|
Ibn Khordadbeh
Abu'l-Qasim Ubaydallah ibn Abdallah ibn Khordadbeh (; 820/825–913), commonly known as Ibn Khordadbeh (also spelled Ibn Khurradadhbih; ), was a high-ranking bureaucrat and geographer of Persian descent in the Abbasid Caliphate. He is the author of the earliest surviving Arabic book of administrative geography. Biography Ibn Khordadbeh was the son of Abdallah ibn Khordadbeh, who had governed the northern Iranian region of Tabaristan under the Abbasid caliph al-Mamun (), and in 816/17 conquered the neighbouring region of Daylam, as well as repelled the Bavandid '' ispahbadh'' (ruler) Shahriyar I () from the highlands of Tabaristan. Ibn Khordadbeh's grandfather was Khordadbeh, a former Zoroastrian who was convinced by the Barmakids to convert to Islam. He may have been the same person as Khordadbeh al-Razi, who had provided Abu'l-Hasan al-Mada'ini (died 843) the details regarding the flight of the last Sasanian emperor Yazdegerd III during the Arab conquest of Iran. Ib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khurasan
KhorasanDabeersiaghi, Commentary on Safarnâma-e Nâsir Khusraw, 6th Ed. Tehran, Zavvâr: 1375 (Solar Hijri Calendar) 235–236 (; , ) is a historical eastern region in the Iranian Plateau in West Asia, West and Central Asia that encompasses western and northern Afghanistan, northeastern Iran, the eastern halves of Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, and portions of Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan. The extent of the region referred to as ''Khorasan'' varied over time. In its stricter historical sense, it comprised the present territories of Khorasan Province, northeastern Iran, parts of Afghanistan and southern parts of Central Asia, extending as far as the Amu Darya (Oxus) river. However, the name has often been used in a loose sense to include a wider region that included most of Transoxiana (encompassing Bukhara and Samarqand in present-day Uzbekistan), extended westward to the Caspian Sea, Caspian coast and to the Dasht-e Kavir southward to Sistan, and eastward to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yazdegerd III
Yazdegerd III (also Romanized as ''Yazdgerd'', ''Yazdgird'') was the last Sasanian Empire, Sasanian King of Kings from 632 to 651. His father was Shahriyar (son of Khosrow II), Shahriyar and his grandfather was Khosrow II. Ascending the throne at the age of eight, the young shah lacked authority and reigned as a figurehead, whilst real power was in the hands of the army commanders, courtiers, and powerful members of the aristocracy, who engaged in internecine warfare. The Sasanian Empire was weakened severely by these internal conflicts, resulting in invasions by the Göktürks from the east, and Khazars from the west. Yazdegerd was unable to contain the Muslim conquest of Persia, Rashidun conquest of Iran, and spent most of his reign fleeing from one province to another in the vain hope of raising an army. Yazdegerd met his end at the hands of a miller near Merv, Marw in 651, bringing an end to the last pre-Islamic Iranian empire after more than 400 years of rule. Etymology Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilisation, and a Golden age (metaphor), golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivalled that of the Han dynasty. The House of Li, Li family founded the dynasty after taking advantage of a period of Sui decline and precipitating their final collapse, in turn inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The An Lushan rebellion (755 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java (island)
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, projected to rise to 158 million at mid 2025, Java is the world's List of islands by population, most populous island, home to approximately 55.7% of the Demographics of Indonesia, Indonesian population (only approximately 44.3% of Indonesian population live outside Java). Indonesia's capital city, Jakarta, is on Java's northwestern coast. Many of the best known events in Indonesian history took place on Java. It was the centre of powerful Hindu-Buddhist empires, the Islamic sultanates, and the core of the colonial Dutch East Indies. Java was also the center of the History of Indonesia, Indonesian struggle for independence during the 1930s and 1940s. Java dominates Indonesia politically, economically and culturally. Four of Indonesia's e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peninsular Malaysia
Peninsular Malaysia, historically known as Malaya and also known as West Malaysia or the Malaysian Peninsula, is the western part of Malaysia that comprises the southern part of the Malay Peninsula on Mainland Southeast Asia and the list of islands of Malaysia, nearby islands. Its area totals approximately , which is nearly 40% of the total area of the country; the other 60% is in East Malaysia on the island of Borneo. It shares a land border with Thailand to the north and a maritime border with Singapore to the south. Across the Strait of Malacca to the west lies the island of Sumatra, and across the South China Sea to the east lie the Natuna Islands of Indonesia. At its southern tip, across the Strait of Johor, lies the island country of Singapore. Most of Peninsular Malaysia's interior is forested, mountainous and rural; the majority of Malaysia's population and economy are concentrated on the coastal western half, which is where the country's prominent urban areas are located ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andaman Islands
The Andaman Islands () are an archipelago, made up of 200 islands, in the northeastern Indian Ocean about southwest off the coasts of Myanmar's Ayeyarwady Region. Together with the Nicobar Islands to their south, the Andamans serve as a maritime boundary between the Bay of Bengal to the west and the Andaman Sea to the east. Most of the islands are part of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a Union Territory of India, while the Coco Islands and Preparis Island are part of the Yangon Region of Myanmar. The Andaman Islands are home to the Andamanese peoples, Andamanese, a group of indigenous people made up of a number of tribes, including the Jarawas (Andaman Islands), Jarawa and Sentinelese. While some of the islands can be visited with permits, entry to others, including North Sentinel Island, is banned by law. The Sentinelese are generally hostile to visitors and have had Uncontacted peoples, little contact with any other people. The Indian government and coast guard protect th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilisations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. Asia shares the landmass of Eurasia with Europe, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Europe and Africa. In general terms, it is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a social constructionism, historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. A commonly accepted division places Asia to the east of the Suez Canal separating it from Africa; and to the east of the Turkish straits, the Ural Mountains an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Roads And Kingdoms (ibn Khordadbeh)
The ''Book of Roads and Kingdoms'' () is a 9th-century geography text written by the Persian geographer Ibn Khordadbeh. It maps and describes the major trade routes of the time within the Muslim world, and discusses distant trading regions such as Japan, Korea, and China. It was written around 870 CE, during the reign of Al-Muʿtamid of the Abbasid Caliphate, while its author was Director of Posts and Police for the Abbasid province of Jibal in modern-day Iran Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort .... The work uses much of the Persian administrative terms, gives considerable attention to pre-Islamic Iranian history, and uses the "native Iranian cosmological division system of the world". These all show "the existence of Iranian sources at the core of the work". pp. 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
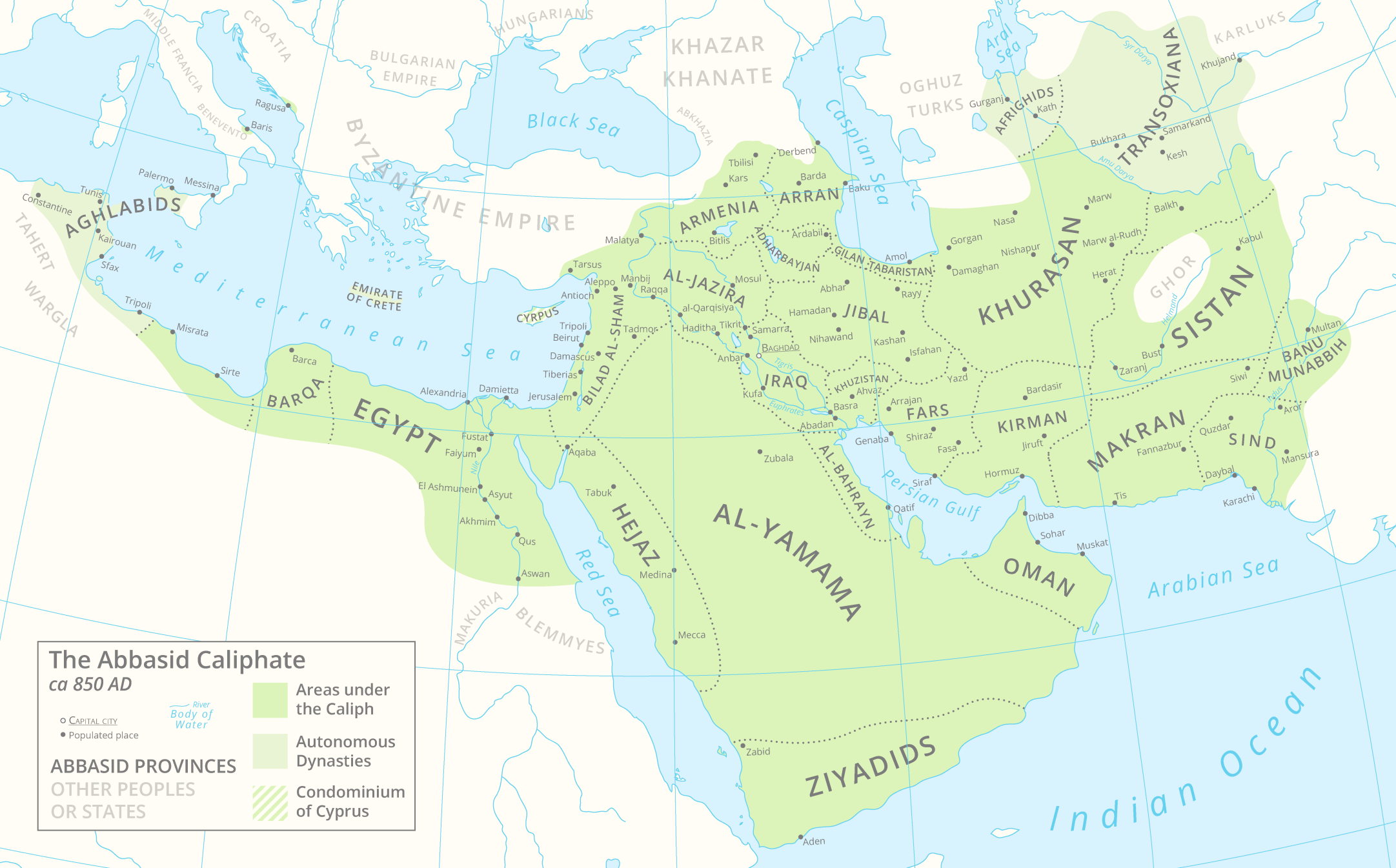
Abbasid Caliphate 850AD
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes its name. After overthrowing the Umayyad Caliphate in the Abbasid Revolution of 750 CE (132 AH), they ruled as caliphs based in modern-day Iraq, with Baghdad being their capital for most of their history. The Abbasid Revolution had its origins and first successes in the easterly region of Khurasan, far from the Levantine center of Umayyad influence. The Abbasid Caliphate first centered its government in Kufa, modern-day Iraq, but in 762 the caliph al-Mansur founded the city of Baghdad as the new capital. Baghdad became the center of science, culture, arts, and invention in what became known as the Golden Age of Islam. By housing several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom, as well as a multiethnic and multi-rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
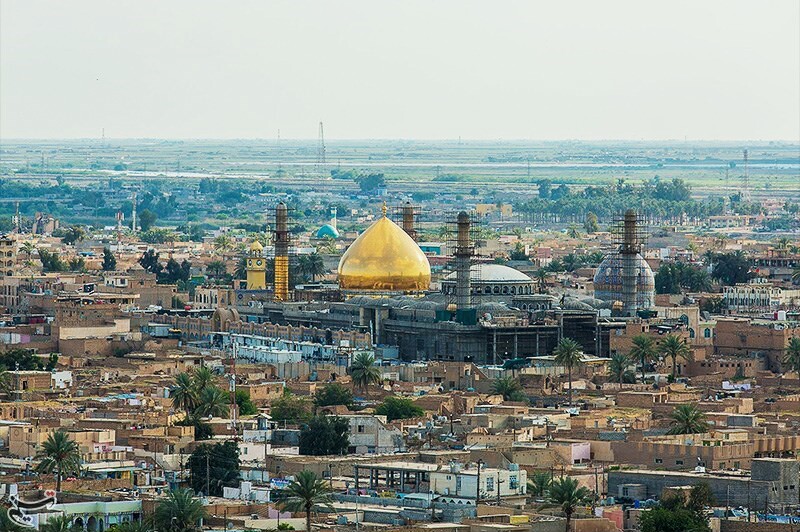
Samarra
Samarra (, ') is a city in Iraq. It stands on the east bank of the Tigris in the Saladin Governorate, north of Baghdad. The modern city of Samarra was founded in 836 by the Abbasid caliph al-Mu'tasim as a new administrative capital and military base. In 2003 the city had an estimated population of 348,700. During the Iraqi Civil War (2006–08), Samarra was in the " Sunni Triangle" of resistance. The archeological site of Samarra still retains much of the historic city's original plan, architecture and artistic relics. In 2007, UNESCO designated it a World Heritage Site. History Prehistoric Samarra The remains of prehistoric Samarra were first excavated between 1911 and 1914 by the German archaeologist Ernst Herzfeld. Samarra became the type site for the Samarra culture. Since 1946, the notebooks, letters, unpublished excavation reports and photographs have been in the Freer Gallery of Art in Washington, D.C. The civilization flourished alongside the Ubaid per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jibal
Jibāl (), also al-Jabal (), was the name given by the Arabs to a region and province located in western Iran, under the Umayyad and Abbasid Caliphates. Its name means "the Mountains", being the plural of ''jabal'' ("mountain, hill"), highlighting the region's mountainous nature in the Zagros. Between the 12th and 14th centuries, the name Jibal was progressively abandoned, and it came to be mistakenly referred to as ''ʿIrāq ʿAjamī'' ("Persian Iraq") to distinguish it from "Arab Iraq" in Mesopotamia. The region never had any precisely defined boundaries, but was held to be bounded by the Maranjab Desert in the east, by Fars and Khuzistan in the south, by Iraq in the south-west and west, by Adharbayjan in the north-west and by the Alborz Mountains in the north, making it roughly coterminous with the ancient country of Media. Under the Abbasid Caliphate, Jibal formed a separate province, with its capital usually at Rayy, until the Abbasids lost control in the early 10th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ishaq Al-Mawsili
Ishaq al-Mawsili (; 767/772 – March 850) was an Arab musician of Persian origin active as a composer, singer and music theorist. The leading musician of his time in the Abbasid Caliphate, he served under six successive Abbasid caliphs: Harun al-Rashid, Al-Amin, Al-Ma'mun, Al-Mu'tasim, Al-Wathiq and Al-Mutawakkil. The caliphs and Abbasid court held him in high regard, and his diverse intellect elevated him to a social status that was highly unusual for musicians of the time. Taught by his renowned father Ibrahim al-Mawsili, the singer Atika bint Shuhda and the noted lutenist Zalzal, he succeeded his father in leading the conservative musical establishment. This put him at odds with progressive musicians such as Ibrahim ibn al-Mahdi and Ziryab, whose style later dominated in popularity. He has appeared in the '' Maqamat'' of Al-Hariri of Basra and ''One Thousand and One Nights''. His creation of a comprehensive theoretical system for Arab music, without Ancient Greek i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |