|
Imperial Castle
An imperial castle or ''Reichsburg'' was a castle built by order of (or acquired by) the King of the Romans or the Holy Roman Emperor on land that was owned by the crown ''(Reichsgut)''. While in the early middle ages, in Francia, as well as in the early Holy Roman Empire, kings and emperors travelled around their realm with their ''itinerant courts'', using their ''Kaiserpfalzen'' (imperial palaces) as transit stations and temporary residences, the weakly fortified ''pfalzen'' were replaced by ''imperial castles'' from the 13th century onwards. However, the stronger fortification of palaces had already begun in the Hohenstaufen period, as shown by the 3D reconstruction of the castle-like imperial ''pfalz'' of Haguenau designed by emperor Frederick Barbarossa in the middle of the 12th century. After the fall of the Hohenstaufen dynasty, the royal power temporarily lapsed during the interregnum. One weak king after another was elected, but no one was able to exercise sovereign pow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
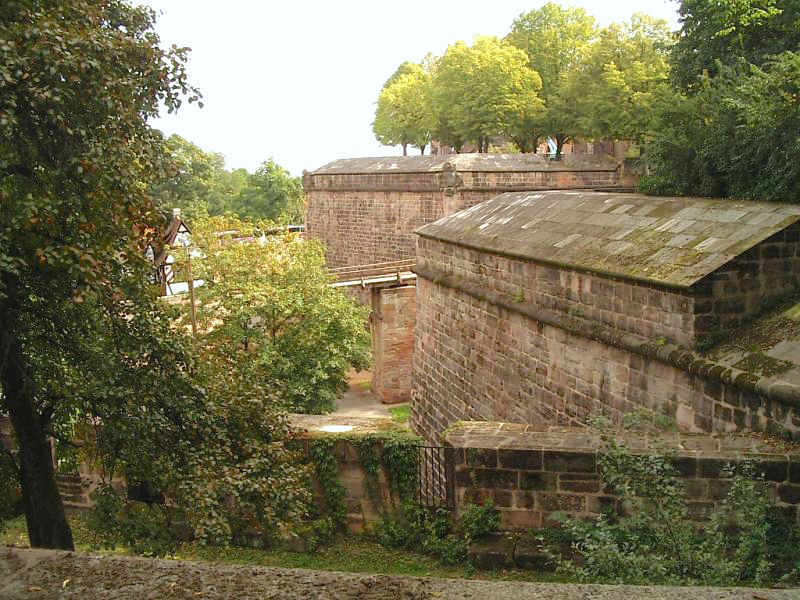
Nuernberg Burg Panorama PtGUI
Nuremberg (, ; ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the Franconia#Towns and cities, largest city in Franconia, the List of cities in Bavaria by population, second-largest city in the States of Germany, German state of Bavaria, and its 544,414 (2023) inhabitants make it the List of cities in Germany by population, 14th-largest city in Germany. Nuremberg sits on the Pegnitz (river), Pegnitz, which carries the name Regnitz from its confluence with the Rednitz in Fürth onwards (), and on the Rhine–Main–Danube Canal, that connects the North Sea to the Black Sea. Lying in the Bavarian Regierungsbezirk, administrative region of Middle Franconia, it is the largest city and unofficial capital of the entire cultural region of Franconia. The city is surrounded on three sides by the , a large forest, and in the north lies (''garlic land''), an extensive vegetable growing area and cultural landscape. The city forms a continuous conurbation with the neighbouring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
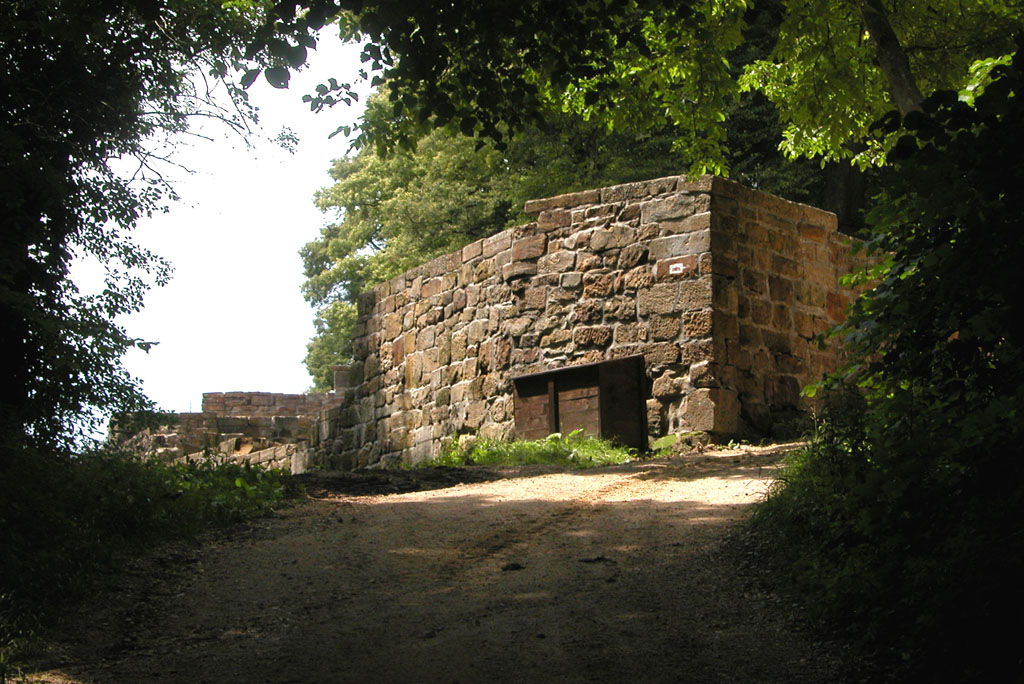
Trifels Castle
Trifels Castle () is a reconstructed medieval castle at an elevation of near the small town of Annweiler, in the Palatinate region of southwestern Germany. It is located high above the Queich valley within the Palatinate Forest on one peak of a red sandstone mountain split into three. Trifels Castle is on the peak of the ''Sonnenberg'', and on both of the other two rock elevations there are castle ruins: Anebos Castle and Scharfenberg Castle (demotically called Münz). Trifels Castle has been gradually restored since the 19th century and today replicas of the Imperial Regalia (''Reichskleinodien'') of the Holy Roman Empire are on display here. It is—together with Hambach Castle—one of the most popular tourist destinations in the state of Rhineland-Palatinate. History The castle in Rhenish Franconia was first mentioned in a 1081 deed of donation, when it was held by a local noble Diemar, a relative of Archbishop Siegfried I of Mainz. From him Trifels passed to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministerialis
The ''ministeriales'' (singular: ''ministerialis'') were a legally unfree but socially elite class of knights, administrators, and officials in the High Middle Ages in the Holy Roman Empire, drawn from a mix of servile origins, free commoners, and even cadet sons of minor noble families, who served secular and ecclesiastical lords and often rose to hold hereditary land, noble titles, and political power indistinguishable from the free nobility. The word and its German translations, ''Ministeriale(n)'' and ''Dienstmann'', came to describe those unfree nobles who made up a large majority of what could be described as the German knighthood during that time. What began as an irregular arrangement of workers with a wide variety of duties and restrictions rose in status and wealth to become the power brokers of an empire. The ''ministeriales'' were not legally free people, but held social rank. Legally, their liege lord determined whom they could or could not marry, and they were not ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manorialism
Manorialism, also known as seigneurialism, the manor system or manorial system, was the method of land ownership (or "Land tenure, tenure") in parts of Europe, notably France and later England, during the Middle Ages. Its defining features included a large, sometimes fortified manor house in which the lord of the manor and his dependants lived and administered a rural estate, and a population of labourers or Serfdom, serfs who worked the surrounding land to support themselves and the lord. These labourers fulfilled their obligations with labour time or in-kind produce at first, and later by cash payment as commercial activity increased. Manorialism was part of the Feudalism, feudal system. Manorialism originated in the Roman villa system of the Late Roman Empire, and was widely practised in Middle Ages, medieval western Europe and parts of central Europe. An essential element of feudal society, manorialism was slowly replaced by the advent of a money-based market economy and new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Royal And Imperial Elections In The Holy Roman Empire
The following is a list of imperial elections in the Holy Roman Empire. Entries ''in italics'' are for elections where the claim of the man elected to be King of the Romans was disputed. {{Holy Roman Empire elections Holy Roman Empire The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ... Imperial elections ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Election
The election of a Holy Roman Emperor was generally a two-stage process whereby the King of the Romans was elected by a small body of the greatest princes of the realm, the prince-electors. This was then followed shortly thereafter by his coronation as king, originally at Aachen and later at Frankfurt. The king was then expected to march to Rome, to be Coronation of the Holy Roman Emperor, crowned Emperor by the pope. In 1356, the Emperor Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles IV promulgated the Golden Bull of 1356, Golden Bull, which became the fundamental law by which all future kings and emperors were elected. After 1508, rulers usually were recognized as "Emperor elect" after their first, royal coronation. Background The ''Königswahl'' was the election of royal candidates in the Holy Roman Empire and its predecessors as king by a specified elective body. Whilst the succession to the throne of the monarch in some cultures is governed by the rules of hereditary succession, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Palace Of Westminster
The history of the Palace of Westminster The Palace of Westminster is the meeting place of the Parliament of the United Kingdom and is located in London, England. It is commonly called the Houses of Parliament after the House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two legislative ch ... began in the Middle Ages – in the early eighth century – when there was an Anglo-Saxon church dedicated to St. Peter the Apostle which became known as the West Minster (St. Paul's being the East Minster). In the tenth century the church became a Benedictines, Benedictine abbey and was adopted as a royal church, which subsequently became a royal palace in the 11th century. Edward the Confessor, the penultimate Anglo-Saxon king, began the building of Westminster Abbey and a neighbouring palace to oversee its construction. After the Norman Conquest of 1066, William the Conqueror adopted the Palace of Westminster as his own. His son, William II of England, William II (William Rufus) laid th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
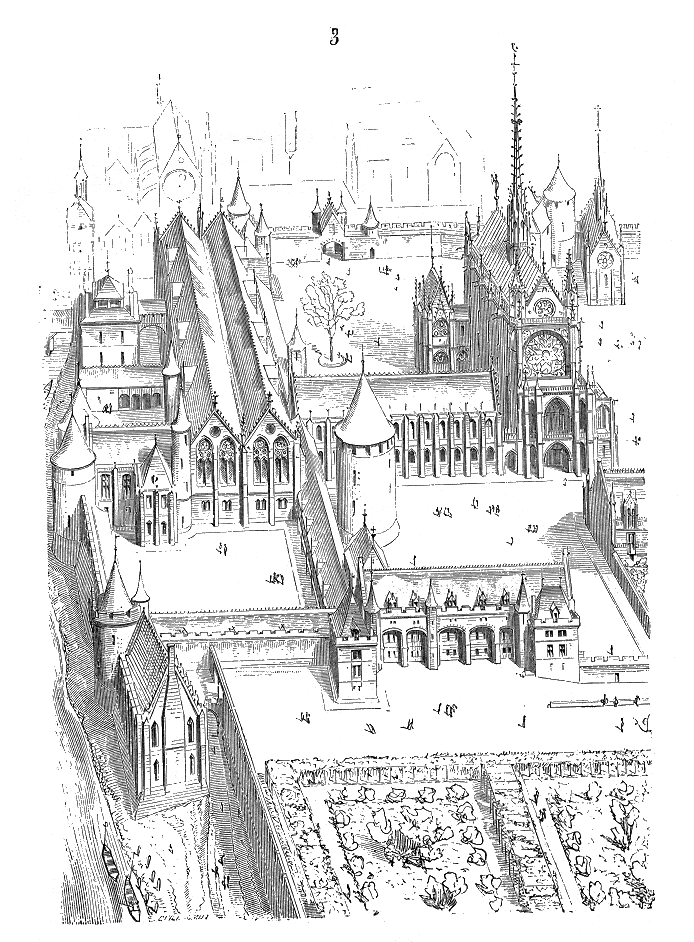
Palais De La Cité
The Palais de la Cité (), located on the Seine River's Île de la Cité, is a major historic building in the centre of Paris, France. It was an occasional residence of the Kings of France from the early 6th to the 12th century and a permanent one from the late 12th to the 14th century, and has been the center of the Judiciary of France, French justice system ever since, for which it is also referred to as the Palais de Justice, Paris, Palais de Justice. From the 14th century until the French Revolution, the Palais was the headquarters of the Parlement of Paris. During the Revolution it served as a courthouse and prison, where Marie Antoinette and other prisoners were held and tried by the Revolutionary Tribunal. Since the early 19th century, it has been the seat of the Tribunal de grande instance de Paris, the Court of Appeal of Paris, and the Court of Cassation (France), Court of Cassation. The first of these moved to Tribunal de grande instance de Paris, another Parisian locatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital City
A capital city, or just capital, is the municipality holding primary status in a country, state (polity), state, province, department (administrative division), department, or other administrative division, subnational division, usually as its Seat of government, seat of the government. A capital is typically a city that physically encompasses the government's offices and meeting places; the status as capital is often designated by its law or constitution. In some jurisdictions, including several countries, different branches of government are in different settlements, sometimes meaning multiple official capitals. In some cases, a distinction is made between the official (constitutional) capital and the seat of government, which is in list of countries with multiple capitals, another place. English language, English-language media often use the name of the capital metonymy, metonymically to refer to the government sitting there. Thus, "London-Washington relations" is widely unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hohenstaufen Era
The Hohenstaufen dynasty (, , ), also known as the Staufer, was a noble family of unclear origin that rose to rule the Duchy of Swabia from 1079, and to royal rule in the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages from 1138 until 1254. The dynasty's most prominent rulers – Frederick I (1155), Henry VI (1191) and Frederick II (1220) – ascended the imperial throne and also reigned over Italy and Burgundy. The non-contemporary name of 'Hohenstaufen' is derived from the family's Hohenstaufen Castle on Hohenstaufen mountain at the northern fringes of the Swabian Jura, near the town of Göppingen. Under Hohenstaufen rule, the Holy Roman Empire reached its greatest territorial extent from 1155 to 1268. Name The name Hohenstaufen was first used in the 14th century to distinguish the 'high' (''hohen'') conical hill named Staufen in the Swabian Jura (in the district of Göppingen) from the village of the same name in the valley below. The new name was applied to the hill castle of S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alsace
Alsace (, ; ) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in the Grand Est administrative region of northeastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine, next to Germany and Switzerland. In January 2021, it had a population of 1,919,745. Alsatian culture is characterized by a blend of German and French influences. Until 1871, Alsace included the area now known as the Territoire de Belfort, which formed its southernmost part. From 1982 to 2016, Alsace was the smallest administrative in metropolitan France, consisting of the Bas-Rhin and Haut-Rhin Departments of France, departments. Territorial reform passed by the French Parliament in 2014 resulted in the merger of the Alsace administrative region with Champagne-Ardenne and Lorraine to form Grand Est. On 1 January 2021, the departments of Bas-Rhin and Haut-Rhin merged into the new European Collectivity of Alsace but remained part of the region Grand Est. Alsatian dialect, Alsatian is an Alemannic German, Alemannic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |