|
Helix
A helix (; ) is a shape like a cylindrical coil spring or the thread of a machine screw. It is a type of smooth space curve with tangent lines at a constant angle to a fixed axis. Helices are important in biology, as the DNA molecule is formed as two intertwined helices, and many proteins have helical substructures, known as alpha helices. The word ''helix'' comes from the Greek word , "twisted, curved". A "filled-in" helix – for example, a "spiral" (helical) ramp – is a surface called a '' helicoid''. Properties and types The pitch of a helix is the height of one complete helix turn, measured parallel to the axis of the helix. A double helix consists of two (typically congruent) helices with the same axis, differing by a translation along the axis. A circular helix (i.e. one with constant radius) has constant band curvature and constant torsion. The slope of a circular helix is commonly defined as the ratio of the circumference of the circular cylinder that it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Helix
An alpha helix (or α-helix) is a sequence of amino acids in a protein that are twisted into a coil (a helix). The alpha helix is the most common structural arrangement in the Protein secondary structure, secondary structure of proteins. It is also the most extreme type of local structure, and it is the local structure that is most easily predicted from a sequence of amino acids. The alpha helix has a right-handed helix conformation in which every backbone amino, N−H group hydrogen bonds to the backbone carbonyl, C=O group of the amino acid that is four residue (biochemistry), residues earlier in the protein sequence. Other names The alpha helix is also commonly called a: * Pauling–Corey–Branson α-helix (from the names of three scientists who described its structure) * 3.613-helix because there are 3.6 amino acids in one ring, with 13 atoms being involved in the ring formed by the hydrogen bond (starting with amidic hydrogen and ending with carbonyl oxygen) Discovery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helix
A helix (; ) is a shape like a cylindrical coil spring or the thread of a machine screw. It is a type of smooth space curve with tangent lines at a constant angle to a fixed axis. Helices are important in biology, as the DNA molecule is formed as two intertwined helices, and many proteins have helical substructures, known as alpha helices. The word ''helix'' comes from the Greek word , "twisted, curved". A "filled-in" helix – for example, a "spiral" (helical) ramp – is a surface called a '' helicoid''. Properties and types The pitch of a helix is the height of one complete helix turn, measured parallel to the axis of the helix. A double helix consists of two (typically congruent) helices with the same axis, differing by a translation along the axis. A circular helix (i.e. one with constant radius) has constant band curvature and constant torsion. The slope of a circular helix is commonly defined as the ratio of the circumference of the circular cylinder that it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Helix
In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by base pair, double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double Helix, helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its Nucleic acid secondary structure, secondary structure, and is a fundamental component in determining its Nucleic acid tertiary structure, tertiary structure. The structure was discovered by Rosalind Franklin and her student Raymond Gosling, Maurice Wilkins, James Watson, and Francis Crick, while the term "double helix" entered popular culture with the 1968 publication of Watson's ''The Double Helix, The Double Helix: A Personal Account of the Discovery of the Structure of DNA''. The DNA double helix biopolymer of nucleic acid is held together by nucleotides which base pair together. In B-DNA, the most common double helical structure found in nature, the double helix is right-handed with about 10–10.5 base pairs per turn. The double helix struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Spiral
In mathematics, a spiral is a curve which emanates from a point, moving further away as it revolves around the point. It is a subtype of whorled patterns, a broad group that also includes concentric objects. Two-dimensional A two-dimensional, or plane, spiral may be easily described using polar coordinates, where the radius r is a monotonic continuous function of angle \varphi: * r=r(\varphi)\; . The circle would be regarded as a degenerate case (the function not being strictly monotonic, but rather constant). In ''x-y-coordinates'' the curve has the parametric representation: * x=r(\varphi)\cos\varphi \ ,\qquad y=r(\varphi)\sin\varphi\; . Examples Some of the most important sorts of two-dimensional spirals include: * The Archimedean spiral: r=a \varphi * The hyperbolic spiral: r = a/ \varphi * Fermat's spiral: r= a\varphi^ * The lituus: r = a\varphi^ * The logarithmic spiral: r=ae^ * The Cornu spiral or ''clothoid'' * The Fibonacci spiral and golden spiral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
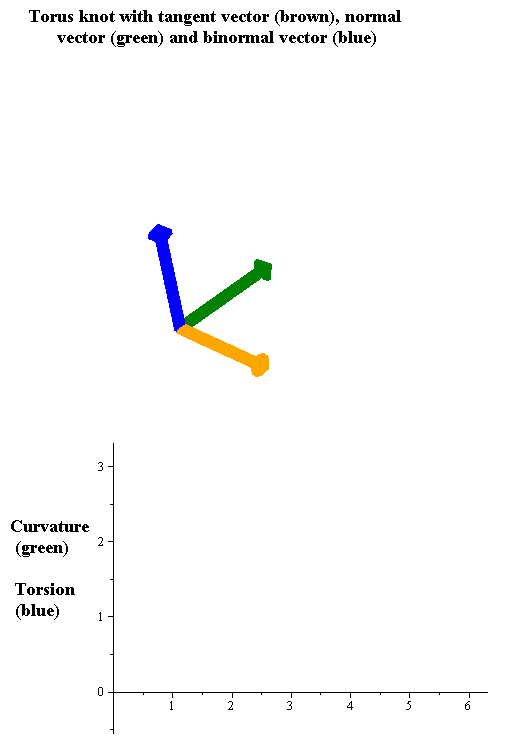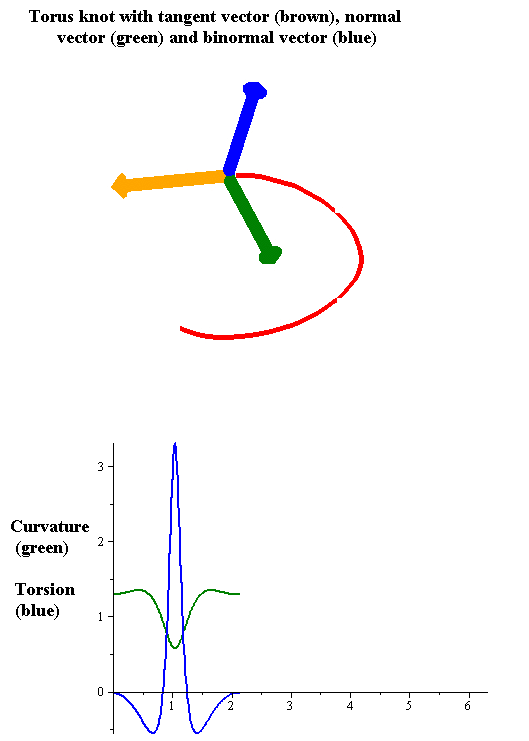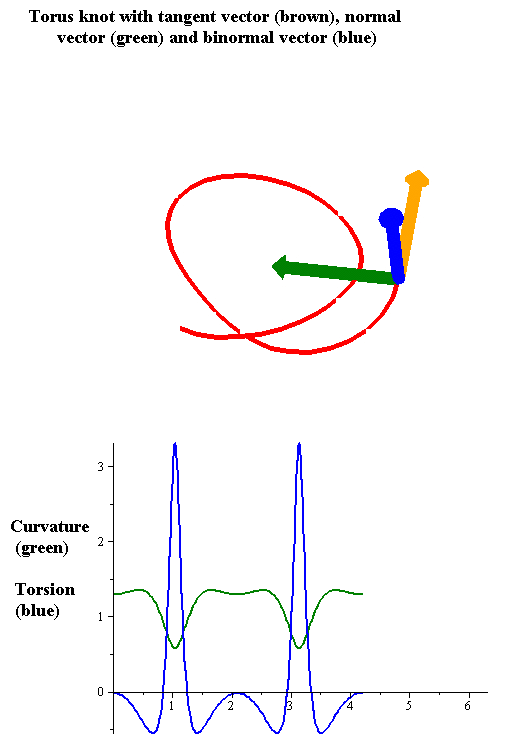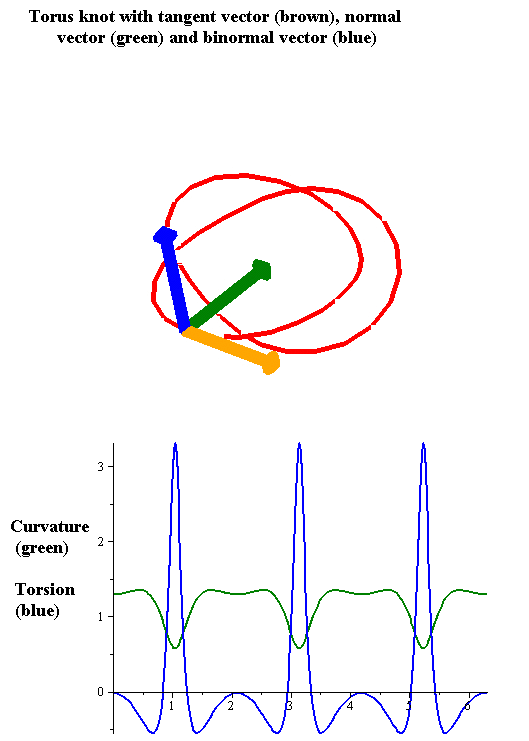
Torsion Of Curves
In the differential geometry of curves in three dimensions, the torsion of a curve measures how sharply it is twisting out of the osculating plane. Taken together, the curvature and the torsion of a space curve are analogous to the curvature of a plane curve. For example, they are coefficients in the system of differential equations for the Frenet frame given by the Frenet–Serret formulas. Definition Let be a space curve parametrized by arc length and with the unit tangent vector . If the curvature of at a certain point is not zero then the principal normal vector and the binormal vector at that point are the unit vectors : \mathbf=\frac, \quad \mathbf=\mathbf\times\mathbf respectively, where the prime denotes the derivative of the vector with respect to the parameter . The torsion measures the speed of rotation of the binormal vector at the given point. It is found from the equation : \mathbf' = -\tau\mathbf. which means : \tau = -\mathbf\ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parametric Equation
In mathematics, a parametric equation expresses several quantities, such as the coordinates of a point (mathematics), point, as Function (mathematics), functions of one or several variable (mathematics), variables called parameters. In the case of a single parameter, parametric equations are commonly used to express the trajectory of a moving point, in which case, the parameter is often, but not necessarily, time, and the point describes a curve, called a parametric curve. In the case of two parameters, the point describes a Surface (mathematics), surface, called a parametric surface. In all cases, the equations are collectively called a parametric representation, or parametric system, or parameterization (also spelled parametrization, parametrisation) of the object. For example, the equations \begin x &= \cos t \\ y &= \sin t \end form a parametric representation of the unit circle, where is the parameter: A point is on the unit circle if and only if there is a value of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential Geometry Of Curves
Differential geometry of curves is the branch of geometry that deals with smooth curves in the plane and the Euclidean space by methods of differential and integral calculus. Many specific curves have been thoroughly investigated using the synthetic approach. Differential geometry takes another path: curves are represented in a parametrized form, and their geometric properties and various quantities associated with them, such as the curvature and the arc length, are expressed via derivatives and integrals using vector calculus. One of the most important tools used to analyze a curve is the Frenet frame, a moving frame that provides a coordinate system at each point of the curve that is "best adapted" to the curve near that point. The theory of curves is much simpler and narrower in scope than the theory of surfaces and its higher-dimensional generalizations because a regular curve in a Euclidean space has no intrinsic geometry. Any regular curve may be parametrized by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
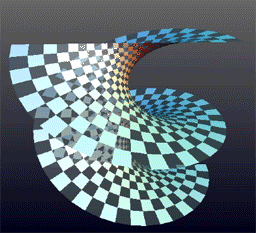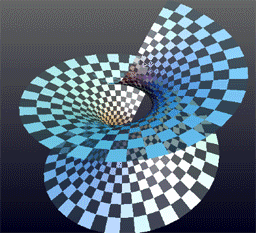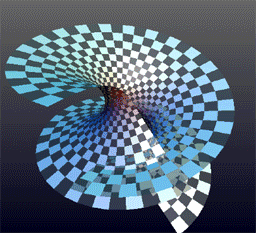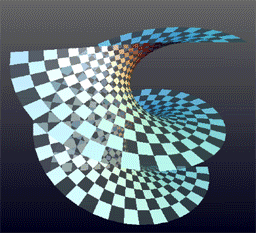
Helicoid
The helicoid, also known as helical surface, is a smooth Surface (differential geometry), surface embedded in three-dimensional space. It is the surface traced by an infinite line that is simultaneously being rotated and lifted along its Rotation around a fixed axis, fixed axis of rotation. It is the third minimal surface to be known, after the Plane (geometry), plane and the catenoid. Description It was described by Euler in 1774 and by Jean Baptiste Meusnier in 1776. Its Nomenclature, name derives from its similarity to the helix: for every Point (geometry), point on the helicoid, there is a helix contained in the helicoid which passes through that point. The helicoid is also a ruled surface (and a right conoid), meaning that it is a trace of a line. Alternatively, for any point on the surface, there is a line on the surface passing through it. Indeed, Eugène Charles Catalan, Catalan proved in 1842 that the helicoid and the plane were the only ruled minimal surfaces. A helic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conic Helix
In mathematics, a conical spiral, also known as a conical helix, is a space curve on a right circular cone, whose Orthographic projection, floor projection is a plane spiral. If the floor projection is a logarithmic spiral, it is called ''conchospiral'' (from conch). Parametric representation In the x-y-plane a spiral with parametric representation : x=r(\varphi)\cos\varphi \ ,\qquad y=r(\varphi)\sin\varphi a third coordinate z(\varphi) can be added such that the space curve lies on the cone with equation \;m^2(x^2+y^2)=(z-z_0)^2\ ,\ m>0\; : * x=r(\varphi)\cos\varphi \ ,\qquad y=r(\varphi)\sin\varphi\ , \qquad \color \ . Such curves are called conical spirals. They were known to Pappos. Parameter m is the slope of the cone's lines with respect to the x-y-plane. A conical spiral can instead be seen as the orthogonal projection of the floor plan spiral onto the cone. Examples : 1) Starting with an ''archimedean spiral'' \;r(\varphi)=a\varphi\; gives the conical spiral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |