|
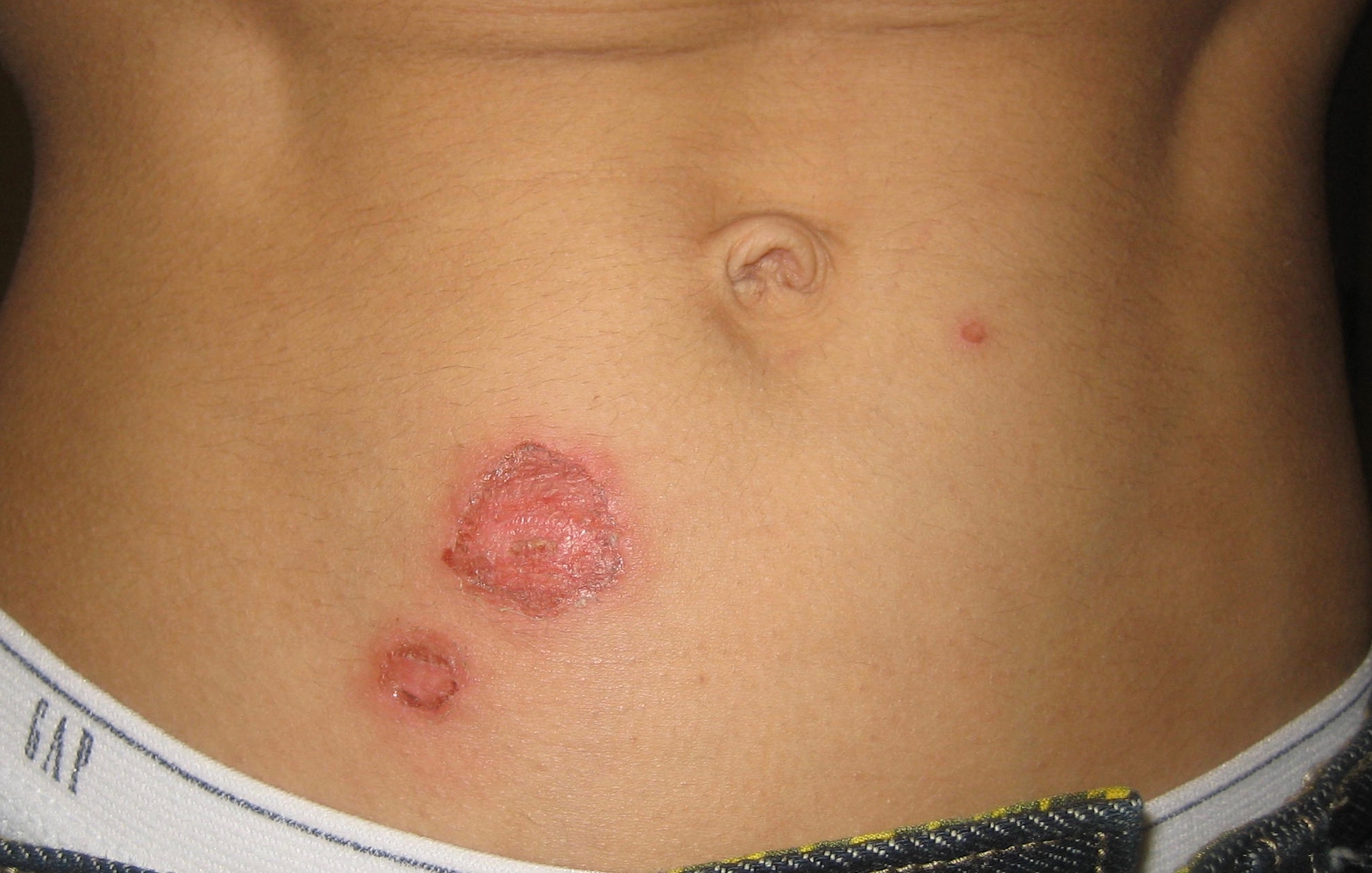
Impetigo
Impetigo is a bacterial infection that involves the superficial skin. The most common presentation is yellowish crusts on the face, arms, or legs. Less commonly there may be large blisters which affect the groin or armpits. The lesions may be painful or itchy. Fever is uncommon. It is typically due to either ''Staphylococcus aureus'' or ''Streptococcus pyogenes''. Risk factors include attending day care, crowding, poor nutrition, diabetes mellitus, contact sports, and breaks in the skin such as from mosquito bites, eczema, scabies, or herpes. With contact it can spread around or between people. Diagnosis is typically based on the symptoms and appearance. Prevention is by hand washing, avoiding people who are infected, and cleaning injuries. Treatment is typically with antibiotic creams such as mupirocin or fusidic acid. Antibiotics by mouth, such as cefalexin, may be used if large areas are affected. Antibiotic-resistant forms have been found. Impetigo affected ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial Infection
Pathogenic bacteria are bacteria that can cause disease. This article focuses on the bacteria that are pathogenic to humans. Most species of bacteria are harmless and are often beneficial but others can cause infectious diseases. The number of these pathogenic species in humans is estimated to be fewer than a hundred. By contrast, several thousand species are part of the gut flora present in the digestive tract. The body is continually exposed to many species of bacteria, including beneficial commensals, which grow on the skin and mucous membranes, and saprophytes, which grow mainly in the soil and in decaying matter. The blood and tissue fluids contain nutrients sufficient to sustain the growth of many bacteria. The body has defence mechanisms that enable it to resist microbial invasion of its tissues and give it a natural immunity or innate resistance against many microorganisms. Pathogenic bacteria are specially adapted and endowed with mechanisms for overcoming the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
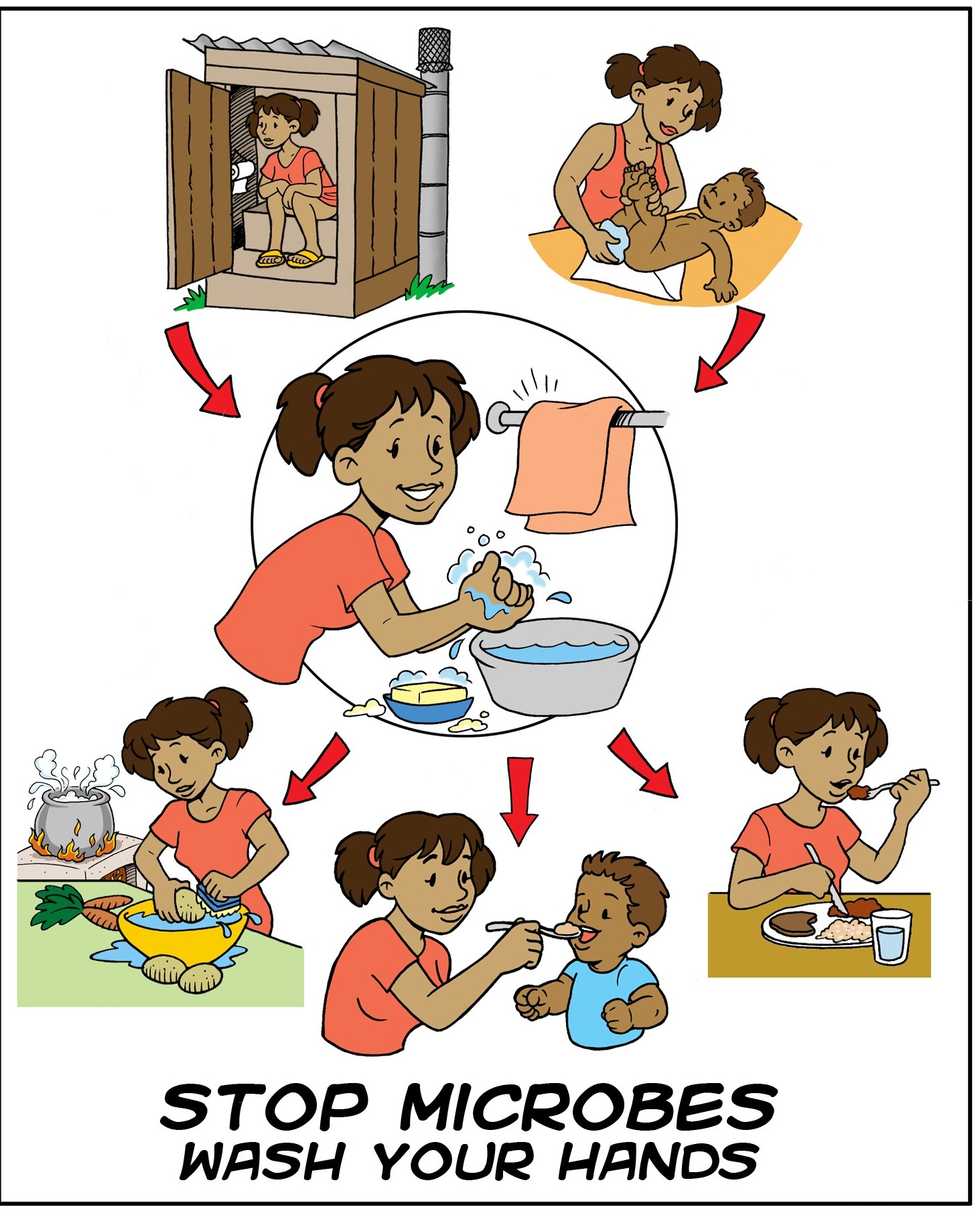
Hand Washing
Hand washing (or handwashing), also known as hand hygiene, is the act of cleaning one's hands with soap or handwash and water to remove viruses/bacteria/microorganisms, dirt, grease, or other harmful and unwanted substances stuck to the hands. Drying of the washed hands is part of the process as wet and moist hands are more easily recontaminated. If soap and water are unavailable, hand sanitizer that is at least 60% ( v/v) alcohol in water can be used as long as hands are not visibly excessively dirty or greasy. Hand hygiene is central to preventing the spread of infectious diseases in home and everyday life settings. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends washing hands for at least 20 seconds before and after certain activities. These include the five critical times during the day where washing hands with soap is important to reduce fecal-oral transmission of disease: after using the toilet (for urination, defecation, menstrual hygiene), after cleaning a child's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mupirocin
Mupirocin, sold under the brand name Bactroban among others, is a topical antibiotic useful against superficial skin infections such as impetigo or folliculitis. It may also be used to get rid of methicillin-resistant ''S. aureus'' (MRSA) when present in the nose without symptoms. Due to concerns of developing resistance, use for greater than ten days is not recommended. It is used as a cream or ointment applied to the skin. Common side effects include itchiness and rash at the site of application, headache, and nausea. Long term use may result in increased growth of fungi. Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding appears to be safe. Mupirocin is in the carboxylic acid class of medications. It works by blocking a bacteria's ability to make protein, which usually results in bacterial death. Mupirocin was initially isolated in 1971 from ''Pseudomonas fluorescens''. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In 2020, it was the 203rd most commonly pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poststreptococcal Glomerulonephritis
Acute proliferative glomerulonephritis is a disorder of the small blood vessels of the kidney. It is a common complication of bacterial infections, typically skin infection by ''Streptococcus'' bacteria types 12, 4 and 1 (impetigo) but also after streptococcal pharyngitis, for which it is also known as postinfectious glomerulonephritis (PIGN) or poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN). It can be a risk factor for future albuminuria. In adults, the signs and symptoms of infection may still be present at the time when the kidney problems develop, and the terms ''infection-related glomerulonephritis'' or ''bacterial infection-related glomerulonephritis'' are also used. Acute glomerulonephritis resulted in 19,000 deaths in 2013, down from 24,000 deaths in 1990 worldwide. Signs and symptoms Among the signs and symptoms of acute proliferative glomerulonephritis are the following: * Hematuria * Oliguria * Edema * Hypertension * Fever (headache, malaise, anorexia, nausea.) Causes Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus Aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe that can grow without the need for oxygen. Although ''S. aureus'' usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota, it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing virulence factors such as potent protein toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies. ''S. aureus'' is one of the leading pathogens for deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, such as methicillin-resistant ''S. aureu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hand Washing
Hand washing (or handwashing), also known as hand hygiene, is the act of cleaning one's hands with soap or handwash and water to remove viruses/bacteria/microorganisms, dirt, grease, or other harmful and unwanted substances stuck to the hands. Drying of the washed hands is part of the process as wet and moist hands are more easily recontaminated. If soap and water are unavailable, hand sanitizer that is at least 60% ( v/v) alcohol in water can be used as long as hands are not visibly excessively dirty or greasy. Hand hygiene is central to preventing the spread of infectious diseases in home and everyday life settings. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends washing hands for at least 20 seconds before and after certain activities. These include the five critical times during the day where washing hands with soap is important to reduce fecal-oral transmission of disease: after using the toilet (for urination, defecation, menstrual hygiene), after cleaning a child's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
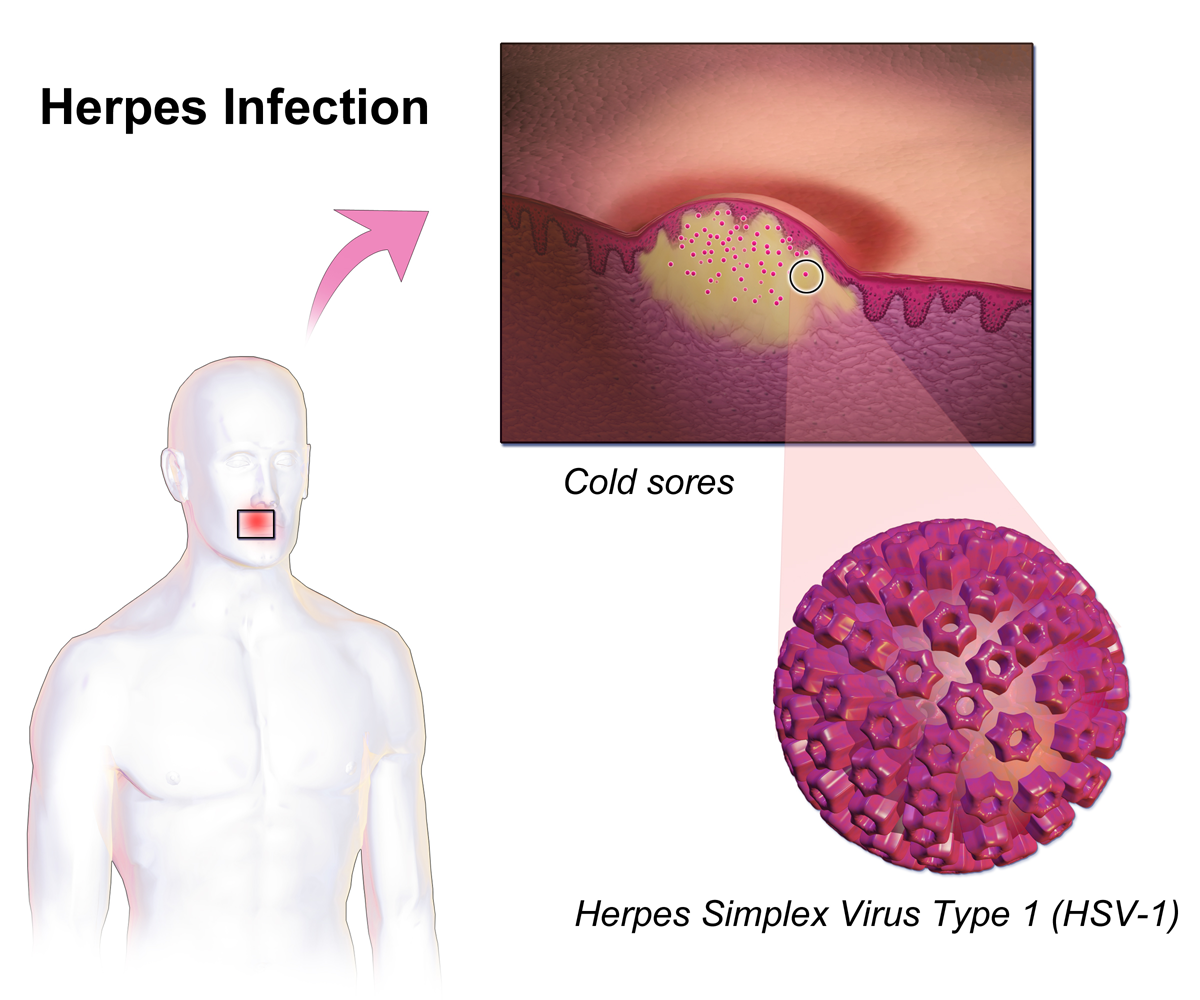
Herpes
Herpes simplex is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. Infections are categorized based on the part of the body infected. Oral herpes involves the face or mouth. It may result in small blisters in groups often called cold sores or fever blisters or may just cause a sore throat. Genital herpes, often simply known as herpes, involves the genitalia. It may have minimal symptoms or form blisters that break open and result in small ulcers. These typically heal over two to four weeks. Tingling or shooting pains may occur before the blisters appear. Herpes cycles between periods of active disease followed by periods without symptoms. The first episode is often more severe and may be associated with fever, muscle pains, swollen lymph nodes and headaches. Over time, episodes of active disease decrease in frequency and severity. Herpetic whitlow typically involves the fingers or thumb. Herpes simplex keratitis involves the eye. Herpesviral encephalitis involv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptococcus Pyogenes
''Streptococcus pyogenes'' is a species of Gram-positive, aerotolerant bacteria in the genus '' Streptococcus''. These bacteria are extracellular, and made up of non-motile and non-sporing cocci (round cells) that tend to link in chains. They are clinically important for humans, as they are an infrequent, but usually pathogenic, part of the skin microbiota that can cause Group A streptococcal infection. ''S. pyogenes'' is the predominant species harboring the Lancefield group A antigen, and is often called group A ''Streptococcus'' (GAS). However, both '' Streptococcus dysgalactiae'' and the '' Streptococcus anginosus'' group can possess group A antigen as well. Group A streptococci, when grown on blood agar, typically produce small (2–3 mm) zones of beta-hemolysis, a complete destruction of red blood cells. The name group A (beta-hemolytic) ''Streptococcus'' (GABHS) is thus also used. The species name is derived from Greek words meaning 'a chain' () of berri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, treatment and antibiotic prophylaxis, prevention of such infections. They may either bactericide, kill or bacteriostatic agent, inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek language, Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced naturally (by one microorgani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic Resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistance. Protozoa evolve antiprotozoal resistance, and bacteria evolve antibiotic resistance. Those bacteria that are considered extensively drug resistant (XDR) or totally drug-resistant (TDR) are sometimes called "superbugs".A.-P. Magiorakos, A. Srinivasan, R. B. Carey, Y. Carmeli, M. E. Falagas, C. G. Giske, S. Harbarth, J. F. Hinndler ''et al''Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria... Clinical Microbiology and Infection, Vol 8, Iss. 3 first published 27 July 2011 ia Wiley Online Library Retrieved 28 August 2020 Although antimicrobial resistance is a naturally-occurring process, it is often the result of improper usage of the drugs and management of the infections. Antibiotic resistance is a major su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Groin
In human anatomy, the groin (the adjective is ''inguinal'', as in inguinal canal) is the junctional area (also known as the inguinal region) between the abdomen and the thigh on either side of the pubic bone. This is also known as the medial compartment of the thigh that consists of the adductor muscles of the hip or the groin muscles. A pulled groin muscle usually refers to a painful injury sustained by straining the hip adductor muscles. These hip adductor muscles that make up the groin consist of the adductor brevis, adductor longus, adductor magnus, gracilis, and pectineus. These groin muscles adduct the thigh (bring the femur and knee closer to the midline). The groin is innervated by the obturator nerve, with two exceptions: the pectineus muscle is innervated by the femoral nerve, and the hamstring portion of adductor magnus is innervated by the tibial nerve. In the groin, underneath the skin, there are three to five deep inguinal lymph nodes that play a ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scabies
Scabies (; also sometimes known as the seven-year itch) is a contagious skin infestation by the mite '' Sarcoptes scabiei''. The most common symptoms are severe itchiness and a pimple-like rash. Occasionally, tiny burrows may appear on the skin. In a first-ever infection, the infected person usually develops symptoms within two to six weeks. During a second infection, symptoms may begin within 24 hours. These symptoms can be present across most of the body or just certain areas such as the wrists, between fingers, or along the waistline. The head may be affected, but this is typically only in young children. The itch is often worse at night. Scratching may cause skin breakdown and an additional bacterial infection in the skin. Scabies is caused by infection with the female mite '' Sarcoptes scabiei ''var.'' hominis'', an ectoparasite. The mites burrow into the skin to live and deposit eggs. The symptoms of scabies are due to an allergic reaction to the mites. Often, only bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |