|
Ichirgu-boil
The Ichirgu-boila or Chargobilya (; Old Bulgarian: , ) was a high-ranking official in the First Bulgarian Empire The First Bulgarian Empire (; was a medieval state that existed in Southeastern Europe between the 7th and 11th centuries AD. It was founded in 680–681 after part of the Bulgars, led by Asparuh of Bulgaria, Asparuh, moved south to the northe .... The holder of the post was the commander of the garrison of the capital and was the third most important person in the state after the ruler and the Kavkhan. In peace-time the ichirgu-boila had diplomatic functions. According to some data the ichirgu-boila personally commanded a squad of 400 heavy cavalrymen. Origin According to Veselin Besheliev the word "ichirgu" was of Turkic- Altay origin and meant "internal".Бешевлиев В.''Прабългарски епиграфски паметници'' Издателство на Отечествения фронт, София, 1981 One funeral inscription found d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boila
Boila (; ) was a title worn by some of the Bulgar and Göktürk aristocrats (mostly of regional governors and noble warriors) in the early First Bulgarian Empire (681-1018) and Second Turkic Khaganate (682-744). For the linguists, the title "Boila" is the predecessor or an old form of the title " Bolyar". The ''Boil(a)s'' were two types: internal ("great") and external ("small"). The internal ''Boil(a)s'' were governors of the ''Comitates (administrative regions)''. Most of the popular linguists believe that "''Boila''" has Old Turkic origin and the meaning of the word can be translated as "noble". The title appears on the 7th/8th century Buyla inscription, with the Greek Greek may refer to: Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe: *Greeks, an ethnic group *Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family **Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ... spelling ΒΟΥΗΛΑ (''buila''). See also * Ichirgu- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kavkhan (title)
The ''kavkhan'' (; ) was one of the most important officials in the First Bulgarian Empire. Role and status According to the generally accepted opinion, he was the second most important person in the state after the Bulgarian ruler. He had a number of responsibilities and concentrated huge power and authority. The ''kavkhan'' was a commander-in-chief of the Bulgarian army and one of the primary diplomats in the state. He was a member of the ' Bolyar Counsel' and one of the most important advisers to the Bulgarian ruler; the ''kavkhan'' was sometimes his regent or co-ruler. The ''kavkhan'' was a high magistrate and substitute to the ruler when the latter is absent from the capital. He is also attributed to have been a judge. It is assumed that there was a prominent bolyar family in Bulgaria from which the ''kavkhan'' was chosen generation after generation - the so-called "''kavkhan'' kin". The title was therefore hereditary and for life. According to most historians the title ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preslav
The modern Veliki Preslav or Great Preslav (, ), former Preslav (; until 1993), is a city and the seat of government of the Veliki Preslav Municipality (Great Preslav Municipality, new Bulgarian: ''obshtina''), which in turn is part of Shumen Province, Bulgaria. Veliki Preslav is situated at an altitude of 132 m (92 m above sea level). A former village, it assumed the name of the medieval capital in 1878 and became a town in 1883. As of December 2009, it had a population of 8,951. Preslav was the capital of the First Bulgarian Empire from 893 to 972 and was one of the most important cities in medieval Southeastern Europe. The ruins of the city are situated in modern northeastern Bulgaria, some 20 kilometres southwest of the regional capital of Shumen, and are currently a national archaeological reserve. History The name of Preslav is of Slavic origin; apparently it was initially founded and functioned as a Slavic settlement until its fortification at the beginning of the ni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mostich
Mostich (, Old Bulgarian: МОСТИЧЬ) was a high-ranking official in the 10th-century First Bulgarian Empire, during the rule of Simeon I and Peter I. He bore the title of Ichirgu-boil and was most likely the commander of the state capital Preslav's garrison. Mostich is known from the 10th-century Old Bulgarian inscription on his tombstone, found in a church (now known as "Mostich's Church") in the Selishte area of Preslav, then the inner city of the Bulgarian capital. The tombstone was discovered in 1952 by Professor Stancho Vaklinov and is preserved in the National Archaeological Museum. The inscription is Mostich's epitaph, indicating that he was buried in the church: his remains were also found, revealing that he was relatively short (165–170 cm). The text is notable for being one of the earliest sources mentioning the title "Цѣсарь" (" Tsesar"Станислав Станилов, Българската монархия през средните векове, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Bulgarian Language
The history of the Bulgarian language can be divided into three major periods: * Old Bulgarian (from the late 9th until the 11th century); * Middle Bulgarian (from the 12th century to the 15th century); * Modern Bulgarian (since the 16th century). Bulgarian is a written South Slavic language that dates back to the end of the 9th century. Old Bulgarian Old Bulgarian was the first literary period in the development of the language. It was a highly synthetic language with a rich declension system as attested by a number of manuscripts from the late 10th and the early 11th centuries. Those originate mostly from the Preslav and the Ohrid Literary School, although smaller literary centers also contributed to the tradition. The language became a medium for rich scholarly activity — chiefly in the late 9th and the early 10th century — with writers such as Constantine of Preslav, John Exarch, Clement of Ohrid, Chernorizetz Hrabar and Naum of Preslav (Naum of Ohrid). Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
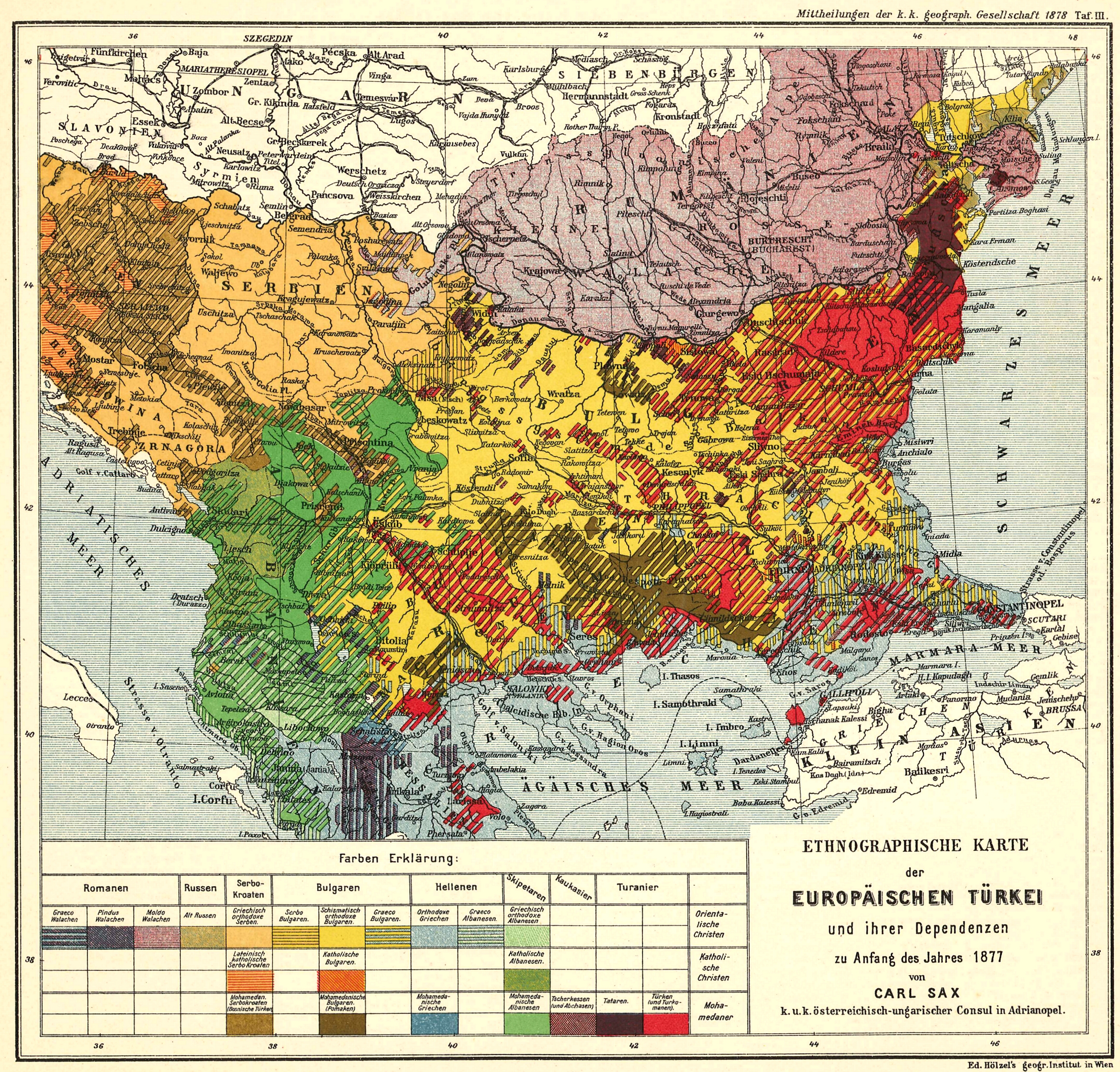
First Bulgarian Empire
The First Bulgarian Empire (; was a medieval state that existed in Southeastern Europe between the 7th and 11th centuries AD. It was founded in 680–681 after part of the Bulgars, led by Asparuh of Bulgaria, Asparuh, moved south to the northeastern Balkans. There they secured Byzantine Empire, Byzantine recognition of their right to settle south of the Danube by Battle of Ongal, defeatingpossibly with the help of Seven Slavic tribes, local South Slavic tribesthe Byzantine army led by Constantine IV. During the 9th and 10th century, Bulgaria at the height of its power spread from the Danube Bend to the Black Sea and from the Dnieper River to the Adriatic Sea and became an important power in the region competing with the Byzantine Empire. As the state solidified its position in the Balkans, it entered into a centuries-long interaction, sometimes friendly and sometimes hostile, with the Byzantine Empire. Bulgaria emerged as Byzantium's chief antagonist to its north, resulting in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veselin Besheliev
Veselin Ivanov Beshevliev (; 25 March 1900 – ) was a Bulgarian historian and philologist. He was a correspondent member of the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences from 1941 to his death. He was the author of ''Old Bulgarian Inscriptions''. Career He studied history and Slavic philology in the Sofia University (1919-1920) and classical philology in Germany - Halle, Jena and Würzburg (1920-1925) where he took doctorate. He became teaching assistant (1925-1929), docent (1929-1933) and professor in Classical philology in the Sofia University. He was awarded the Herder Prize The Herder Prize (), named after the German philosopher Johann Gottfried Herder (1744–1803), was a prestigious international prize awarded every year from 1964 to 2006 to scholars and artists from Central and Southeast Europe whose life and wor ... in 1972. Publications * 1979, ''Old Bulgarian Inscriptions'', first edition; 1992, second edition * 1981, ''Proto-Bulgarian Epigraphic Monuments'' References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkic Languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of more than 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and West Asia. The Turkic languages originated in a region of East Asia spanning from Mongolia to Northwest China, where Proto-Turkic language, Proto-Turkic is thought to have been spoken, from where they Turkic migration, expanded to Central Asia and farther west during the first millennium. They are characterized as a dialect continuum. Turkic languages are spoken by some 200 million people. The Turkic language with the greatest number of speakers is Turkish language, Turkish, spoken mainly in Anatolia and the Balkans; its native speakers account for about 38% of all Turkic speakers, followed by Uzbek language, Uzbek. Characteristic features such as vowel harmony, agglutination, subject-object-verb order, and lack of grammatical gender, are almost universal within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altay Language
Altai or Altay () is a set of Turkic languages spoken officially in the Altai Republic, Russia. The standard vocabulary is based on the Southern Altai language, though it is also taught to and used by speakers of the Northern Altai language as well. Gorno–Altai refers to a subgroup of languages in the Altai Mountains. The languages were called Oyrot (ойрот) prior to 1948. Altai is spoken primarily in the Altai Republic. There is a small community of speakers in the neighbouring Altai Krai as well. Classification Due to its isolated position in the Altai Mountains and contact with surrounding languages, the exact classification of Altai within the Turkic languages has often been disputed. Because of its geographic proximity to the Shor and Khakas languages, some classifications place it in a Northern Turkic subgroup. Due to certain similarities with Kyrgyz, it has been grouped as the Kyrgyz–Kipchak subgroup with the Kypchak languages which is within the Turkic langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
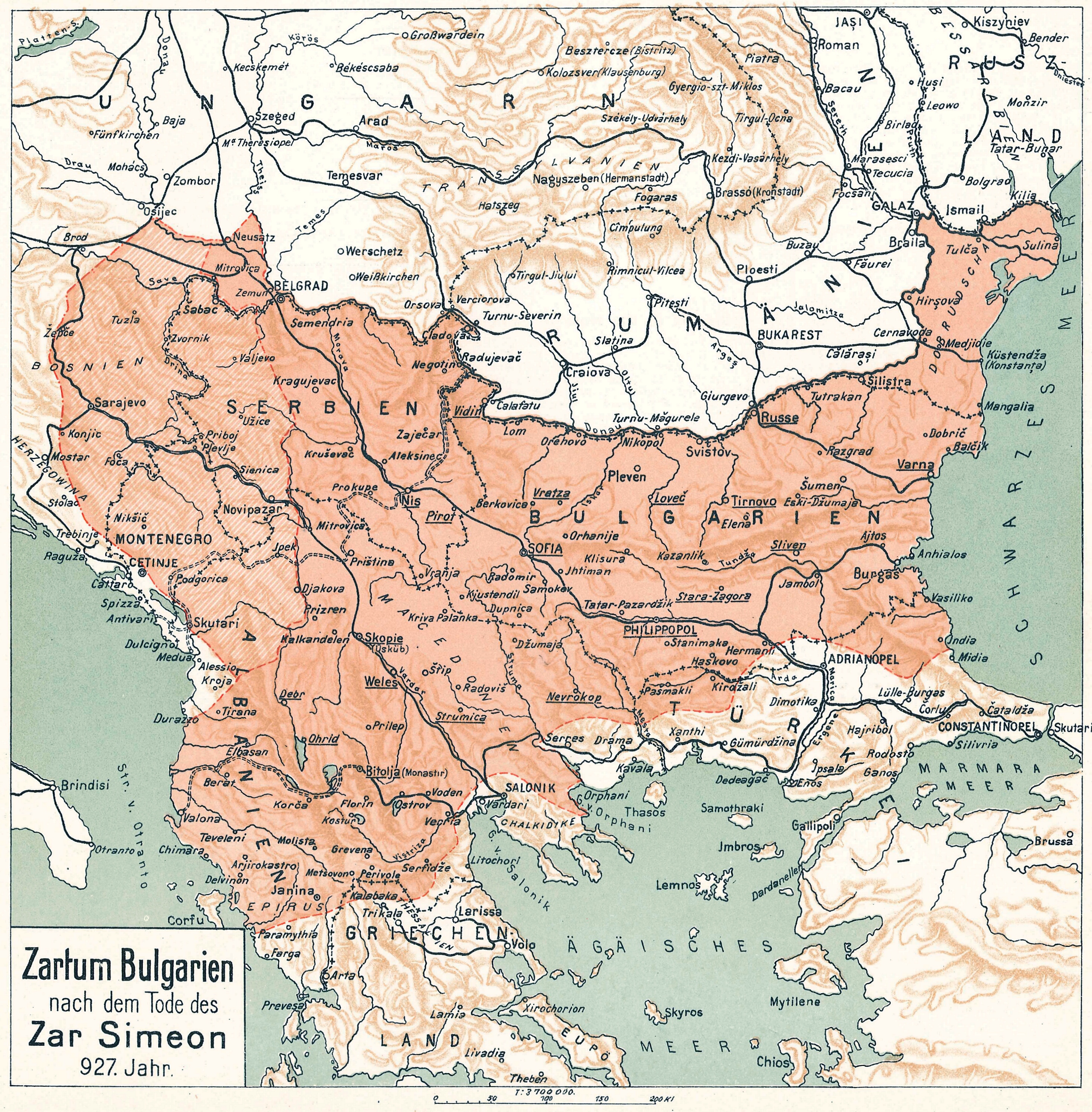
Simeon I Of Bulgaria
Simeon I the Great (; ; ) ruled over Bulgaria from 893 to 927,Lalkov, ''Rulers of Bulgaria'', pp. 23–25. during the First Bulgarian Empire. Simeon's successful campaigns against the Byzantines, Magyars and Serbs led Bulgaria to its greatest territorial expansion ever, making it the most powerful state in contemporary Eastern and Southeast Europe. His reign was also a period of unmatched cultural prosperity and enlightenment later deemed the Golden Age of Bulgarian culture. During Simeon's rule, Bulgaria spread over a territory between the Aegean, the Adriatic and the Black seas.Bakalov, ''Istorija na Bǎlgarija'', "Simeon I Veliki". The newly independent Bulgarian Orthodox Church became the first new patriarchate besides the Pentarchy, and Bulgarian Glagolitic and Cyrillic translations of Christian texts spread all over the Slavic world of the time. It was at the Preslav Literary School in the 890s that the Cyrillic alphabet was developed. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter I Of Bulgaria
Peter I (; ; died 30 January 970) was the emperor (tsar) of Bulgaria from 27 May 927 to 969. Facing Bogomilism and rebellions by his brothers and also by Časlav Klonimirović early on in his reign, Peter secured more success later in life; he ensured the retreat of the invading Rus by inciting Bulgaria's allies, the Pechenegs, to attack Kiev itself. Traditionally seen as a weak ruler who lost land and prestige, recent scholarship challenges this view, emphasizing the empire's affluence and internal peace. Considered a good ruler during the Middle Ages, his name was adopted by later leaders trying to restore Bulgarian independence under Byzantine rule to emphasize legitimacy and continuity. Early reign Peter I was the son of Simeon I of Bulgaria by his second marriage to the sister of George Sursuvul. Peter had been born early in the 10th century, but it appears that his maternal uncle was very influential at the beginning of his reign. In 913 Peter may have visited the impe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |