|
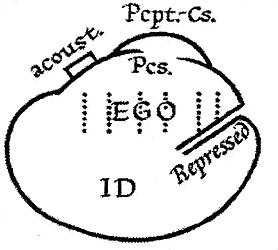
Id, Ego And Super-ego
In psychoanalytic theory, the id, ego, and superego are three distinct, interacting agents in the psychic apparatus, outlined in Sigmund Freud's structural model of the psyche. The three agents are theoretical constructs that Freud employed to describe the basic structure of mental life as it was encountered in psychoanalytic practice. Freud himself used the German terms ''das Es'', ''Ich'', and ''Über-Ich'', which literally translate as "the it", "I", and "over-I". The Latin terms id, ego and superego were chosen by his original translators and have remained in use. The structural model was introduced in Freud's essay '' Beyond the Pleasure Principle'' (1920) and further refined and formalised in later essays such as '' The Ego and the Id'' (1923). Freud developed the model in response to the perceived ambiguity of the terms "conscious" and "unconscious" in his earlier ''topographical'' model. Broadly speaking, the id is the organism's unconscious array of uncoordinated i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychoanalytic Theory
Psychoanalytic theory is the theory of the innate structure of the human soul and the dynamics of personality development relating to the practice of psychoanalysis, a method of research and for treating of Mental disorder, mental disorders (psychopathology). Laid out by Sigmund Freud in the late 19th century (s. ''The Interpretation of Dreams''), he developed the theory and practice of psychoanalysis until his death in 1939. Since then, it has been further refined, also divided into various sub-areas, but independent of this, Freuds structural distinction of the soul into three functionally interlocking instances has been largely retained. Psychoanalysis with its theoretical core came to full prominence in the last third of the twentieth century, as part of the flow of critical discourse regarding psychological treatments in the 1970s. Freud himself had ceased his Physiology, physiological research of the Neurology, neural brain organisation in 1906 (cf. Psychoanalysis#History, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Pronoun
Personal pronouns are pronouns that are associated primarily with a particular grammatical person – first person (as ''I''), second person (as ''you''), or third person (as ''he'', ''she'', ''it''). Personal pronouns may also take different forms depending on number (usually singular or plural), grammatical or natural gender, case, and formality. The term "personal" is used here purely to signify the grammatical sense; personal pronouns are not limited to people and can also refer to animals and objects (as the English personal pronoun ''it'' usually does). The re-use in some languages of one personal pronoun to indicate a second personal pronoun with formality or social distance – commonly a second person plural to signify second person singular formal – is known as the T–V distinction, from the Latin pronouns and . Examples are the majestic plural in English and the use of in place of in French. For specific details of the personal pronouns used in the Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society For Research In Child Development
The Society for Research in Child Development (SRCD) is a professional society for the field of human development, focusing specifically on child development. It is a multidisciplinary, not-for-profit, professional association with a membership of approximately 5,500 researchers, practitioners, and human development professionals from over 50 countries. The purposes of the society are to promote multidisciplinary research in the field of human development, to foster the exchange of information among scientists and other professionals of various disciplines, and to encourage applications of research findings. History The field of child development received formal recognition in 1922-23 through the appointment of a subcommittee on Child Development of the National Research Council. In 1925, under the direction of Robert S. Woodworth, an eminent experimental psychologist, this group became the Committee in Child Development with offices and staff in the National Academy of Scienc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackwell Publishing
Wiley-Blackwell is an international scientific, technical, medical, and scholarly publishing business of John Wiley & Sons. It was formed by the merger of John Wiley & Sons Global Scientific, Technical, and Medical business with Blackwell Publishing in 2007. Wiley-Blackwell is now an imprint that publishes a diverse range of academic and professional fields, including biology, medicine, physical sciences, technology, social science, and the humanities. Blackwell Publishing history Blackwell Publishing was formed by the 2001 merger of two Oxford-based academic publishing companies, Blackwell Science, founded in 1939 as Blackwell Scientific Publishing, and Blackwell Publishers, founded in 1922 as Basil Blackwell & Mott. Blackwell Publishers, founded in 1926, had its origins in the 19th century Blackwell's family bookshop and publishing business. The merger between the two publishing companies created the world's leading learned society publisher. The group then acquired BMJ B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model
A model is an informative representation of an object, person, or system. The term originally denoted the plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin , . Models can be divided into physical models (e.g. a ship model or a fashion model) and abstract models (e.g. a set of mathematical equations describing the workings of the atmosphere for the purpose of weather forecasting). Abstract or conceptual models are central to philosophy of science. In scholarly research and applied science, a model should not be confused with a theory: while a model seeks only to represent reality with the purpose of better understanding or predicting the world, a theory is more ambitious in that it claims to be an explanation of reality. Types of model ''Model'' in specific contexts As a noun, ''model'' has specific meanings in certain fields, derived from its original meaning of "structural design or layout": * Model (art), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reality Principle
In Freudian psychology and psychoanalysis, the reality principle () is the ability of the mind to assess the reality of the external world, and to act upon it accordingly, as opposed to acting according to the pleasure principle. The reality principle is the governing principle of the actions taken by the ego, after its slow development from a "pleasure-ego" into a "reality-ego". History Freud argued that "an ego thus educated has become 'reasonable'; it no longer lets itself be governed by the pleasure principle, but obeys the reality principle, which also, at bottom, seeks to obtain pleasure, but pleasure which is assured through taking account of reality, even though it is pleasure postponed and diminished". In his introductory lectures of 1915, at the University of Vienna, Freud popularized the concept of the unconscious as the largest and most influential part of the mind, including those drives, instincts and motives humans are often forced to deny except in disguised f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eros (concept)
Eros (, ; ) is a concept in ancient Greek philosophy referring to sensual or passionate love, from which the term ''eroticism, erotic'' is derived. ''Eros'' has also been used in philosophy and psychology in a much wider sense, almost as an equivalent to "life energy". Psychoanalysis uses the term to describe the ''universal desire'' that drives all innate needs (of the ''Id, ego and superego, id''), which according to Freud is identical to Plato's conception. The Protestant philosopher C. S. Lewis posits it as one of the four Greek words for love, ancient Greek words for love in Christianity, alongside ''storge'', ''philia'', and ''agape''. In literature Classical Greek tradition In the classical world, erotic love was generally described as a kind of madness or ''theia mania'' ("madness from the gods"). This erotic love was described through an elaborate metaphoric and mythological schema (psychology), schema involving "love's arrows" or "love darts", the source of which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Death Drive
In classical psychoanalysis of Sigmund Freud, the death drive () is the Drive theory, drive toward destruction in the sense of breaking down complex phenomena into their constituent parts or bringing life back to its inanimate 'dead' state, often expressed through behaviour such as aggression, repetition compulsion, and self-destructive behavior, self-destructiveness.Eric Berne, ''What Do You say After You Say Hello?'' (London, 1975) pp. 399–400. The Terminology, term was originally proposed by Sabina Spielrein in her paper "Destruction as the Cause of Coming Into Being" (''Die Destruktion als Ursache des Werdens'') in 1912, then taken up by Sigmund Freud, Freud in ''Beyond the Pleasure Principle'' (1920). He has related this concept with a kind of opposition between the ''ego's'' aspect of death drive and the ''id's'' aspect of life drive. Life drive and death drive – also referred to as Thanatos and used in plural (''Todestriebe'') – represent two complementary functions o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libido
In psychology, libido (; ) is psychic drive or energy, usually conceived of as sexual in nature, but sometimes conceived of as including other forms of desire. The term ''libido'' was originally developed by Sigmund Freud, the pioneering originator of psychoanalysis. With direct reference to Plato's Eros, the term initially referred only to specific sexual desire, later expanded to the concept of a universal psychic energy that drives all instincts and whose '' great reservoir is the id''. The libido partly according to its synthesising, partly to its analytical aspect called ''life-'' and ''death-drive'' - thus becomes the source of all natural forms of expression: the behaviour of sexuality as well as striving for social commitment (''maternal love instinct'' etc.), skin pleasure, food, knowledge and victory in the areas of species- and self-preservation. In common or colloquial usage, a person's overall sexual drive is often referred to as that person's "libido". In this sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self
In philosophy, the self is an individual's own being, knowledge, and values, and the relationship between these attributes. The first-person perspective distinguishes selfhood from personal identity. Whereas "identity" is (literally) sameness and may involve categorization and labeling, selfhood implies a first-person perspective and suggests potential uniqueness. Conversely, "person" is used as a third-person reference. Personal identity can be impaired in late-stage Alzheimer's disease and in other neurodegenerative diseases. Finally, the self is distinguishable from "others". Including the distinction between sameness and otherness, the self versus other is a research topic in contemporary philosophy and contemporary phenomenology (see also psychological phenomenology), psychology, psychiatry, neurology, and neuroscience. Although subjective experience is central to selfhood, the privacy of this experience is only one of many problems in the philosophy of self and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathexis
In psychoanalysis, cathexis (or emotional investment) is defined as the process of allocation of mental or emotional energy to a person, object, or idea. Origin of term The Greek term ''cathexis'' (κάθεξις) was chosen by James Strachey to render the German term ''Besetzung'' in his translation of Sigmund Freud's complete works. Freud himself used the word "interest" in English in an early letter to Ernest Jones. Peter Gay objected that Strachey's use of cathexis was an unnecessarily esoteric replacement for Freud's use of ''Besetzung'' – "a word from common German speech rich in suggestive meanings, among them 'occupation' (by troops) and 'charge' (of electricity)", though Gay is mistaken regarding his latter example. Usage Freud defined cathexis as an allocation of libido, pointing out for example how dream thoughts were charged with different amounts of affect. A cathexis or allocation of emotional charge might be positive or negative, leading some of his fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleasure Principle (psychology)
In Freudian psychoanalysis, the pleasure principle () is the instinctive seeking of pleasure and avoiding of pain to satisfy biological and psychological needs. Specifically, the pleasure principle is the animating force behind the id. Precursors Epicurus in the ancient world, and later Jeremy Bentham, laid stress upon the role of pleasure in directing human life, the latter stating: "Nature has placed mankind under the governance of two sovereign masters, ''pain'' and ''pleasure''". Freud's most immediate predecessor and guide however was Gustav Theodor Fechner and his psychophysics. Freudian developments Freud used the idea that the mind seeks pleasure and avoids pain in his ''Project for a Scientific Psychology'' of 1895, as well as in the theoretical portion of '' The Interpretation of Dreams'' of 1900, where he termed it the 'unpleasure principle'.''On Metapsychology'', p. 36. In the ''Two Principles of Mental Functioning'' of 1911, contrasting it with the reality prin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |