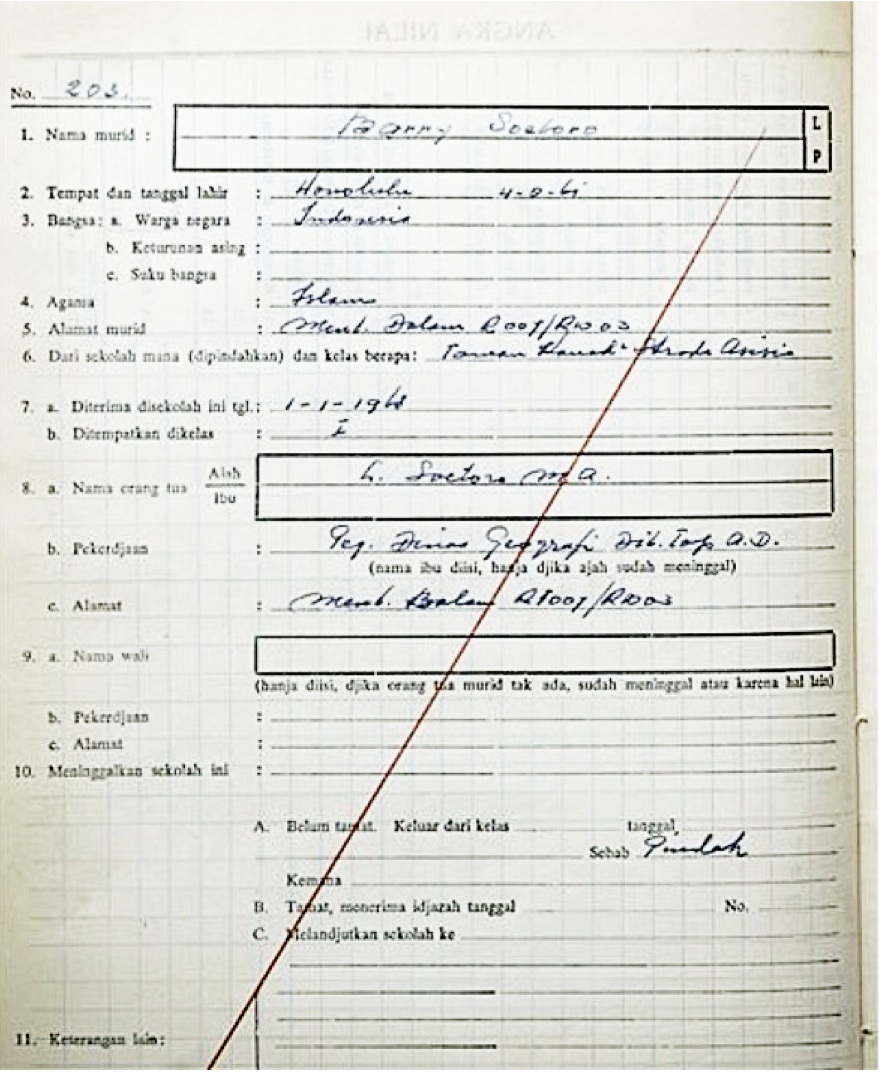 |
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II (born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who was the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the first African American president in American history. Obama previously served as a U.S. senator representing Illinois from 2005 to 2008 and as an Illinois state senator from 1997 to 2004. Born in Honolulu, Hawaii, Obama graduated from Columbia University in 1983 with a Bachelor of Arts degree in political science and later worked as a community organizer in Chicago. In 1988, Obama enrolled in Harvard Law School, where he was the first black president of the ''Harvard Law Review''. He became a civil rights attorney and an academic, teaching constitutional law at the University of Chicago Law School from 1992 to 2004. In 1996, Obama was elected to represent the 13th district in the Illinois Senate, a position he held until 2004, when he successfully ran for the U.S. Senate. In the 2008 pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Auto Mechanic
An auto mechanic is a mechanic who services and repairs automobiles, sometimes specializing in one or more List of car brands, automobile brands or sometimes working with any brand. In fixing cars, their main role is to Diagnosis, diagnose and repair the problem accuratelSeasoned auto repair shops start with a (Digital) Inspection to determine the vehicle conditions, independent of the customers concern. Based on the concern, the inspection results and preventative maintenance needs, the mechanic/technician returns the findings to the service advisor who then gets approval for any or all of the proposed work. The approved work will be assigned to the mechanic on a work order. Their work may involve the repair of a specific part or the replacement of one or more parts as assemblies. Basic Service (motor vehicle), vehicle maintenance is a fundamental part of a mechanic's work in modern industrialized countries, while in others they are only consulted when a vehicle is already show ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Confederate (psychology)
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a political union of sovereign states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issues, such as defence, foreign relations, internal trade or currency, with the central government being required to provide support for all its members. Confederalism represents a main form of intergovernmentalism, defined as any form of interaction around states that takes place on the basis of sovereign independence or government. The nature of the relationship among the member states constituting a confederation varies considerably. Likewise, the relationship between the member states and the general government and their distribution of powers varies. Some looser confederations are similar to intergovernmental organization, international organisations. Other confederations with stricter rules may resemble federal systems. These elements o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |