|
ISCSI Extensions For RDMA
The iSCSI Extensions for RDMA (iSER) is a computer Communications protocol, network protocol that extends the Internet Small Computer System Interface (iSCSI) protocol to use Remote Direct Memory Access (Remote direct memory access, RDMA). RDMA can be provided by: - Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) with RDMA services (iWARP), which uses an existing Ethernet setup and therefore has lower hardware costs. - RoCE (RDMA over Converged Ethernet), which does not need the TCP layer and therefore provides lower latency. - InfiniBand iSER permits data to be transferred directly into and out of SCSI computer memory buffers (those which connect computers and storage devices) without intermediate data copies and with minimal CPU involvement. History An RDMA consortium was announced on May 31, 2002, with a goal of product implementations by 2003. The consortium released their proposal in July, 2003. The protocol specifications were published as drafts in September 2004 in the Internet E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communications Protocol
A communication protocol is a system of rules that allows two or more entities of a communications system to transmit information via any variation of a physical quantity. The protocol defines the rules, syntax, semantics (computer science), semantics, and synchronization of communication and possible Error detection and correction, error recovery methods. Protocols may be implemented by Computer hardware, hardware, software, or a combination of both. Communicating systems use well-defined formats for exchanging various messages. Each message has an exact meaning intended to elicit a response from a range of possible responses predetermined for that particular situation. The specified behavior is typically independent of how it is to be Implementation, implemented. Communication protocols have to be agreed upon by the parties involved. To reach an agreement, a protocol may be developed into a technical standard. A programming language describes the same for computations, so there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenFabrics Alliance
The OpenFabrics Alliance is a non-profit organization that promotes remote direct memory access (RDMA) switched fabric technologies for server and storage connectivity. These high-speed data-transport technologies are used in high-performance computing facilities, in research and various industries. The OpenFabrics Alliance aims to develop open-source software that supports the three major RDMA fabric technologies: InfiniBand, RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) and iWARP. The software includes two packages, one that runs on Linux and FreeBSD and one that runs on Microsoft Windows. The alliance worked with two large Linux distributors—SUSE and Red Hat—as well as Microsoft on compatibility with their operating systems. History Founded in June 2004 as the OpenIB Alliance, the organization originally developed an InfiniBand software stack for Linux. Initial funding for the Alliance was provided by the United States Department of Energy. The alliance released the first versi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pat Thaler
Pat Thaler is an American electrical engineer recognized for her contributions to the development of Ethernet and leadership within the IEEE 802 standards community. She has been instrumental in advancing several networking standards, including StarLAN, 10BASE-T, and 100VG-AnyLAN. Early life and education Thaler was born in Utica, New York. She earned a Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering (BSEE) from the University of California in 1974 and a Master of Science in Electrical Engineering (MSEE) from Stanford University in 1978. Career Thaler began her career at IBM, where she worked on machines for the manufacture of magnetic disks. She joined Hewlett-Packard in 1976, initially working on the HP 8660 signal synthesizer and later on computer interface card hardware design. She became a principal engineer for LAN architecture and standards at HP’s Roseville Networks Division. Her work included development of Ethernet network interface cards, repeaters, and 10BASE- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCSI RDMA Protocol
In computing the SCSI RDMA Protocol (SRP) is a protocol that allows one computer to access SCSI devices attached to another computer via remote direct memory access (RDMA).ANSI T10 SRPr16a, www.t10.org ANSI T10 SRPr16a, web.archive.org /ref> The SRP protocol is also known as the SCSI Remote Protocol. The use of RDMA makes higher throughput and lower latency possible than what is generally available through e.g. the TCP/IP communication protocol. Though the SRP protocol has been designed to use RDMA networks efficiently, it is also possible to implement the SRP protocol over networks that do not support RDMA.
|
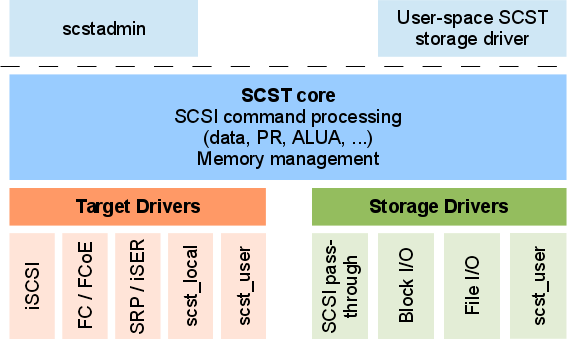
SCST
SCST is a GPL licensed SCSI target software stack. The design goals of this software stack are high performance, high reliability, strict conformance to existing SCSI standards, being easy to extend and easy to use. SCST does not only support multiple SCSI protocols (iSCSI, FC, SRP, ...) but also supports multiple local storage interfaces (SCSI pass-through, block I/O and file I/O) and also storage drivers implemented in user-space via the scst_user driver. In order to reach maximum performance SCST has been implemented as a set of kernel drivers. SCST is often combined with RAID, data deduplication and/or high-availability cluster software to augment its functionality. The SCST software stack is the basis software of many SAN systems. Several world records have been set with SAN systems based on SCST. SCST competes with LIO Target for the same purpose of providing a generic SCSI target module inside the Linux kernel. For the narrower purpose providing a Linux iSCSI target, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LIO Target
The Linux-IO Target (LIO) is an open-source Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) target implementation included with the Linux kernel. Unlike initiators, which begin sessions, LIO functions as a target, presenting one or more Logical Unit Numbers (LUNs) to a SCSI initiator, receiving SCSI commands, and managing the input/output data transfers. LIO supports a wide range of storage protocols and transport fabrics, including but not limited to Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE), Fibre Channel, IEEE 1394 and iSCSI. It is utilized in several Linux distributions and is a popular choice for cloud environments due to its integration with tools like QEMU/ KVM, libvirt, and OpenStack. The LIO project is maintained by Datera, Inc., a Silicon Valley-based storage solutions provider. On January 15, 2011, LIO was merged into the Linux kernel mainline with version 2.6.38, which was officially released on March 14, 2011. Subsequent versions of the Linux kernel have introduced additiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open-source Software
Open-source software (OSS) is Software, computer software that is released under a Open-source license, license in which the copyright holder grants users the rights to use, study, change, and Software distribution, distribute the software and its source code to anyone and for any purpose. Open-source software may be developed in a collaborative, public manner. Open-source software is a prominent example of open collaboration, meaning any capable user is able to online collaboration, participate online in development, making the number of possible contributors indefinite. The ability to examine the code facilitates public trust in the software. Open-source software development can bring in diverse perspectives beyond those of a single company. A 2024 estimate of the value of open-source software to firms is $8.8 trillion, as firms would need to spend 3.5 times the amount they currently do without the use of open source software. Open-source code can be used for studying and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Request For Comments
A Request for Comments (RFC) is a publication in a series from the principal technical development and standards-setting bodies for the Internet, most prominently the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). An RFC is authored by individuals or groups of engineers and computer scientists in the form of a memorandum describing methods, behaviors, research, or innovations applicable to the working of the Internet and Internet-connected systems. It is submitted either for peer review or to convey new concepts, information, or, occasionally, engineering humor. The IETF adopts some of the proposals published as RFCs as Internet Standards. However, many RFCs are informational or experimental in nature and are not standards. The RFC system was invented by Steve Crocker in 1969 to help record unofficial notes on the development of ARPANET. RFCs have since become official documents of Internet specifications, communications protocols, procedures, and events. According to Crocker, the docu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISCSI
Internet Small Computer Systems Interface or iSCSI ( ) is an Internet Protocol-based storage networking standard for linking data storage facilities. iSCSI provides block-level access to storage devices by carrying SCSI commands over a TCP/IP network. iSCSI facilitates data transfers over intranets and to manage storage over long distances. It can be used to transmit data over local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), or the Internet and can enable location-independent data storage and retrieval. The protocol allows clients (called ''initiators'') to send SCSI commands (''CDBs'') to storage devices (''targets'') on remote servers. It is a storage area network (SAN) protocol, allowing organizations to consolidate storage into storage arrays while providing clients (such as database and web servers) with the illusion of locally attached SCSI disks. It mainly competes with Fibre Channel, but unlike traditional Fibre Channel which usually requires dedicated cabling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Engineering Task Force
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) is a standards organization for the Internet standard, Internet and is responsible for the technical standards that make up the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP). It has no formal membership roster or requirements and all its participants are volunteers. Their work is usually funded by employers or other sponsors. The IETF was initially supported by the federal government of the United States but since 1993 has operated under the auspices of the Internet Society, a non-profit organization with local chapters around the world. Organization There is no membership in the IETF. Anyone can participate by signing up to a working group mailing list, or registering for an IETF meeting. The IETF operates in a bottom-up task creation mode, largely driven by working groups. Each working group normally has appointed two co-chairs (occasionally three); a charter that describes its focus; and what it is expected to produce, and when. It is open ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |