|
Iliac Fascia
The iliac fascia (or Abernethy's fascia) is the fascia overlying the iliacus muscle. Superiorly and laterally, the iliac fascia is attached to the inner aspect of the iliac crest; inferiorly and laterally, it extends into the thigh to unite with the femoral sheath; medially, it attaches to the periosteum of the ilium and iliopubic eminence near the linea terminalis, and blends with the psoas fascia and - over the quadratus lumborum muscle - with the anterior layer of thoracolumbar fascia. The iliac fascia overlies the femoral nerve, and lateral femoral cutaneous nerve. Structure It has the following connections: * ''laterally'', to the whole length of the inner lip of the iliac crest. * ''medially'', to the linea terminalis of the lesser pelvis, where it is continuous with the periosteum. At the iliopectineal eminence it receives the tendon of insertion of the psoas minor, when that muscle exists. Lateral to the femoral vessels it is intimately connected to the poster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fascia
A fascia (; : fasciae or fascias; adjective fascial; ) is a generic term for macroscopic membranous bodily structures. Fasciae are classified as superficial, visceral or deep, and further designated according to their anatomical location. The knowledge of fascial structures is essential in surgery, as they create borders for infectious processes (for example Psoas abscess) and haematoma. An increase in pressure may result in a compartment syndrome, where a prompt fasciotomy may be necessary. For this reason, profound descriptions of fascial structures are available in anatomical literature from the 19th century. Function Fasciae were traditionally thought of as passive structures that transmit mechanical tension generated by muscular activities or external forces throughout the body. An important function of muscle fasciae is to reduce friction of muscular force. In doing so, fasciae provide a supportive and movable wrapping for nerves and blood vessels as they pass thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
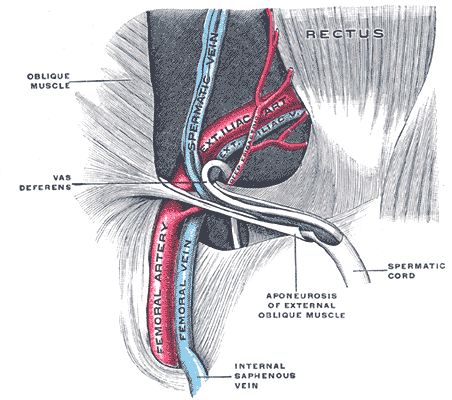
Femoral Vessel
The femoral vessels are those blood vessels passing through the femoral ring into the femoral canal thereby passing down the length of the thigh until behind the knee. These large vessel are the: * Femoral artery (also known in this location as the common femoral artery) and * Femoral vein Lymphatic vessels found in the thigh aren’t usually included in this collective noun. As the blood vessels pass along the thigh, they branch, with their main branches remaining closely associated, where they are still referred to collectively as femoral vessels. The adjective femoral, in this case, relates to the thigh, which contains the femur. The relative position of these two large vessels is very important in medicine and surgery, because several medical interventions involve puncturing one or the other of them. Reliably distinguishing between them is therefore important. The location of the vessel is also used as an anatomical landmark for the femoral nerve The femoral nerve is a n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fascia Iliaca Block
Fascia iliaca blocks (FIC, FICB) is a local anesthetic nerve block, a type of regional anesthesia technique, used to provide analgesia or anaesthesia to the hip and thigh. FICB can performed by using ultrasound or with a loss of resistance technique, the latter sometimes referred to as the "''two-pop-method''". FICB works by affecting the femoral, obturator and the lateral cutaneous nerves with a local anesthetic. Technique When FICB is performed with the loss of resistance technique, the injection site for FICB is found by drawing an imaginary line between the pubic tubercle to the anterior superior iliac spine. The injection site is 1 cm. below the lateral one third and the medial two thirds of this line. Two losses of resistances are felt as the fascia lata and the fascia iliaca is penetrated by a semi-blunt cannula. Aspiration (drawing back the cannula) is performed, after which a local anaesthetic is injected while compressing on the skin distally to increase cran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjoint Tendon
also known as superior tendon of abdominal cavity. The conjoint tendon (previously known as the inguinal aponeurotic falx) is a sheath of connective tissue formed from the lower part of the common aponeurosis of the abdominal internal oblique muscle and the transversus abdominis muscle, joining the muscle to the pelvis. It forms the medial part of the posterior wall of the inguinal canal. Structure The conjoint tendon is formed from the lower part of the common aponeurosis of the abdominal internal oblique muscle and the transversus abdominis muscle. It inserts into the pubic crest and the pectineal line immediately behind the superficial inguinal ring. It is usually conjoint with the tendon of the internal oblique muscle, but they may be separate as well. It forms the medial part of the posterior wall of the inguinal canal. Clinical significance The conjoint tendon serves to protect what would otherwise be a weak point in the abdominal wall. A weakening of the conjoint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pectineal Line (pubis)
The pectineal line of the pubis (also pecten pubis) is a ridge on the superior ramus of the pubic bone. It forms part of the pelvic brim. Lying across from the pectineal line are fibers of the pectineal ligament, and the proximal origin of the pectineus muscle. In combination with the arcuate line, it makes the iliopectineal line. References External links * () {{Authority control Bones of the pelvis Pubis (bone) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femoral Nerve
The femoral nerve is a nerve in the thigh that supplies skin on the upper thigh and inner leg, and the muscles that extend the knee. It is the largest branch of the lumbar plexus. Structure The femoral nerve is the major nerve supplying the anterior compartment of the thigh. It is the largest branch of the lumbar plexus, and arises from the dorsal divisions of the ventral rami of the second, third, and fourth lumbar nerves (L2, L3, and L4). The nerve enters Scarpa's triangle by passing beneath the inguinal ligament, just lateral to the femoral artery. In the thigh, the nerve lies in a groove between iliacus muscle and psoas major muscle, outside the femoral sheath, and lateral to the femoral artery. After a short course of about 4 cm in the thigh, the nerve is divided into anterior and posterior divisions, separated by lateral femoral circumflex artery. The branches are shown below: Muscular branches * The nerve to the pectineus muscle arises immediately above the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iliacus
The iliacus is a flat, triangular muscle which fills the iliac fossa. It forms the lateral portion of iliopsoas, providing flexion of the thigh and lower limb at the acetabulofemoral joint. Structure The iliacus arises from the iliac fossa on the interior side of the hip bone, and also from the region of the anterior inferior iliac spine (AIIS). It joins the psoas major to form the iliopsoas. It proceeds across the iliopubic eminence through the muscular lacuna to its insertion on the lesser trochanter of the femur. Its fibers are often inserted in front of those of the psoas major and extend distally over the lesser trochanter.Platzer (2004), p 234 Nerve supply The iliopsoas is innervated by the femoral nerve and direct branches from the lumbar plexus.''Thieme Atlas of Anatomy'' (2006), p 422 Function In open-chain exercises, as part of the iliopsoas, the iliacus is important for lifting (flexing) the femur forward (e.g. front scale). In closed-chain exercises, the iliops ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psoas Major
The psoas major ( or ; from ) is a long fusiform muscle located in the lateral lumbar region between the vertebral column and the brim of the lesser pelvis. It joins the iliacus muscle to form the iliopsoas. In other animals, this muscle is equivalent to the tenderloin. Structure The psoas major is divided into a superficial and a deep part. The deep part originates from the transverse processes of lumbar vertebrae L1–L5. The superficial part originates from the lateral surfaces of the last thoracic vertebra, lumbar vertebrae L1–L4, and the neighboring intervertebral discs. The lumbar plexus lies between the two layers. Together, the iliacus muscle and the psoas major form the iliopsoas, which is surrounded by the iliac fascia. The iliopsoas runs across the iliopubic eminence through the muscular lacuna to its insertion on the lesser trochanter of the femur. The iliopectineal bursa separates the tendon of the iliopsoas muscle from the external surface of the hip-j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscular Lacuna
The muscular lacuna (Latin: ''lacuna musculorum'') is the lateral compartment of the thigh beneath the inguinal ligament. It is separated from the medial vascular lacuna by the iliopectineal arch. It is occupied/traversed by the iliopsoas muscle, and femoral nerve The femoral nerve is a nerve in the thigh that supplies skin on the upper thigh and inner leg, and the muscles that extend the knee. It is the largest branch of the lumbar plexus. Structure The femoral nerve is the major nerve supplying the ant .... The lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh may pass through the muscular lacuna, or it may pierce the inguinal ligament itself. References Muscular system {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Lacuna
The vascular lacuna (Latin: ''lacuna vasorum (retroinguinalis)'') is the medial compartment beneath the inguinal ligament. It is separated from the lateral muscular lacuna by the iliopectineal arch.Ross, L.M., Lamperti, E.D. (2006). Thieme: Atlas of Anatomy: 489 It gives passage to the femoral vessels, lymph vessels and lymph nodes. The lacunar ligament can be a site of entrapment for femoral hernias. Anatomy Its boundaries are the iliopectineal arch, the inguinal ligament, the lacunar ligament, and the superior border of the pubis. Contents The structures found in the vascular lacuna, from medial to lateral, are: * Cloquet's node; * Femoral vein; * Femoral artery; and * Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve The genitofemoral nerve is a mixed branch of the lumbar plexus derived from anterior rami of lumbar nerves L1–L2. It splits into a genital branch and a femoral branch. It provides sensory innervation to the upper anterior thigh, as well as t ... Refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iliopectineal Fascia
The iliopectineal arch is a thickened band of fused iliac fascia and psoas fascia passing from the posterior aspect of the inguinal ligament anteriorly across the front of the femoral nerve to attach to the iliopubic eminence of the hip bone posteriorly. The iliopectineal arch thus forms a septum which subdivides the space deep to the inguinal ligament into a lateral muscular lacuna and a medial vascular lacuna. When a psoas minor muscle is present, its tendon of insertion blends with the iliopectineal arch It is sometimes transected in treatment of femoral nerve The femoral nerve is a nerve in the thigh that supplies skin on the upper thigh and inner leg, and the muscles that extend the knee. It is the largest branch of the lumbar plexus. Structure The femoral nerve is the major nerve supplying the ant ... entrapment. Additional images File:Slide2gala.JPG, Iliopectal arch. Deep dissection. Anterior view. References {{Authority control Pelvis Fascia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transversalis Fascia
The transversalis fascia (or transverse fascia) is the fascial lining of the anterolateral abdominal wall situated between the inner surface of the transverse abdominal muscle, and the preperitoneal fascia. It is directly continuous with the iliac fascia, the internal spermatic fascia, and pelvic fascia. Structure In the inguinal region, the transversalis fascia is thick and dense; here, it is joined by fibers of the aponeurosis of the transverse abdominal muscle. It becomes thin towards to the diaphragm, blending with the fascia covering the inferior surface of the diaphragm. Posteriorly, it is lost in Below, it has the following attachments: posteriorly, to the whole length of the iliac crest, between the attachments of the transverse abdominal and Iliacus; between the anterior superior iliac spine and the femoral vessels it is connected to the posterior margin of the inguinal ligament, and is there continuous with the iliac fascia. Medial to the femoral vessels it is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |